 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1850260
網路安全保險:市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Cybersecurity Insurance - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
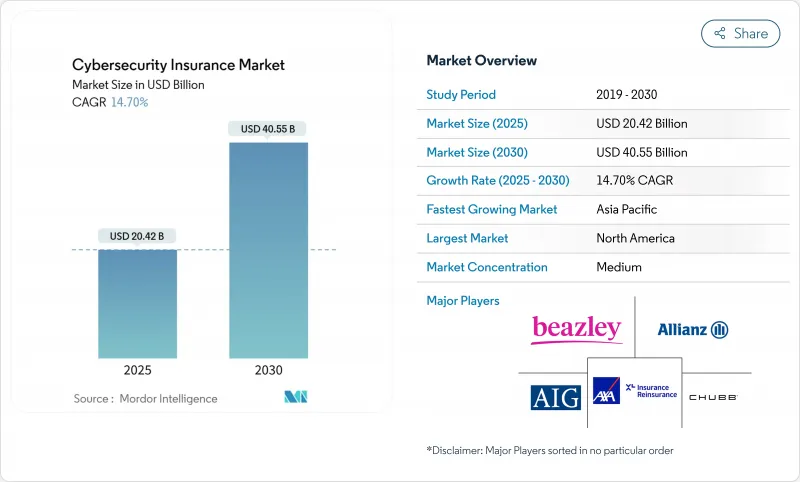
網路安全保險市場預計到 2025 年將達到 204.2 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 405.5 億美元,複合年成長率為 14.7%。
強勁的需求主要受歐盟《數位和營運彈性法案》(DORA) 和美國證券交易委員會 (SEC) 四天揭露規則等日益嚴格的監管法規所推動。此外,勒索軟體攻擊激增(目前平均每 11 秒發生一次)、董事會層級要求提供可量化的網路風險指標,以及旨在縮短中小企業 (SME) 理賠時間的新型參數化產品也正在蓬勃發展。對雲端(尤其是混合雲和多供應商架構)的日益依賴,迫使保險公司改善風險累積管理,而投資者正在嘗試使用代幣化網路保險關聯證券來釋放新的投資能力。
全球網路安全保險市場趨勢與洞察
以雲端數位化增加了網路安全風險
向雲端架構的轉型擴大了攻擊面,並加劇了系統中斷的風險。 2024 年 CrowdStrike 軟體故障導致 54 億美元的經濟損失,並表明單一服務提供者的故障可能引發數千起同時發生的索賠。慕尼黑再保險公司針對此推出了名為 Cloud Protection+ 的產品,用於 Google Cloud 工作負載,以承保與服務供應商故障相關的業務中斷損失。醫療保健雲端系統中的人為錯誤事件增加了 13%,佔各行業資料外洩事件的 58%。保險公司現在要求在提供保險之前,必須進行多因素身份驗證並提供加固配置的證據。
強制性法規導致責任增加
DORA要求歐盟金融機構在四小時內通報重大網路安全事件,而美國上市公司在四天內揭露相關資訊。拉丁美洲的情況也與此類似。 75%的內部審核負責人表示,由於監管審查力道加大,網路安全是他們面臨的最大風險。保險公司正在延長保險期限,以支付補救費用和持續的合規監控成本。
數學數據的匱乏和建模的不確定性
網路損失缺乏像自然災害那樣的長期時間序列數據,這削弱了尾部風險模型的可靠性。營運商正在投資開發整合即時威脅情報的專有平台,但在新興市場,由於資料外洩報告機制有限,仍有差距。
細分分析
受業務中斷、事件回應和資料重建成本索賠的推動,第一方責任險在2024年將維持42.7%的市場佔有率。隨著訴訟和監管處罰加大,以及董事會購買更高保額,第三方責任保險的複合年成長率將達到14.9%。製造商擴大選擇涵蓋業務中斷和下游供應鏈責任的混合型保險,這反映出單一資料外洩事件可能同時造成內部損失和客戶損失。
將「第一保障」和「第三方保障」捆綁在一起的保險方案對尋求簡化管理的醫療保健和關鍵基礎設施買家頗具吸引力。醫院更傾向於將違反 HIPAA 規定的罰款和贖金賠償合併在一起的保險方案,以確保營運風險和法律風險之間不存在保障缺口。保險公司正在完善保單條款,以明確與第三方 IT 供應商相關的或有業務中斷事件的承保範圍。
預計到2024年,獨立保單將佔網路安全保險市場規模的53.9%,年複合成長率達15.4%。這是因為財產和產物保險缺乏針對勒索軟體、雲端服務中斷和社會工程攻擊觸發因素的條款。專用保單允許保險公司納入更精細的掃描資料和動態批單,並可使用演算法核保機器人將週轉時間縮短至幾小時。
對於尋求簡化營運的中型企業而言,基於附加條款的解決方案仍然具有吸引力。然而,獨立條款的彈性支持新增加密劫持保障和自願停業補償等附加元件。保險科技公司 At-Bay 和 Cowbell 實施的自動化報價系統降低了分銷成本並提高了定價準確性,從而鞏固了獨立模式的領先地位。
網路安全保險市場按承保類型(第一方責任險、第三方責任險、捆綁/混合型保險)、保險類型(獨立網路安全險、組合險/附加險)、企業規模(中小企業、大型企業)、終端用戶行業(銀行、金融服務和保險、醫療保健、零售、電子商務等)以及地區進行細分。市場預測以美元(USD)計價。
