 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1846357
特種酵素:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據、成長預測(2025-2030 年)Specialty Enzymes - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
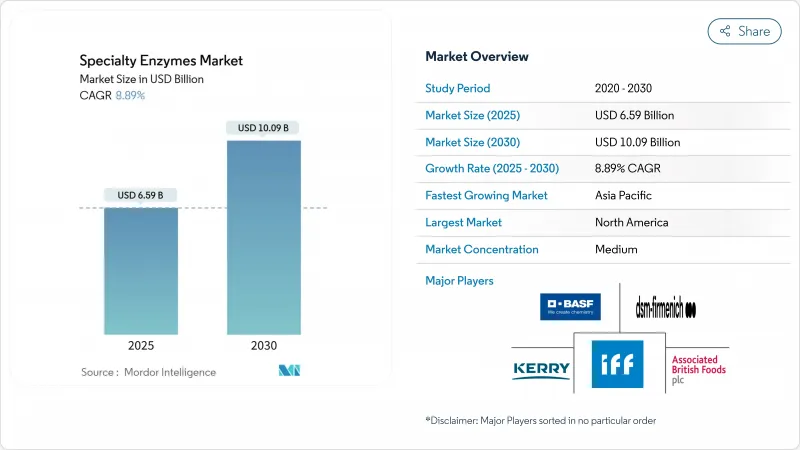
預計到 2025 年,特種酵素市場規模將達到 65.9 億美元,到 2030 年將擴大到 100.9 億美元,複合年成長率為 8.89%。
生物催化在藥物合成中的快速應用、對環境友善工業加工日益成長的需求以及酶核准藥物的廣泛獲批,共同推動了這一成長趨勢。人工智慧引導的酵素工程研發投入正將研發週期從數年縮短至數月,從而促進快速商業化並降低成本壁壘。這些進步使製造商能夠在滿足不斷變化的行業需求的同時,保持成本效益。有利於綠色化學的監管獎勵,以及消費者對天然配方的偏好,正促使製造商轉向重組酶和植物來源酶。諸如CelOCE這樣的突破性技術——一種能夠將纖維素轉化效率提高一倍的金屬酶——凸顯了酶創新在生質燃料和其他資源密集型行業中的變革潛力。此類創新可望顯著提高各種應用領域的永續性和營運效率。
全球特種酵素市場趨勢與洞察
在製藥生產中擴大採用環境友善生物催化劑
為了遵守環境法規並最佳化生產成本,製藥公司正採用生物催化技術取代傳統的化學催化劑。食品藥物管理局(FDA) 將於 2025 年對包括 POMBILITI 和 EPKINLY 在內的生技藥品進行監管審查,這預示著基於酶的治療藥物的核准流程將得到簡化。與傳統方法相比,工程酶能夠以更高的選擇性和更少的廢棄物來生產掌性藥物中間體。計算設計工具縮短了酵素的開發週期,使製藥公司能夠更有效率地開發用於特定藥物合成路線的生物催化劑。這種轉變在生技藥品生產中至關重要,因為酵素的特異性可以減少純化的需求。酶的應用範圍正在擴展到基於酶的藥物遞送系統和用於治療遺傳疾病的酶,這為特種酶生產商創造了新的商機。
政府透過政策和資金支持推動市場成長。
政府舉措正透過政策架構和直接資助,加速特種酵素市場的發展,這些措施支持研究、商業化和產業應用。政府提供津貼、稅收優惠和官民合作關係(PPP)項目,以支持生物製藥、診斷、食品加工和工業生物催化等領域的酵素創新研發。印度的BioE3計畫是政府在生物技術領域的一項重大舉措,該計畫撥款919.7億印度盧比(約合11億美元)用於建立生物基化學品和酵素的生物製造中心。該計畫的目標是到2030年實現3,000億美元的生物經濟規模,使酵素成為包括精準生物治療和氣候適應型農業在內的六大領域的關鍵組成部分。中國更新後的食品安全監管體系透過強制性報名手續,為酵素生產商創造了機遇,該程序有利於那些擁有良好安全記錄的公司。歐盟對食品酵素的上市前核准要求規範了安全評估,並降低了合規生產商的市場進入門檻。
客製化酶的生產成本高昂
客製化酵素的設計、工程和規模化生產涉及複雜的流程,需要對先進技術、熟練勞動力和品管措施進行大量投資。對特殊原料的需求以及嚴格的監管合規性增加了生產成本。為特定工業流程客製化酵素需要大量的研發投入,開發週期通常超過兩到三年,才能實現商業化。中小型生物技術公司在從實驗室生產擴展到商業規模生產方面面臨巨大的挑戰。必要的發酵基礎設施需要大量的資本投入和專業知識。工業酵素和藥用酵素的價格差異反映了它們各自的價值提案:藥用蛋白每公斤價格高達數千美元,而工業酵素每公斤價格僅為幾十美元。為了符合不同最終用途的監管標準,需要專門的純化製程和品管系統,這會影響生產成本。
細分市場分析
由於重組DNA技術在酵素生產中具有擴充性和成本優勢,微生物來源酵素預計在2024年將佔68.84%的市場佔有率。受消費者對天然成分的需求以及食品和化妝品應用領域對永續性要求的推動,植物來源酶預計將以9.97%的複合年成長率成長(2025-2030年)。由於倫理問題和監管限制,動物來源酵素的需求正在下降,尤其是在歐洲市場,該市場對替代供應來源的需求日益成長。
微生物酶因其在可控發酵環境中生產而佔據較高的市場佔有率,與植物或動物組織萃取物相比,這不僅確保了品質的穩定性,還降低了污染風險。微生物生產系統正利用合成生物學的進步來開發生產菌株,從而提高酶的分泌效率並最大限度地減少產品特異性產物的產生。從農業廢棄物中提取酵素的新型萃取方法為植物來源酵素的生產提供了支持,這不僅為循環經濟創造了機遇,也降低了原料成本。
液體製劑將在2024年佔據市場主導地位,市場佔有率高達57.23%,預計到2030年將以10.47%的複合年成長率成長,這主要得益於其卓越的性能和廣泛的應用範圍。乾粉酶製劑在一些特殊應用領域仍佔有一席之地,這些領域對延長保存期限和降低運輸成本至關重要,尤其是在動物飼料和工業清洗領域。市場對液體製劑的偏好源於其即時生物利用度和無需溶解即可無縫整合到生產過程中的優勢。近年來,穩定化技術的進步顯著提高了液體酵素的保存期限,克服了以往液體製劑相對於乾粉製劑的一個主要限制。
非水液體體係正日益被應用於需要更高基材溶解度和更低反饋抑制的領域。濃縮液體配方可在保持酵素活性的同時降低儲存和運輸成本。乾粉配方也隨著先進的噴霧乾燥和冷凍乾燥技術的進步而不斷改進,這些技術能夠在脫水過程中保持酵素的結構和活性。
區域分析
2024年,北美佔據了特種酵素市場33.22%的佔有率,這得益於其強大的醫藥研發體系和高效的監管環境,後者有利於酵素製劑的核准。該地區的頂尖大學正在引領人工智慧主導的酵素設計,推動本土創新。此外,支持永續生產的稅收優惠政策促進了酵素在各種工業流程中的應用,鞏固了北美的市場主導地位。該地區對技術進步和產學夥伴關係的高度重視,進一步增強了其在全球市場的競爭力。
同時,亞太地區預計將以10.04%的複合年成長率佔據市場主導地位。扶持政策和固有的成本優勢是推動這一成長的主要動力。印度的BioE3策略,以及中國修訂後的食品酶法規,為市場准入鋪平了道路。此外,該地區低廉的生產成本、高素質的人才儲備和先進的基礎設施也吸引全球酵素生產商。尤其是在四方機制架構下進行的合作研發,正協助亞太地區實現成為酵素生產中心的願景。該地區對生物技術的日益重視以及政府為提升酵素生產能力所採取的支持性舉措,進一步促進了該地區的快速成長。
歐洲、南美洲以及中東和非洲地區也都取得了長足進展。歐洲的優勢在於其嚴格的安全通訊協定和先進的永續性議程。此外,該地區對綠色化學和環保酵素應用的重視,與永續性目標相契合,也有助於進一步擴大市場。同時,在南美,受益於有利的貿易協定和生物經濟舉措,巴西和阿根廷的生物技術企業正在推動食品和農業領域的成長。中東和非洲地區則因加強醫療保健和解決糧食安全問題而取得進展。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 在製藥生產中擴大採用環境友善生物催化劑
- 政府透過政策和資金支持推動市場成長。
- 酶工程和定向進化的進展
- 化妝品和皮膚科領域對酵素去角質的需求
- 對酵素傷口清除產品的需求激增
- 人們對綠色化學和永續工業過程的興趣日益濃厚
- 市場限制
- 客製化酶的生產成本高昂
- 保存期限短和穩定性挑戰
- 酵素療法中過敏反應和免疫抗原性的風險
- 使用動物性酵素的倫理問題
- 供應鏈分析
- 監理展望
- 五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方/消費者的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭強度
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 按原料
- 植物
- 微生物
- 動物
- 按形式
- 液體
- 烘乾
- 按類型
- 碳水化合物分解酶
- 蛋白酶
- 脂肪酶
- 其他
- 透過使用
- 飲食
- 製藥
- 餵食
- 其他
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地區
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 法國
- 英國
- 西班牙
- 荷蘭
- 義大利
- 瑞典
- 波蘭
- 比利時
- 其他歐洲
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 韓國
- 印尼
- 泰國
- 新加坡
- 亞太其他地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 智利
- 哥倫比亞
- 秘魯
- 其他南美洲
- 中東和非洲
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 南非
- 奈及利亞
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 埃及
- 摩洛哥
- 土耳其
- 其他中東和非洲地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略舉措
- 市場排名分析
- 公司簡介
- International Flavors & Fragrances
- DSM-Firmenich AG
- Kerry Group plc
- BASF SE
- Associated British Foods plc
- Amano Enzyme
- Novozymes A/S
- Specialty Enzymes & Probiotics
- Suntaq International Limited
- Biocatalysts Ltd.
- Advanced Enzyme Technologies
- ENZIQUIM
- Nagase America LLC
- AST Enzymes
- Sunson Industry Group
- Enzyme Development Corporation
- Antozyme Biotech Pvt Ltd,
- NOOR ENZYMES(DWC)LLC
- Bioseutica BV
- Apex International
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The specialty enzymes market size stands at USD 6.59 billion in 2025 and is projected to advance to USD 10.09 billion by 2030, reflecting an 8.89% CAGR.

Rapid adoption of biocatalysts in pharmaceutical synthesis, a rising demand for eco-friendly industrial processing, and broader therapeutic approvals for enzyme-based medicines drive the growth trajectory. Investments in AI-guided enzyme engineering have shortened development cycles from years to months, facilitating quicker commercialization and reducing cost barriers. These advancements are enabling manufacturers to meet evolving industry demands while maintaining cost efficiency. Regulatory incentives favoring greener chemistries, combined with consumer preferences for natural formulations, are pushing manufacturers towards recombinant and plant-derived enzymes. Breakthroughs like the CelOCE metalloenzyme, which can double cellulose conversion efficiency, highlight the transformative potential of enzyme innovation in biofuels and other resource-intensive industries. Such innovations are expected to significantly enhance sustainability and operational efficiency across various applications.
Global Specialty Enzymes Market Trends and Insights
Increasing Adoption of Eco-friendly Biocatalysts in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Pharmaceutical manufacturers are adopting biocatalysts instead of traditional chemical catalysts to comply with environmental regulations and optimize manufacturing costs. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA)'s regulatory review periods for biologics, including POMBILITI and EPKINLY in 2025, indicate streamlined approval processes for enzyme-based therapeutics . Engineered enzymes enable the production of chiral pharmaceutical intermediates with improved selectivity and reduced waste compared to traditional methods. Computational design tools have shortened enzyme development cycles, enabling pharmaceutical companies to develop biocatalysts for specific drug synthesis routes more efficiently. This transition is significant in biologics production, where enzyme specificity reduces purification requirements. The applications have expanded to enzyme-based drug delivery systems and therapeutic enzymes for genetic disorders, creating new opportunities for specialty enzyme manufacturers.
Government Support Drives Market Growth Through Policy and Funding
Government initiatives are accelerating the growth of the specialty enzymes market through policy frameworks and direct funding that support research, commercialization, and industrial adoption. Governments provide grants, tax incentives, and public-private partnership (PPP) programs to support research and development in enzymatic innovations across biopharmaceuticals, diagnostics, food processing, and industrial biocatalysis sectors. India's BioE3 policy represents a major government intervention in biotechnology, with an allocation of INR 9,197 crore (USD 1.1 billion) to establish biomanufacturing hubs for bio-based chemicals and enzymes. The policy aims to achieve a USD 300 billion bioeconomy by 2030, identifying enzymes as essential components across six areas, including precision biotherapeutics and climate-resilient agriculture . China's updated food safety regulatory system has created opportunities for enzyme manufacturers through mandatory registration procedures that benefit established companies with proven safety records . The European Union's pre-market approval requirements for food enzymes have standardized safety assessments, reducing market entry barriers for compliant manufacturers.
High Production Cost for Customised Enzymes
The complex processes involved in designing, engineering, and scaling up tailored enzymes require substantial investment in advanced technologies, skilled labor, and quality control measures. The need for specialized raw materials and stringent regulatory compliance increases production costs. Customizing enzymes for specific industrial processes demands extensive research and development investments, with development timelines typically exceeding 2-3 years before commercial viability. Small and medium-sized biotechnology companies encounter significant challenges in scaling production from laboratory to commercial quantities. The required fermentation infrastructure demands substantial capital investment and specialized expertise. The pricing difference between industrial and pharmaceutical enzymes reflects their distinct value propositions, with pharmaceutical proteins priced at thousands of dollars per kilogram compared to tens of dollars for industrial applications. Manufacturing economics are impacted by the requirement for specialized purification processes and quality control systems that comply with regulatory standards for different end-use applications.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Advancement in Enzyme Engineering and Directed Evolution
- Demand from Cosmetic and Dermatology Sectors for Enzymatic Peels
- Short Shelf Life and Stability Challenges
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Microbial sources hold a 68.84% market share in 2024, due to the scalability and cost advantages of recombinant DNA technology for enzyme production. Plant-derived enzymes are growing at 9.97% CAGR (2025-2030), driven by consumer demand for natural ingredients and sustainability requirements in food and cosmetic applications. Animal-derived enzymes experience declining demand due to ethical concerns and regulatory restrictions, especially in European markets where alternative sources are increasingly required.
The high market share of microbial enzymes results from their production in controlled fermentation environments, ensuring consistent quality and reduced contamination risks compared to plant or animal tissue extraction. Microbial production systems leverage advances in synthetic biology to develop production strains with improved enzyme secretion and minimized by-product formation. The growth in plant sources is supported by new enzyme extraction methods from agricultural waste, which create circular economy opportunities and lower raw material costs.
Liquid formulations dominate the market with a 57.23% share in 2024 and are projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.47% through 2030, driven by their superior performance characteristics and application versatility. Dry enzyme formulations maintain their position in specialized applications where extended shelf life and reduced shipping costs are essential, particularly in animal feed and industrial cleaning sectors. The market preference for liquid formulations stems from their immediate bioavailability and seamless integration into manufacturing processes without dissolution requirements. Recent advances in stabilization technologies have improved the shelf life of liquid enzymes, addressing a key historical limitation compared to dry formulations.
Non-aqueous liquid systems are increasing in adoption for applications that require better substrate solubility and reduced feedback inhibition. Concentrated liquid formulations offer reduced storage and transportation costs while maintaining enzyme activity. Dry formulations continue to improve through advanced spray-drying and freeze-drying techniques that maintain enzyme structure and activity during dehydration.
The Specialty Enzymes Market is Segmented by Source (Plant, Microbial, and Animal), by Form (Liquid, and Dry), by Enzyme Type (Carbohydrases, Proteases, Lipases, and Others), by Application (Food and Beverages, Pharmaceutical, Animal Feed, and Others), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
In 2024, North America clinched a commanding 33.22% share of the specialty enzymes market, bolstered by its robust pharmaceutical research and development landscape and efficient regulatory pathways that expedite enzyme-based drug approvals. Leading universities in the region spearhead AI-driven enzyme design, propelling domestic innovation. Furthermore, tax incentives championing sustainable manufacturing have amplified enzyme utilization across various industrial processes, solidifying North America's preeminence. The region's strong focus on technological advancements and partnerships between academia and industry further strengthens its competitive edge in the global market.
Asia-Pacific, on the other hand, is set to outpace others with a projected 10.04% CAGR. Supportive policies and inherent cost advantages underpin this growth. India's BioE3 strategy, coupled with China's revamped food-enzyme regulations, has smoothed the path for market entry. Moreover, the region's affordable production costs, a reservoir of skilled talent, and state-of-the-art infrastructure are luring global enzyme manufacturers. Collaborative research and development efforts, particularly under the Quad framework, bolster Asia-Pacific's aspirations of becoming a dominant enzyme production hub. The region's growing focus on biotechnology and government-backed initiatives to enhance enzyme production capacity further contribute to its rapid growth.
Europe, South America, the Middle East, and the Africa region are also making strides. Europe's edge lies in its stringent safety protocols and a forward-thinking sustainability agenda, both of which enhance product quality and bolster consumer trust. Additionally, the region's emphasis on green chemistry and eco-friendly enzyme applications aligns with its sustainability goals, driving further market expansion. Meanwhile, in South America, biotech ventures in Brazil and Argentina, buoyed by favorable trade agreements and bioeconomy initiatives, are driving growth in the food and agriculture sectors. The Middle East and Africa region is witnessing advancements, owing to healthcare enhancements and initiatives aimed at food security.
- International Flavors & Fragrances
- DSM-Firmenich AG
- Kerry Group plc
- BASF SE
- Associated British Foods plc
- Amano Enzyme
- Novozymes A/S
- Specialty Enzymes & Probiotics
- Suntaq International Limited
- Biocatalysts Ltd.
- Advanced Enzyme Technologies
- ENZIQUIM
- Nagase America LLC
- AST Enzymes
- Sunson Industry Group
- Enzyme Development Corporation
- Antozyme Biotech Pvt Ltd,
- NOOR ENZYMES (DWC) LLC
- Bioseutica BV
- Apex International
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increasing Adoption of Eco-friendly Biocatalysts in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
- 4.2.2 Government Support Drives Market Growth Through Policy and Funding
- 4.2.3 Advancement in Enzyme Engineering and Directed Evolution
- 4.2.4 Demand from Cosemetic and Dermatology Sectors for Enzymatic Peels
- 4.2.5 Surge in Demand for Enzymatic Wound Debridement Products
- 4.2.6 Growing Focus on Green Chemistry and Sustainable Industrial Process
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Production Cost for Customised Enzymes
- 4.3.2 Short Shelf Life and Stability Challenges
- 4.3.3 Risk of Allergic Reaction and Immunogenicity in Enzyme Therapy
- 4.3.4 Ethical Concern in Use of Animal-Derived Enzymes
- 4.4 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Source
- 5.1.1 Plant
- 5.1.2 Microbial
- 5.1.3 Animal
- 5.2 By Form
- 5.2.1 Liquid
- 5.2.2 Dry
- 5.3 By Type
- 5.3.1 Carbohydrases
- 5.3.2 Proteases
- 5.3.3 Lipases
- 5.3.4 Others
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Food and Beverages
- 5.4.2 Pharmaceutical
- 5.4.3 Animal Feed
- 5.4.4 Others
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 France
- 5.5.2.3 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.4 Spain
- 5.5.2.5 Netherlands
- 5.5.2.6 Italy
- 5.5.2.7 Sweden
- 5.5.2.8 Poland
- 5.5.2.9 Belgium
- 5.5.2.10 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 India
- 5.5.3.3 Japan
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 South Korea
- 5.5.3.6 Indonesia
- 5.5.3.7 Thailand
- 5.5.3.8 Singapore
- 5.5.3.9 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Chile
- 5.5.4.4 Colombia
- 5.5.4.5 Peru
- 5.5.4.6 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.2 South Africa
- 5.5.5.3 Nigeria
- 5.5.5.4 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.5 Egypt
- 5.5.5.6 Morocco
- 5.5.5.7 Turkey
- 5.5.5.8 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials (if available), Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 International Flavors & Fragrances
- 6.4.2 DSM-Firmenich AG
- 6.4.3 Kerry Group plc
- 6.4.4 BASF SE
- 6.4.5 Associated British Foods plc
- 6.4.6 Amano Enzyme
- 6.4.7 Novozymes A/S
- 6.4.8 Specialty Enzymes & Probiotics
- 6.4.9 Suntaq International Limited
- 6.4.10 Biocatalysts Ltd.
- 6.4.11 Advanced Enzyme Technologies
- 6.4.12 ENZIQUIM
- 6.4.13 Nagase America LLC
- 6.4.14 AST Enzymes
- 6.4.15 Sunson Industry Group
- 6.4.16 Enzyme Development Corporation
- 6.4.17 Antozyme Biotech Pvt Ltd,
- 6.4.18 NOOR ENZYMES (DWC) LLC
- 6.4.19 Bioseutica BV
- 6.4.20 Apex International










