 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1849873
毫米波技術:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2031)Millimeter Wave Technology - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
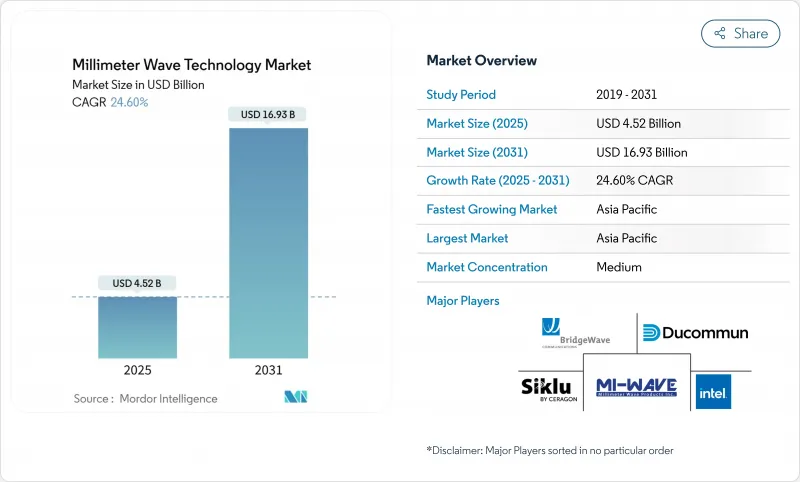
據估計,毫米波技術市場規模預計將在 2025 年達到 45.2 億美元,到 2031 年達到 169.3 億美元,預測期內(2025-2031 年)的複合年成長率為 24.60%。
網路營運商正在轉向 24 GHz 以上的頻率以緩解容量壓力,而國防機構則正在將雷達系統升級到 94 GHz 以實現更高解析度的瞄準。密集的 5G 部署和早期 6G 試驗的雙重需求正在支持資本投資,而設備成本的下降則推動了醫療成像、工業自動化和汽車 ADAS 等領域的採用。亞太地區將以數百萬個 5G 部署佔據主導地位,而北美將受益於頻譜自由化和《晶片法案》(CHIPS Act) 支持的半導體資金,推動創新。零件供應商將受益於受專利保護的射頻前端,但供應鏈暴露於氮化鎵晶圓會帶來策略風險。
全球毫米波技術市場趨勢與洞察
5G網路密集化及小型基地台回程傳輸需求
通訊業者很快發現,當小型基地台密度超過都市區分區限制時,光纖變得不經濟。在中國、美國和印度進行的現場試驗已實現數Gigabit的吞吐量,並證實毫米波回程傳輸可以取代高成本的挖溝。設備供應商目前正在整合軟體定義的波束控制以縮短對準時間,市政當局也在簡化屋頂許可核准以加快站點啟動。資本效率和縮短時間使無線回程傳輸成為毫米波技術市場的基石。
24-100 GHz 頻段行動與固定無線資料流量的成長
固定無線用戶的資料消耗量比行動用戶高出五倍,這迫使通訊業者必須為住宅閘道分配連續的28 GHz頻段。監管機構已做出回應,協調了70/80/90 GHz頻段的規則,以允許更寬的通道,晶片組製造商也推出了整合AI技術進行鏈路最佳化的第二代CPE平台。這些進步支持了農村寬頻項目,並刺激了整個市場對毫米波技術的需求。
100 GHz以上射頻前端的溫度控管限制
隨著頻率的升高,熱集中度會急劇上升,導致氮化鎵裝置的結溫不穩定。雖然採用鑽石基板和微流體冷卻的先進封裝技術正在評估中,但這些方法會增加材料成本並延長認證週期。在可擴展的熱感解決方案出現之前,短期內此技術的應用將集中在100 GHz以下頻段,限制毫米波技術市場在高頻段的成長。
細分分析
由於兆赫成像技術能夠實現腫瘤學和燒燙傷評估中的無標定組織診斷,到2030年,成像感測器的複合年成長率將達到最快。相比之下,天線和收發器將透過為行動基地台提供無線電前端,在2024年保持38%的最大佔有率。預計到2030年,毫米波技術在影像感測器中的市場規模將超過30億美元,這得益於醫院採用非電離診斷工具的推動。通訊和網路積體電路將在大型基地台緻密化的推動下實現互補成長,而介面和控制積體電路將順應片上雷達整合的趨勢。
NTT 在 300GHz 下實現 280Gbps 訊號產生等熱感突破改善了鏈路預算,刺激了對頻率捷變合成器的需求,而隨著整合商尋求更高的功率密度,其他組件(尤其是先進的基板和熱界面材料)也變得越來越重要,從而支援毫米波技術市場的組件堆疊不斷擴大。
到2024年,完全或部分授權頻譜將佔總收入的78%,這反映了電訊大型基地台和國防網路對無干擾運作的重視。然而,隨著監管機構制定簡化的工業存在感知規則,95 GHz以上未授權頻譜分配將以26.43%的複合年成長率成長。中小企業正在利用這項簡化的製度,在工廠車間部署用於機器人和品質檢測的雷達,為毫米波技術市場增添新的收益來源。
供應商現在正在推出雙模晶片組,可以自動檢測法規環境並即時調整 EIRP 設置,從而消除主要的採用障礙。雖然授權頻譜對於關鍵任務鏈路仍然至關重要,但非授權頻譜的激增正在擴大整體可尋址基礎。
mmWave 技術市場報告按組件(天線和收發器、通訊和網路 IC、介面和控制 IC、頻率產生和濾波器等)、授權模式(完全/部分授權和未授權)、頻段(24-57GHz、57-95GHz、95-300GHz)、應用(通訊基礎設施、行動和消費性設備、固定式接取)和消費性設備、固定區域進行無線存取。
區域分析
預計到2024年,亞太地區將佔全球收益的42%,到2030年,複合年成長率將達到28.02%,這得益於中國440萬個5G基地台的建設以及印度FWA的快速普及。地方政府正在撥出公共資金用於5G-Advanced研究,委託製造也在投資氮化鎵晶圓生產線以實現在地化供應。在日本的私有5G模式中,由於土地徵用複雜,毫米波的普及進展緩慢,但企業園區正在試用60GHz室內網路進行AR訓練。
在北美,頻譜政策與產業創新相契合,開放了37 GHz和70/80/90 GHz頻段,而CHIPS法案的獎勵則瞄準了國內工廠。國防雷達升級和固定無線部署支撐了穩健的基本客群,而諾基亞-T-Mobile等夥伴關係則確保了多年的設備供應管道。加拿大採用毫米波進行農村寬頻試驗,進一步擴大了毫米波技術的市場。
歐洲正將自己定位為科技實驗室。德國正在支持6G試驗台和微電子叢集,監管機構正在製定優先考慮製造業創新的42GHz競標條款。德國OEM廠商對汽車雷達的需求正在推動與專業晶片製造商的合作,英國正在探索60GHz交通基礎設施連結。中東正在投資智慧城市示範,南非正在試行28GHz FWA,巴西正在推出針對毫米波CPE組裝的有針對性的稅收優惠政策。雖然這些新興市場的收益貢獻仍維持在個位數,但成長率正超過成熟地區,為市場動態增添活力。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場狀況
- 市場概況
- 市場促進因素
- 5G 網路密集化和小型基地台回程傳輸需求
- 24-100 GHz 頻段行動與固定無線資料流量的成長
- 40GHz以上頻段的自由化與新的競標
- 國防雷達升級至 94GHz,實現低延遲瞄準
- 室內毫米波 FWA 用於最後 50 公尺光纖替換
- 122 GHz 工業存在感知法規訂定
- 市場限制
- 100 GHz以上射頻前端的溫度控管限制
- 量產中高成本相相位陣列校準
- 人口密集地區市政「街道家具」分區的障礙
- 氮化鎵晶圓供應鏈集中風險
- 價值鏈/供應鏈分析
- 監管格局
- 技術展望
- GaN 在毫米波應用的重要性
- 毫米波基板前景:LCP、PI 和 PTFE 如何影響 5G 硬體
- 波特五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
- 替代品的威脅
- COVID-19影響評估
第5章市場規模及成長預測
- 按組件
- 天線和收發器
- 通訊與網路 IC
- 介面和控制IC
- 頻率產生和濾波器
- 影像感測器
- 其他組件
- 按許可模式
- 全部/部分許可
- 未經許可
- 按頻寬
- 24~57GHz
- 57~95GHz
- 95~300GHz
- 按用途
- 通訊基礎設施(RAN 和回程傳輸)
- 行動和消費設備
- 固定無線接入(FWA)
- 雷達和安全成像
- 汽車ADAS和V2X
- 工業自動化和工業物聯網
- 醫療和生命科學成像
- 航太和國防通訊
- 其他用途
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 南美洲其他地區
- 歐洲
- 英國
- 德國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 韓國
- 其他亞太地區
- 中東和非洲
- 中東
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 土耳其
- 其他中東地區
- 非洲
- 奈及利亞
- 南非
- 其他非洲國家
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭態勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Anokiwave Inc.
- Aviat Networks
- Broadcom Inc.
- BridgeWave Communications(REMEC)
- Ducommun Incorporated
- Eravant(SAGE Millimeter)
- Farran Technology
- Huawei Technologies
- Intel Corporation
- Keysight Technologies
- L3Harris Technologies
- Millimeter Wave Products Inc.
- NEC Corporation
- Nokia Corporation
- NXP Semiconductors
- Qualcomm Technologies
- Samsung Electronics
- Sivers Semiconductors
- Siklu Communication(Ceragon)
- Smiths Interconnect
- Vubiq Networks
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Millimeter Wave Technology Market size is estimated at USD 4.52 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 16.93 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 24.60% during the forecast period (2025-2031).

Network operators are turning to frequencies above 24 GHz for capacity relief, and defense agencies are upgrading radar systems to 94 GHz for higher-resolution targeting. Dual demand arising from dense 5G rollouts and early 6G trials sustains capital spending, while falling device costs encourage adoption in medical imaging, industrial automation, and automotive ADAS. Asia Pacific commands the largest regional position thanks to multi-million-site 5G deployments, whereas North America drives innovation through spectrum liberalization and CHIPS-Act-backed semiconductor funding. Component suppliers benefit from patent-protected RF front-ends, yet supply-chain exposure to gallium-nitride wafers introduces strategic risk.
Global Millimeter Wave Technology Market Trends and Insights
5G network densification and small-cell backhaul demand
Operators quickly discover that fiber becomes uneconomical when small-cell density exceeds urban zoning caps, so 60 GHz and E-band radio links are adopted to connect sites within weeks instead of months. Field trials in China, the United States, and India deliver multi-gigabit throughput, confirming that millimeter-wave backhaul can substitute for high-cost trenching activities. Equipment vendors now integrate software-defined beam steering to reduce alignment time, while urban authorities streamline rooftop permitting to accelerate site activation. Capital efficiency and time-to-market gains make wireless backhaul a cornerstone of the millimeter wave technology market.
Rising mobile and fixed-wireless data traffic in 24-100 GHz bands
Fixed-wireless customers consume up to five times the data of mobile subscribers, forcing operators to allocate contiguous 28 GHz blocks to residential gateways. Regulatory agencies respond by harmonizing 70/80/90 GHz rules to enable wider channels, and chipset makers have announced second-generation CPE platforms with integrated AI for link optimization. These advances support rural broadband programs and stimulate demand across the millimeter wave technology market.