區域分析
由於資訊揭露標準成熟、精算資料豐富、仲介、再保險公司和資本市場替代方案(例如2024年發行的5.75億美元網路災難債券)等因素,北美在2024年維持了36.2%的保費佔有率。然而,戰爭風險除外條款和關鍵基礎設施保險的總額上限仍然是癥結所在,引發了關於聯邦擔保計劃的討論。
亞太地區預計到2030年將以16.7%的複合年成長率快速成長。中國的數據主權規則、日本的製造業整合以及印度蓬勃發展的金融科技產業將擴大該地區的風險池。全球通訊業者的市場准入以及本地能力的提升正在縮小保障缺口,儘管目前只有15%的合格的機構購買了保險。
在GDPR和DORA的推動下,歐洲正保持穩定成長。倫敦市場正在為產能提供支持,而德國和法國正在加速Mittelstandard製造地的採用。成員國之間分散的法規使跨國公司的保險投保變得複雜,但參數型中小企業保險正逐漸成為統一的解決方案。北歐國家作為數位化領域的領導者,正將嚴格的隱私原則與早期採用捆綁式安全和保險產品相結合。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場狀況
- 市場概況
- 市場促進因素
- 以雲端數位化會增加網路損失的風險
- 監管義務(GDPR、紐約州金融服務部法規、DORA、美國證券交易委員會規則)增加了責任。
- 董事會層級關注量化網路風險
- 為中小企業推出低成本參數化保險絲盒
- 「InsurSec」是一家集保全服務和保險於一體的公司。
- 代幣化網路保險系統獲得新的容量
- 市場限制
- 精算資料短缺與模型不確定性
- 高昂的保險費和維護標準阻礙了中小企業進入市場。
- 合約戰爭和系統風險排除
- 關鍵基礎設施風險的再保險能力限制
- 供應鏈分析
- 監管現狀和行業指南
- 技術展望(人工智慧核保、巨災模型、區塊鏈參數化)
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
- 對宏觀經濟趨勢的市場評估
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 按補償類型
- 第一方報道
- 第三方責任
- 捆綁式/混合式
- 按保險類型
- 獨立網路
- 套餐/推薦
- 按公司規模
- 小型企業
- 主要企業
- 按最終用戶產業
- BFSI
- 衛生保健
- 零售與電子商務
- 資訊科技和通訊
- 製造業
- 政府和公共部門
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美
- 歐洲
- 英國
- 德國
- 法國
- 瑞典
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 澳洲
- 韓國
- 其他亞太地區
- 中東和非洲
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 土耳其
- 南非
- 其他中東和非洲地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- American International Group(AIG)
- Chubb
- Zurich
- AXA XL
- Allianz(AGCS)
- Beazley
- Munich Re
- Berkshire Hathaway
- Travelers
- CNA
- Hiscox
- AXIS Capital
- Tokio Marine
- Sompo
- Aon
- Marsh McLennan
- Lockton
- Insureon
- Coalition
- SecurityScorecard
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The cybersecurity insurance market stands at USD 20.42 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 40.55 billion by 2030, translating into a 14.7% CAGR.

Strong demand stems from regulatory mandates such as the EU's Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) and the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) four-day disclosure rule, both of which push companies to secure balance-sheet protection against fines and operational losses. Additional momentum comes from the surge in ransomware now striking every 11 seconds board-level demand for quantified cyber-risk metrics, and new parametric offerings that cut claims settlement time for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Rising cloud reliance, especially hybrid and multi-vendor architectures, is forcing insurers to refine accumulation controls, while investors experiment with tokenized cyber insurance-linked securities to unlock fresh capacity.
Global Cybersecurity Insurance Market Trends and Insights
Cloud-First Digitalization Upsizes Cyber-Loss Exposure
Migration to cloud architectures enlarges the attack surface and amplifies systemic outage risk. The 2024 CrowdStrike software failure generated USD 5.4 billion in economic losses and exposed how a single provider disruption can trigger thousands of simultaneous claims. Munich Re responded with Cloud Protection+, a product targeted at Google Cloud workloads that reimburses business-interruption losses tied to provider outages. Hybrid environments heighten complexity, while human-error incidents in healthcare cloud systems rose 13%, representing 58% of sector breaches. Insurers now require multi-factor authentication and evidence of hardened configurations before binding cover.
Regulatory Mandates Raise Liability Stakes
DORA obliges EU financial institutions to report material cyber incidents within 4 hours, and the SEC stipulates a 4-day disclosure for U.S.-listed firms, creating twin obligations for multinationals.Non-EU vendors serving European banks must also comply, widening the addressable pool for coverage. Latin America mirrors the trend; 75% of internal-audit leaders rank cyber as the top risk due to escalating regulatory scrutiny. Insurers are adding extensions that fund remediation costs and ongoing compliance monitoring.
Actuarial Data Scarcity and Modeling Uncertainty
Cyber losses lack the long time series seen in natural-catastrophe lines, hampering credibility of tail-risk models; correlated events magnify pricing error. Carriers are investing in proprietary platforms that ingest real-time threat-intelligence, yet gaps persist in emerging markets where breach reporting is limited.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Board-Level Focus on Quantifying Cyber Risk
- SME-Specific Low-Cost Parametric Covers Emerging
- High Premium and Retention Levels Deter SMEs
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
First-party coverage retained a 42.7% cybersecurity insurance market share in 2024, driven by claims for business-interruption, incident-response, and data-rebuild costs. Third-party liability is accelerating at a 14.9% CAGR as litigation and regulatory penalties rise, nudging boards to buy higher limits. Manufacturers increasingly opt for blended policies that address operational disruption and downstream supply-chain liability, reflecting how a single breach can trigger both internal and customer losses.
Bundled covers that merge first- and third-party protections appeal to healthcare and critical-infrastructure buyers seeking streamlined administration. Hospitals favor packages that wrap HIPAA violation fines with ransom-payment reimbursement, ensuring no gaps between operational and legal exposures. Underwriters, for their part, are refining policy language to clarify coverage for contingent-business-interruption events tied to third-party IT vendors.
Stand-alone contracts captured 53.9% of the cybersecurity insurance market size in 2024 and will expand at 15.4% CAGR because property-and-casualty riders lack the parameters to address ransomware, cloud-outage, or social-engineering triggers. Dedicated forms let carriers incorporate granular scanning data and dynamic endorsements, offering turnaround times of a few hours via algorithmic underwriting bots.
Endorsement-based solutions still appeal to mid-market buyers wanting administrative simplicity. Yet the flexibility of stand-alone wording supports emerging add-ons such as cryptojacking cover or voluntary shutdown reimbursement. Automated quote systems deployed by InsurTechs At-Bay and Cowbell cut distribution costs and increase pricing accuracy, reinforcing the stand-alone model's leadership.
Cyber Security and Insurance Market is Segmented by Coverage Type (First-Party Coverage, Third-Party Liability, and Bundled/Hybrid), Insurance Type (Stand-Alone Cyber and Packaged/Endorsement), Organization Size (SMEs and Large Enterprises), End-User Industry (BFSI, Healthcare, Retail and E-Commerce, and More), by Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America retained 36.2% of 2024 premium thanks to mature disclosure norms, deep actuarial datasets, and a robust ecosystem of brokers, reinsurers, and capital-markets alternatives such as the USD 575 million of cyber catastrophe bonds issued in 2024. However, war-risk exclusions and aggregation caps on critical-infrastructure covers remain sticking points, prompting debate over federal backstop programmes.
Asia-Pacific posts the fastest 16.7% CAGR through 2030. China's data-sovereignty rules, Japan's manufacturing integration, and India's booming fintech sector enlarge the region's risk pool. Market entry by global carriers plus rising local capacity are shrinking the protection gap, though only 15% of eligible organisations currently buy cover.
Europe enjoys stable growth underpinned by GDPR and DORA. London's market anchors capacity, and Germany along with France accelerate adoption within the Mittelstand manufacturing base. Fragmented member-state rules complicate multinational placement, but parametric SME covers emerge as a unifying solution. Nordic countries, already digital leaders, combine strong privacy ethos with early uptake of bundled security-plus-insurance products.
- American International Group (AIG)
- Chubb
- Zurich
- AXA XL
- Allianz (AGCS)
- Beazley
- Munich Re
- Berkshire Hathaway
- Travelers
- CNA
- Hiscox
- AXIS Capital
- Tokio Marine
- Sompo
- Aon
- Marsh McLennan
- Lockton
- Insureon
- Coalition
- SecurityScorecard
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Cloud-first digitalization upsizes cyber-loss exposure
- 4.2.2 Regulatory mandates (GDPR, NY DFS, DORA, SEC rules) raise liability
- 4.2.3 Board-level focus on quantifying cyber risk
- 4.2.4 SME-specific low-cost parametric covers emerging
- 4.2.5 "InsurSec" models bundling security services and cover
- 4.2.6 Tokenized cyber ILS attracting new capacity
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Actuarial data scarcity and modeling uncertainty
- 4.3.2 High premium and retention levels deter SMEs
- 4.3.3 Contractual war and systemic-risk exclusions
- 4.3.4 Reinsurance capacity caps for critical-infra risks
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape and Industry Guidelines
- 4.6 Technological Outlook (AI underwriting, CAT models, blockchain parametrics)
- 4.7 Porter's Five Force Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Assesment of Macroeconomic Trends on the Market
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Coverage Type
- 5.1.1 First-party Coverage
- 5.1.2 Third-party Liability
- 5.1.3 Bundled/Hybrid
- 5.2 By Insurance Type
- 5.2.1 Stand-alone Cyber
- 5.2.2 Packaged/Endorsement
- 5.3 By Organisation Size
- 5.3.1 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
- 5.3.2 Large Enterprises
- 5.4 By End-user Industry
- 5.4.1 BFSI
- 5.4.2 Healthcare
- 5.4.3 Retail and e-Commerce
- 5.4.4 IT and Telecom
- 5.4.5 Manufacturing
- 5.4.6 Government and Public Sector
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.2 Germany
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Sweden
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 Japan
- 5.5.4.3 India
- 5.5.4.4 Australia
- 5.5.4.5 South Korea
- 5.5.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.3 Turkey
- 5.5.5.4 South Africa
- 5.5.5.5 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 American International Group (AIG)
- 6.4.2 Chubb
- 6.4.3 Zurich
- 6.4.4 AXA XL
- 6.4.5 Allianz (AGCS)
- 6.4.6 Beazley
- 6.4.7 Munich Re
- 6.4.8 Berkshire Hathaway
- 6.4.9 Travelers
- 6.4.10 CNA
- 6.4.11 Hiscox
- 6.4.12 AXIS Capital
- 6.4.13 Tokio Marine
- 6.4.14 Sompo
- 6.4.15 Aon
- 6.4.16 Marsh McLennan
- 6.4.17 Lockton
- 6.4.18 Insureon
- 6.4.19 Coalition
- 6.4.20 SecurityScorecard
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment












