 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1850109
收割機:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Harvesting Machinery - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
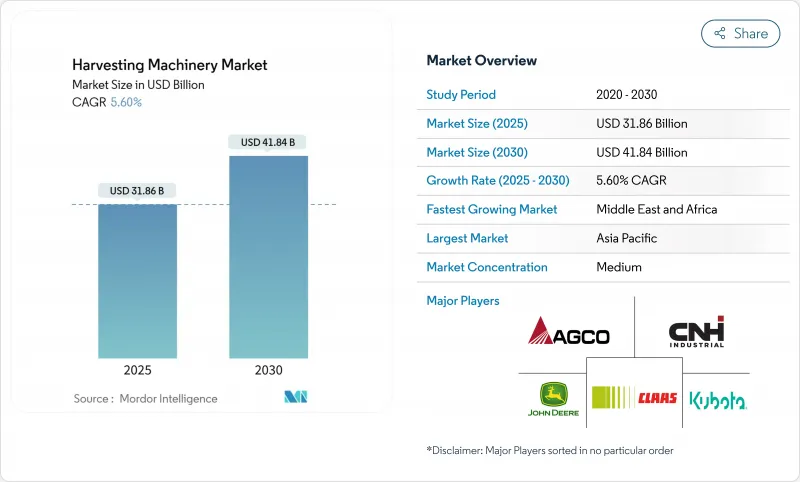
預計到 2025 年,收割機市場規模將達到 318.6 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 418.4 億美元,預測期內複合年成長率為 5.60%。
機械化進程的穩定推進、精密農業的普及以及減少勞動力依賴的自主化能力的出現,正在推動農業成長。亞太地區仍然是需求中心,而隨著補貼和合約收割模式的普及,中東和非洲地區也將快速成長。柴油引擎仍然是主要的動力傳動系統多樣化,特別是特色作物的興起,正在拓寬高性能機械的應用範圍,並為數據主導服務創造新的收入來源。
全球收割機械市場趨勢與洞察
對大容量聯合收割機的需求不斷成長
在中國和印度,隨著大型農業叢集的出現以及政策制定者對現代化設備的補貼,機械化收割正蓬勃發展。使用高效率聯合收割機收割大面積作物,可以減少收穫後損失,提高糧食質量,並縮短播種週期。規模、技術和政策的結合有望幫助該地區在中期內保持聯合收割機改進的領先地位。
政府獎勵加速新興經濟體的機械化進程
公共部門補貼、稅收優惠和貸款補貼正在重塑收割機械市場,尤其是在非洲和南美洲部分地區。各國機械化發展藍圖如今將收割機與曳引機並列為優先事項,認為其對於減少收穫後和實現糧食安全目標至關重要。一些國家將補貼與國內組裝選項掛鉤,鼓勵全球品牌建立散件組裝廠,並與當地合作夥伴合作提供售後服務支援。
小農戶的初始成本高,收入水準低。
現代聯合收割機的價格在30萬至50萬美元之間。在非洲和南亞,土地所有權分散導致機器利用率低,投資回收期長。巨大的融資缺口加劇了技術普及的差距,催生了老舊、高排放氣體次市場。
細分市場分析
聯合收割機將在2024年成為收入最高的收割機,佔據收割機市場65%的佔有率。感測模組和自動化系統的不斷改進,使得操作員可以將大部分脫粒、分離和清理工作交給軟體完成,從而在提高產量的同時節省燃油。成本效益的提案正在推動勞動市場緊張的商業農場對聯合收割機的更換需求。人工收割造成的產量損失,以及相關的健康和安全法規,正在推動這些地區對自走式甘蔗收割機的需求。
相較之下,甘蔗收割機雖然數量仍較少,但預計到2030年將以7.5%的複合年成長率成長,因為巴西、印度和泰國正在擴大其機械化甘蔗種植面積。人工收割甘蔗造成的產量損失日益增加,以及健康和安全法規的日益嚴格,正在推動這些地區採用自走式甘蔗收割機。製造商正在針對窄行、陡坡和潮濕土壤等情況客製化甘蔗收割機型號,並整合遠端資訊處理系統,用於報告甘蔗段長度均勻性和抽吸風扇轉速。這些針對特定作物的改良措施支撐了其溢價。對乳牛品質至關重要的牧草收割機,隨著操作人員升級到具有精確切碎長度控制和青貯接種劑施用器的型號,正保持著中等個位數的成長。
區域分析
亞太地區佔全球收割機市場佔有率的45%,並將於2030年之前繼續保持高於全球平均的成長速度。中國土地集約化程度的快速提高以及印度合約收割車隊的成長將刺激車隊的持續更新。中國各省的補貼政策可報銷符合條件的機械設備成本的30%,促使技術選擇傾向採用精準導航的機型,以符合國家提高產量的目標。
中東和非洲:中東和非洲是成長最快的地區,儘管目前基數不大,但預計2025年至2030年複合年成長率將達到8%。各國政府優先發展機械化,以確保糧食自給自足並減少收穫後後損失,小農戶的損失率可能超過20%。零件進口關稅豁免和合作社車隊的信貸擔保旨在發揮規模效應。中東仍是一個新興地區,該地區的溫室番茄、葉菜類蔬菜和椰棗等作物需要專門的收割機械。投資獎勵措施和自由區物流使跨國品牌能夠設立區域分銷中心,縮短前置作業時間,並確保零件供應。
北美和歐洲合計佔全球銷售量的四分之一,但兩地的車輛更換趨勢卻截然不同。北美生產商致力於將自動駕駛和互聯功能整合到現有車隊中,這促使改裝套件既能延長車輛壽命,又能提供更先進的功能。而歐洲則在嚴格的排放法規和通用農業政策獎勵的推動下,加速採用混合動力和電動車。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 對大容量聯合收割機的需求不斷成長
- 政府獎勵加速新興經濟體的機械化進程
- 勞動力短缺和工資上漲正在推動自動化
- 拓展合約收割經營模式
- 將精密農業和遠端資訊處理技術整合到收割機中
- 原廠融資和租賃方案可減輕資本支出負擔
- 市場限制
- 與小農戶的收入水準相比,前期投入成本較高。
- 商品價格波動導致機械設備採購放緩
- 在中東和非洲的經銷商和服務網路有限
- 柴油排放氣體引發的環境問題
- 波特五力模型
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 按機器類型
- 結合
- 飼料收割機
- 其他收割機(甘蔗收割機、馬鈴薯收割機、甜菜收割機、棉花收割機等)
- 透過動力來源
- 柴油引擎
- 油電混合/電動車
- 按作物類型
- 穀物和穀類
- 飼料作物
- 園藝作物
- 特色作物(甘蔗、棉花等)
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地區
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 西班牙
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 亞太其他地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 中東和非洲
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 土耳其
- 南非
- 其他中東和非洲地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Deere & Company
- CNH Industrial NV
- AGCO Corporation
- CLAAS KGaA mbH
- Kubota Corporation
- Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd.
- Yanmar Co., Ltd.
- SDF Group(Same Deutz-Fahr)
- Tractors & Farm Equipment Ltd.
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Harvesting Equipment Market size is estimated at USD 31.86 billion in 2025, and is anticipated to reach USD 41.84 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.60% during the forecast period.

Growth is propelled by steady mechanization, the spread of precision agriculture, and the arrival of autonomous functions that reduce labor dependence. The Asia-Pacific remains the center of demand, while the Middle East and Africa post the quickest gains as subsidy programs and contract-harvesting models take hold. Diesel engines still dominate powertrains, yet double-digit growth for hybrid and electric solutions signals an important transition that aligns with tightening emissions rules. Crop diversification, particularly the rise of specialty crops, is broadening the application base for sophisticated machinery and creating new revenue streams for data-driven service offerings.
Global Harvesting Machinery Market Trends and Insights
Rising Demand for High-Capacity Combine Harvesters
Mechanical harvesting is gaining momentum across China and India as larger farm clusters emerge and policymakers channel subsidies toward modern equipment. Broad-acre crops harvested with high throughput combine lower post-harvest losses, improve grain quality, and shorten turnaround times between planting cycles. This confluence of scale, technology, and policy is projected to maintain the region's leadership in combined upgrades through the medium term.
Government Incentives Accelerating Mechanization in Developing Economies
Public-sector grants, tax rebates, and subsidized loans are reshaping the harvesting equipment market, particularly in Africa and parts of South America. National mechanization roadmaps now prioritize harvesters alongside tractors, viewing them as essential to post-harvest loss reduction and food-security targets. Several countries are linking subsidies to domestic assembly conditions, nudging global brands to establish knock-down facilities and engage local partners for after-sales support.
High Upfront Cost Versus Small-Farm Income Levels
Modern combines can cost between USD 300,000 and USD 500,000, a figure beyond the reach of most smallholders. Fragmented land holdings in Africa and South Asia dilute machinery utilization rates and elongate payback periods. Acute financing gaps widen technology adoption divides and sustain a secondary market for aging, high-emission machines that underperform on fuel and grain quality.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Labor Scarcity And Wage Inflation Are Pushing Automation
- Integration of Precision Agriculture and Telematics into Harvesters
- Limited Dealer and Service Networks in Africa and the Middle East
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Combine harvesters generated the highest revenue in 2024, accounting for 65% of the harvesting equipment market. Continuous improvements in sensing modules and automation packages now enable operators to delegate most threshing, separation, and cleaning adjustments to software, which raises throughput while conserving fuel. The cost-benefit proposition drives replacement demand among commercial farms facing tighter labor markets. Rising yield penalties from manual cutting, plus health and safety rules, strengthen the case for self-propelled cane machines in these regions.
In contrast, sugar-cane harvesters, though smaller in volume, are forecast to post a 7.5% CAGR to 2030 as Brazil, India, and Thailand expand the acreage under mechanized cane. Rising yield penalties from manual cutting, plus health and safety rules, strengthen the case for self-propelled cane machines in these regions. Manufacturers tailor sugar-cane models for narrow-row layouts, steep slopes, and wetter soils, integrating telematics that report billet length uniformity and extractor-fan speed. Such crop-specific refinements support premium pricing. Forage harvesters, essential for dairy ration quality, maintain mid-single-digit growth as operators upgrade to models with precision chop length control and silage-inoculant applicators.
The Harvesting Machinery Market Report is Segmented by Machinery Type (Combine Harvester, Forage Harvester, and More), by Power Source (Diesel and Hybrid/Electric), by Crop Type (Grains and Cereals, Forage Crops, and More), and by Geography (North America, Europe, South America, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Units).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific anchors 45% of the harvesting equipment market and continues to outpace global averages through 2030. Rapid consolidation of cropland in China and growing contract-harvesting fleets in India stimulate continual fleet renewal. Provincial subsidies in China reimburse up to 30% of eligible machine costs, influencing technology choices toward models with precision guidance that aligns with national yield-improvement targets.
Middle East and Africa, while representing a modest base today, is the fastest-growing region at an 8% CAGR between 2025 and 2030. Governments prioritize mechanization to secure grain self-sufficiency and reduce post-harvest losses that can exceed 20% in smallholder systems. Import-duty waivers on components and credit guarantees for cooperative fleets aim to leverage scale effects. The Middle East remains an emerging locale where controlled-environment agriculture and government-backed desert farming require specialized harvesters for greenhouse tomatoes, leafy greens, and date palms. Investment incentives and free-zone logistics encourage multinational brands to position regional distribution hubs, closing lead-time gaps and fostering parts availability.
North America and Europe contribute a combined quarter of global sales but differ in replacement dynamics. North American growers focus on integrating autonomy and connectivity into existing fleets, leading to a rise in retrofit kits that extend asset life while delivering advanced functionality. Europe, guided by stringent emissions rules and Common Agricultural Policy incentives, accelerates the adoption of hybrid and electric units.
- Deere & Company
- CNH Industrial N.V.
- AGCO Corporation
- CLAAS KGaA mbH
- Kubota Corporation
- Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd.
- Yanmar Co., Ltd.
- SDF Group (Same Deutz-Fahr)
- Tractors & Farm Equipment Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising demand for high-capacity combine harvesters
- 4.2.2 Government incentives accelerating mechanization in developing economies
- 4.2.3 Labor scarcity and wage inflation are pushing automation
- 4.2.4 Expansion of contract-harvesting business models
- 4.2.5 Integration of precision agriculture and telematics in harvesters
- 4.2.6 OEM financing and leasing programmes easing capital expenditures burden
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High upfront cost versus small-farm income levels
- 4.3.2 Volatility in commodity prices dampening machinery purchases
- 4.3.3 Limited dealer and service networks in Africa and the Middle East
- 4.3.4 Environmental concerns over diesel emissions
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value and Volume)
- 5.1 By Machinery Type
- 5.1.1 Combine Harvesters
- 5.1.2 Forage Harvesters
- 5.1.3 Other Harvesters (Sugarcane Harvesters, Potato Harvesters, Beet Harvesters, Cotton Harvesters, etc.)
- 5.2 By Power Source
- 5.2.1 Diesel
- 5.2.2 Hybrid/Electric
- 5.3 By Crop Type
- 5.3.1 Grains and Cereals
- 5.3.2 Forage Crops
- 5.3.3 Horticultural Crops
- 5.3.4 Speciality Crops (Sugarcane, Cotton, and Others)
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Germany
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Spain
- 5.4.2.5 Russia
- 5.4.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 India
- 5.4.3.3 Japan
- 5.4.3.4 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.2 UAE
- 5.4.5.3 Turkey
- 5.4.5.4 South Africa
- 5.4.5.5 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Deere & Company
- 6.3.2 CNH Industrial N.V.
- 6.3.3 AGCO Corporation
- 6.3.4 CLAAS KGaA mbH
- 6.3.5 Kubota Corporation
- 6.3.6 Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd.
- 6.3.7 Yanmar Co., Ltd.
- 6.3.8 SDF Group (Same Deutz-Fahr)
- 6.3.9 Tractors & Farm Equipment Ltd.