RF front-end thermal management limits above 100 GHz
Heat concentration rises disproportionately as frequency increases, pushing gallium-nitride devices toward junction temperatures that degrade reliability. Advanced packaging using diamond substrates and micro-fluidic cooling is under evaluation, yet these approaches add material cost and prolong qualification cycles. Until scalable thermal solutions emerge, near-term deployments will cluster below 100 GHz, tempering the millimeter wave technology market's upper-band growth.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Spectrum liberalization and new auctions above 40 GHz
- Defense radar upgrades to 94 GHz
- High-cost phased-array calibration in volume production
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Imaging Sensors deliver the fastest 25.32% CAGR through 2030, as terahertz imaging enables label-free tissue diagnosis in oncology and burn assessment. In contrast, Antennas and Transceivers preserve the largest 38% share in 2024 by supplying radio front-ends for mobile base stations. The millimeter wave technology market size for Imaging Sensors is expected to cross USD 3 billion by 2030 as hospitals adopt non-ionizing diagnostic tools. Complementary growth in Communication and Networking ICs arises from densified macro-cell deployments, while Interface and Control ICs ride the trend toward radar-on-chip integration.
R&D breakthroughs such as NTT's 280 Gbps signal generation at 300 GHz improve link budgets and stimulate demand for frequency-agile synthesizers. Meanwhile, Other Components, chiefly advanced substrates and thermal interface materials, gain visibility as integrators seek higher power density. The result is a broadening component stack that anchors the millimeter wave technology market.
Fully or Partly Licensed spectrum delivered 78% of 2024 revenue, reflecting the premium attached to interference-free operations in telecom macro cells and defense networks. However, unlicensed allocations above 95 GHz advance at 26.43% CAGR as regulators create industrial presence-sensing rules that require minimal paperwork. SMEs leverage the simplified regime to deploy factory-floor radar for robotics and quality inspection, adding fresh revenue streams to the millimeter wave technology market.
Vendors now introduce dual-mode chipsets that auto-detect regulatory environments and adjust EIRP settings in real time, removing a key adoption barrier. Licensed spectrum will remain critical for mission-critical links, yet the unlicensed surge broadens the overall addressable base.
The Millimeter Wave Technology Market Report is Segmented by Component (Antennas and Transceivers, Communications and Networking ICs, Interface and Control ICs, Frequency Generation and Filters, and More), Licensing Model (Fully/Partly Licensed and Unlicensed), Frequency Band (24-57 GHz, 57-95 GHz, and 95-300 GHz), Application (Telecom Infrastructure, Mobile and Consumer Devices, Fixed Wireless Access, and More), and Geography.
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific commands 42% of 2024 revenue and is forecast to grow at 28.02% CAGR through 2030, propelled by China's 4.4 million 5G base stations and India's rapid FWA penetration. Regional governments allocate public funds to 5G-Advanced research, and contract manufacturers invest in gallium-nitride wafer lines to localize supply. Japan's private 5G model shows slower mmWave uptake due to site-acquisition complexity, but corporate campuses are piloting 60 GHz indoor networks for AR training.
North America aligns spectrum policy with industrial innovation, releasing 37 GHz and 70/80/90 GHz bands while channeling CHIPS-Act incentives toward domestic fabs. Defense radar upgrades and fixed-wireless deployments underpin a resilient customer base, and partnerships such as Nokia-T-Mobile secure multi-year equipment pipelines. Canada adopts mmWave for rural broadband pilots, further expanding the millimeter wave technology market.
Europe positions itself as a technology laboratory. Germany supports 6G testbeds and micro-electronics clusters, and regulators craft 42 GHz auction terms that prioritize manufacturing innovation. Automotive radar demand from German OEMs drives collaboration with specialist chipmakers, while the UK explores 60 GHz transport-infrastructure links. The Middle East invests in smart-city proof-of-concepts, South Africa pilots 28 GHz FWA, and Brazil introduces targeted tax breaks for mmWave CPE assembly. Although revenue contributions from these emerging markets remain single-digit, growth rates surpass mature regions, adding dynamism to the millimeter wave technology market.
- Anokiwave Inc.
- Aviat Networks
- Broadcom Inc.
- BridgeWave Communications (REMEC)
- Ducommun Incorporated
- Eravant (SAGE Millimeter)
- Farran Technology
- Huawei Technologies
- Intel Corporation
- Keysight Technologies
- L3Harris Technologies
- Millimeter Wave Products Inc.
- NEC Corporation
- Nokia Corporation
- NXP Semiconductors
- Qualcomm Technologies
- Samsung Electronics
- Sivers Semiconductors
- Siklu Communication (Ceragon)
- Smiths Interconnect
- Vubiq Networks
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 5G network densification and small-cell backhaul demand
- 4.2.2 Rising mobile and fixed-wireless data traffic in 24-100 GHz bands
- 4.2.3 Spectrum liberalisation and new auctions above 40 GHz
- 4.2.4 Defense radar upgrades to 94 GHz for low-latency targeting
- 4.2.5 Indoor millimetre-wave FWA for last-50-metre fibre substitution
- 4.2.6 Emerging 122 GHz industrial presence-sensing regulations
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 RF front-end thermal management limits above 100 GHz
- 4.3.2 High-cost phased-array calibration in volume production
- 4.3.3 Municipal "street-furniture" zoning hurdles for dense sites
- 4.3.4 Gallium-nitride wafer supply chain concentration risk
- 4.4 Value/Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.6.1 Significance of GaN across mmWave applications
- 4.6.2 mmWave substrate landscape: LCP, PI, PTFE impact on 5G HW
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.7.5 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.8 COVID-19 Impact Assessment
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Component
- 5.1.1 Antennas and Transceivers
- 5.1.2 Communication and Networking ICs
- 5.1.3 Interface and Control ICs
- 5.1.4 Frequency Generation and Filters
- 5.1.5 Imaging Sensors
- 5.1.6 Other Components
- 5.2 By Licensing Model
- 5.2.1 Fully/Partly Licensed
- 5.2.2 Unlicensed
- 5.3 By Frequency Band
- 5.3.1 24-57 GHz
- 5.3.2 57-95 GHz
- 5.3.3 95-300 GHz
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Telecom Infrastructure (RAN and backhaul)
- 5.4.2 Mobile and Consumer Devices
- 5.4.3 Fixed Wireless Access (FWA)
- 5.4.4 Radar and Security Imaging
- 5.4.5 Automotive ADAS and V2X
- 5.4.6 Industrial Automation and IIoT
- 5.4.7 Medical and Life-Sciences Imaging
- 5.4.8 Aerospace and Defense Communications
- 5.4.9 Other Applications
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.2 Germany
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Russia
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 Japan
- 5.5.4.3 India
- 5.5.4.4 South Korea
- 5.5.4.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.5.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 Nigeria
- 5.5.5.2.2 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Anokiwave Inc.
- 6.4.2 Aviat Networks
- 6.4.3 Broadcom Inc.
- 6.4.4 BridgeWave Communications (REMEC)
- 6.4.5 Ducommun Incorporated
- 6.4.6 Eravant (SAGE Millimeter)
- 6.4.7 Farran Technology
- 6.4.8 Huawei Technologies
- 6.4.9 Intel Corporation
- 6.4.10 Keysight Technologies
- 6.4.11 L3Harris Technologies
- 6.4.12 Millimeter Wave Products Inc.
- 6.4.13 NEC Corporation
- 6.4.14 Nokia Corporation
- 6.4.15 NXP Semiconductors
- 6.4.16 Qualcomm Technologies
- 6.4.17 Samsung Electronics
- 6.4.18 Sivers Semiconductors
- 6.4.19 Siklu Communication (Ceragon)
- 6.4.20 Smiths Interconnect
- 6.4.21 Vubiq Networks
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment










