 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1846276
郵政自動化系統:市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Postal Automation System - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
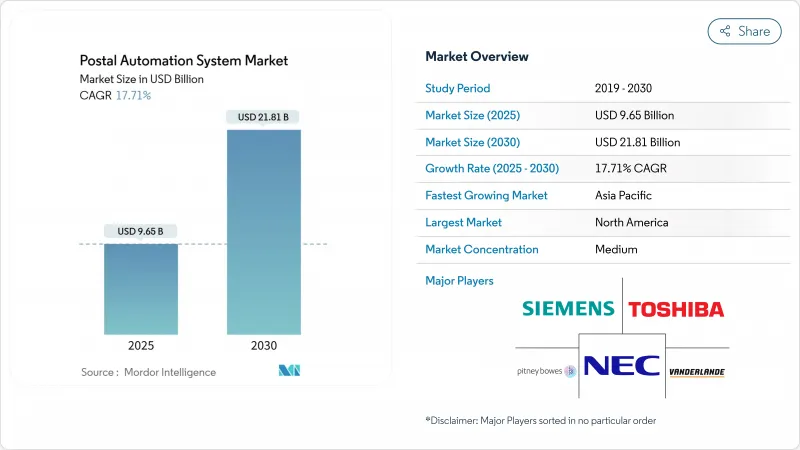
預計到 2025 年郵政自動化系統市場規模將達到 96.5 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 218.1 億美元,複合年成長率為 17.71%。
這一成長反映了跨境電子商務需求的不斷成長、郵政現代化計劃以及持續的人事費用壓力,這些因素使得自動化在經濟上具有吸引力。由於公共部門的大量投資和有利於下一代設備的能源效率法規,北美和歐洲的安裝數量最多。隨著中國郵政、菜鳥網路和日本郵政加快農村和都市區地區的自動化計劃,亞太地區是一個快速成長的地區,這縮短了交貨時間並降低了人事費用。雖然硬體仍然是主要的採購重點,但需求正在轉向服務合約和機器人即服務模式,這些模式將效能風險轉移給供應商。范德蘭德收購西門子物流和 BlueCrest 收購 Fluence Automation 正在透過硬體和軟體的整合重新定義規模優勢。
全球郵政自動化系統市場趨勢與洞察
跨境電商小包裹激增推動高吞吐量分類機的發展
跨境電商小包裹流量持續成長,預計到2023年,美國小包裹量將達到217億件,儘管單件收入有所下降,但這凸顯了對高效高吞吐量自動化的需求。亞馬遜物流的包裹量已超過UPS,證明了速度最佳化的分類網路能夠帶來市場優勢。中國郵政和菜鳥網路引入了自動讀取運單的視覺引導系統,降低了農村地區的人事費用,縮小了都市區服務差距。自動化技術能夠在不增加員工數量的情況下實現大量處理,因此營運商現在更重視處理密度而非單件成本。
美國郵政「為美國遞送」現代化措施推動自動化升級
美國郵政總局 (USPS) 投資 400 億美元進行網路現代化改造,將每日小包裹處理能力提升至 6,000 萬個包裹,並簡化和提升了郵件和小包裹流的可靠性。 Zebra Technologies 印表機、全新遠端傳輸系統以及 USPS Ship 的遷移增強了物理自動化背後的數位層面。供應商正在利用 USPS 規範在全球擴展類似的解決方案,從而產生技術連鎖反應,加速其他地區的採用。
傳統 IT 整合的複雜性限制了新興市場的採用
發展中的郵局通常採用過時的平台營運,無法輕鬆連接現代分揀機,從而延長了計劃工期並增加了成本。國際貨幣基金組織指出,支付管道也面臨類似的挑戰,這反映了物流瓶頸,凸顯了在先進自動化技術推廣之前,基礎數位基礎設施的必要性。
細分分析
2024年,郵件分揀系統市場規模(歸因於硬體)達到62億美元,這反映了對資本密集輸送機、感測器和光學字元辨識(OCR)的投資。服務收益基數較小,但預計到2030年將以20.8%的複合年成長率成長,因為營運商更注重管理成果而非設備所有權。軟體授權連接了兩者,支援即時效能儀錶板、路線最佳化和預測性維護,從而延長資產壽命。
Quadient 和 BlueCrest 透過採用基於績效的契約,保證了吞吐量水準和運作,將風險轉移給供應商。此類安排使中型企業無需前期投資即可使用高級功能,從而擴大了郵件分揀系統市場的潛在用戶群。雖然硬體支出仍將保持高額,但收益結構分析表明,隨著固定費率和按分類付費模式的推廣,到 2030 年,服務收入將縮小差距。
得益於久經考驗的交叉帶式和翻盤式設計,小包裹分揀機將在2024年佔據郵件分揀系統市場佔有率的42%。然而,成長動力將來自自動導引車和協作機器人,到2030年,其複合年成長率將達到24.1%。機器人技術打破了固定軌道的限制,使營運商能夠快速重新配置樞紐,以應對季節性高峰。
根據法國郵政的數據,到2024年,其郵件收入佔有率將從2010年的52%下降到15.8%,這表明其業務結構將從以信件為中心的機器轉向以小包裹為中心的機器人。彩色蓋銷機在高容量郵票領域佔據一席之地,但整合了自動導引車(AGV)、視覺系統和編碼模組的混合站點提供了更大的靈活性。供應商現在正在將車隊管理軟體與移動機器人捆綁在一起,從而提高受城市樞紐房地產限制的營運商的投資回報率。
區域分析
受美國郵政「Delivering for America」(為美國遞送)計畫的推動,北美地區引領全球銷售成長。該計畫投資400億美元用於設施升級,並將每日遞送能力提升至6,000萬個包裹。加拿大也緊跟在後,採用機器人來緩解多倫多和溫哥華等主要城市樞紐的勞動力短缺問題。穩定的管理體制和可預測的包裹流量縮短了回報期,使得供應商越來越傾向於在該地區儘早部署產品。
在《淨零工業法案》的支持下,歐洲正經歷強勁成長。該法案優先考慮節能設備,並加快了設備更換週期。在德國,郵政法的修訂賦予了德國郵政在最佳化路線方面更大的靈活性,而DHL在郵件和小包裹分別擁有63%和40%的市場佔有率,為全國自動化帶來了規模經濟效益。在英國,DHL電子商務與Every的合併獲得核准,這將創建一個每年可處理超過10億小包裹的綜合網路,並帶來進一步的自動化投資。
亞太地區複合年成長率最高,這得益於中國郵政和菜鳥的自動化部署,以及日本為解決駕駛人而提案的500公里自動化輸送機網路。韓國正在利用其先進的通訊基礎設施來推廣RFID分類技術,而印度則正努力應對設備關稅問題,這導致計劃成本不斷上漲。人口分散的澳洲對機器人技術的興趣日益濃厚,希望藉此靈活擴展遠距運輸能力。
拉丁美洲發展不平衡。墨西哥受益於與美國-墨西哥-加拿大協定(USMCA)的接近性,吸引了大量跨境小包裹,這為在北部樞紐部署自動化提供了理由。巴西的合規計畫支持電子商務成長,但進口自動化產品的關稅仍拖累整體擁有成本。阿根廷的經濟波動延長了投資決策週期,限制了高階解決方案的市場滲透。
中東和非洲仍在發展中,但前景光明。海灣國家正在投資城市微型倉配設施,這需要一個緊湊的模組化系統,但在非洲,傳統的IT障礙阻礙了其應用。旨在實現郵政基礎設施現代化的國際援助計畫或許能釋放未來的需求,尤其是在智慧型手機主導的商業活動在主要城市走廊不斷擴張的背景下。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場狀況
- 市場概況
- 市場促進因素
- 亞洲跨境電子商務小包裹數量激增
- 美國郵政「為美國遞送」現代化
- 歐盟綠色交易推動節能系統更換
- 勞動力短缺和工資上漲將推動機器人壟斷
- 日本和韓國採用基於RFID的分類技術
- 都市區的微型倉配將推動對小型分類機的需求
- 市場限制
- 非洲和拉丁美洲郵政系統中的遺留IT整合
- 資本密集投資,投資報酬率可達 7 年以上
- 歐洲信件數量下降
- 巴西和印度對自動化進口徵收關稅
- 價值/供應鏈分析
- 監管和技術展望
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
- 技術簡介
第5章市場規模及成長預測
- 按解決方案
- 硬體
- 軟體
- 服務
- 依技術
- 彩色移相器消除器 (CFC) 系統
- 信件分類器
- 平面郵件分類機
- 小包裹分類機
- 混合郵件分類機
- 編碼、列印和 OCR 系統
- 自動導引車和機器人
- 其他
- 按用途
- 小包裹
- 郵件分類
- 地址列印和標籤
- 資料擷取和OCR
- 最後一哩配送
- 樞紐自動化
- 按最終用戶
- 國家郵政服務
- 宅配、速遞和小包裹(CEP) 公司
- 履約中心
- 政府機關等
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 歐洲
- 英國
- 德國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 其他歐洲國家
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 韓國
- 亞洲其他地區
- 中東
- 以色列
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 土耳其
- 其他中東地區
- 非洲
- 南非
- 埃及
- 其他非洲國家
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 南美洲其他地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭態勢
- 策略舉措
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Siemens Logistics GmbH
- Toshiba Infrastructure Systems and Solutions Corp.
- NEC Corporation
- Pitney Bowes Inc.
- Vanderlande Industries BV
- Beumer Group GmbH and Co. KG
- Solystic SAS
- Fives Group
- Bowe Systec GmbH
- Interroll Holding AG
- BlueCrest Inc.
- Opex Corporation
- EuroSort Systems
- Honeywell Intelligrated
- Dematic(Kion Group)
- KUKA AG
- Zhejiang Libiao Robotics
- Fluence Automation LLC
- Leonardo SpA
- Engineering Production and Installation(EPI)
第7章 市場機會
- 閒置頻段和未滿足需求評估
The postal automation system systems market size was valued at USD 9.65 billion in 2025 and is forecast to grow at a 17.71% CAGR, reaching USD 21.81 billion by 2030.

Growth reflects rising cross-border e-commerce demand, postal modernization programs and sustained labor cost pressures that make automation economically attractive. North America and Europe account for the largest installed base because of sizeable public-sector investments and energy-efficiency regulations that favor next-generation equipment. Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region as China Post, Cainiao and Japan Post accelerate rural and urban automation projects, shortening delivery times and lowering manual labor costs. Hardware continues to dominate purchases, yet demand is shifting toward service contracts and robotics-as-a-service models that transfer performance risk to suppliers. Competitive intensity is moderate, with Vanderlande's purchase of Siemens Logistics and BlueCrest's acquisition of Fluence Automation redefining scale advantages in integrated hardware-software offerings.
Global Postal Automation System Market Trends and Insights
Surge in Cross-Border E-Commerce Parcel Volumes Driving High-Throughput Sorters
E-commerce parcels crossing borders continue to climb, with US parcel volumes reaching 21.7 billion in 2023 even as revenue per piece declined, underscoring the need for efficient high-throughput automation. Amazon Logistics overtook UPS on volume, proving that speed-optimized sorting networks confer a market edge. China Post and Cainiao lowered rural labor costs by deploying vision-guided systems that read waybills automatically, narrowing the urban-rural service gap. Operators now focus on processing density rather than cost per piece, since automation enables higher volumes without proportional staffing increases.
USPS "Delivering for America" Modernization Spurring Automation Upgrades
USPS committed USD 40 billion to revamp its network, expanding daily package capacity to 60 million items and aligning mail and parcel flows for improved reliability. Zebra Technologies printers, a new remote forwarding system, and the USPS Ship migration reinforce the digital layer underpinning physical automation. Suppliers leverage USPS specifications to scale similar solutions globally, creating a technology spill-over that accelerates adoption in other regions.
Legacy IT Integration Complexity Limiting Emerging Market Adoption
Developing posts often run on ageing platforms that cannot easily connect to modern sorters, extending project timelines and raising costs. The IMF highlights similar challenges in payment rails that mirror logistics bottlenecks, stressing a need for basic digital infrastructure before advanced automation can scale.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Labor Shortages Accelerating Robotic Singulation Adoption
- EU Green Deal Demand for Energy-Efficient Systems
- Capital-Intensive Investments Deterring Small CEP Operators
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The mail sorting systems market size attributed to hardware reached USD 6.2 billion in 2024, reflecting capital-intensive conveyor, sensor and OCR investments. Services produced a smaller revenue base but are projected to grow at a 20.8% CAGR to 2030 as operators favor managed outcomes over outright equipment ownership. Software licenses bridge the two, enabling live performance dashboards, route optimization and predictive maintenance that extend asset life.
Adoption of outcome-based contracts shifts risk to vendors, with Quadient and BlueCrest guaranteeing throughput levels and uptime. These arrangements allow even mid-tier operators to access sophisticated capabilities without upfront capital, broadening the addressable base for the mail sorting systems market. Hardware spending will remain sizeable, yet revenue mix analysis shows services closing the gap by 2030 as subscription and pay-per-sort models scale.
Parcel sorters commanded 42% of the mail sorting systems market share in 2024 on the strength of long-established cross-belt and tilt-tray designs. Growth momentum, however, lies with automated guided vehicles and collaborative robots that post a 24.1% CAGR through 2030. Robotics removes fixed-track constraints, letting operators re-configure hubs quickly to manage seasonal peaks.
La Poste's data show mail contributing only 15.8% of revenue in 2024, down from 52% in 2010, signaling a structural shift away from letter-centric machinery toward parcel-centric robotics. Culler-facer-canceller units retain a niche in high-volume philatelic segments, but hybrid sites integrating AGVs, vision systems and coding modules deliver superior flexibility. Vendors now bundle fleet-management software with mobile robots, improving ROI for operators constrained by real estate limits in urban hubs.
The Postal Automation Systems Market Report is Segmented by Solution (Hardware, Software, Services), Technology (Parcel Sorters, Letter Sorters, AGV and Robotics, and More), Application (Parcel Sorting, Mail Sorting, Last-Mile Automation, and More), End User (Postal Operators, CEP Companies, E-Commerce Centers, and More), and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America leads global revenue owing to the USPS "Delivering for America" program that injects USD 40 billion into facility upgrades and boosts daily capacity to 60 million packages. Canada follows a similar trajectory, adopting robotics to mitigate labor shortages in large urban hubs such as Toronto and Vancouver. Stable regulatory regimes and predictable parcel flows shorten payback periods, reinforcing vendor preference for early product rollouts in the region.
Europe contributes robust growth underpinned by the Net Zero Industry Act, which prioritizes energy-efficient equipment and accelerates replacement cycles. Germany's updated postal law gives Deutsche Post flexibility to optimize routes, while DHL holds 63% mail and 40% parcel market shares, creating economies of scale for nationwide automation. The United Kingdom's approval of the DHL eCommerce-Evri merger forms a combined network processing more than 1 billion parcels annually, anchoring further automation investments.
Asia-Pacific records the fastest CAGR, propelled by China Post and Cainiao's automation deployments and Japan's proposed 500-kilometer automated conveyor network to counter driver shortages. South Korea leverages advanced telecom infrastructure to roll out RFID-enabled sortation, while India wrestles with equipment tariffs that raise project costs. Australia's dispersed population boosts interest in robotics that can flexibly scale capacity across long distances.
Latin America delivers uneven performance. Mexico benefits from USMCA proximity, attracting cross-border parcel flows that justify automation in northern hubs. Brazil's compliance program supports e-commerce growth, yet tariffs on imported automation remain a drag on total cost of ownership. Argentina's economic volatility prolongs investment decision cycles, limiting market penetration for high-end solutions.
The Middle East and Africa remain nascent but promising. Gulf states invest in urban micro-fulfillment facilities that demand compact modular systems, while Africa faces legacy IT hurdles that slow deployments. International aid programs targeting postal infrastructure modernization could unlock future demand, especially as smartphone-led commerce expands across major urban corridors.
- Siemens Logistics GmbH
- Toshiba Infrastructure Systems and Solutions Corp.
- NEC Corporation
- Pitney Bowes Inc.
- Vanderlande Industries B.V.
- Beumer Group GmbH and Co. KG
- Solystic SAS
- Fives Group
- Bowe Systec GmbH
- Interroll Holding AG
- BlueCrest Inc.
- Opex Corporation
- EuroSort Systems
- Honeywell Intelligrated
- Dematic (Kion Group)
- KUKA AG
- Zhejiang Libiao Robotics
- Fluence Automation LLC
- Leonardo S.p.A.
- Engineering Production and Installation (EPI)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surge in cross-border e-commerce parcel volumes in Asia
- 4.2.2 USPS "Delivering for America" modernization
- 4.2.3 EU Green Deal boosting energy-efficient system replacement sales
- 4.2.4 Labor shortages and wage inflation driving robotic singulation
- 4.2.5 RFID-enabled sorting adoption in Japan and South Korea
- 4.2.6 Urban micro-fulfilment increasing demand for compact sorters
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Legacy IT integration in Africa and LatAm postal systems
- 4.3.2 Capital-intensive investments with greater than 7-year ROI
- 4.3.3 Declining letter-mail volumes in Europe
- 4.3.4 Import tariffs on automation in Brazil and India
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory and Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.7 Technology Snapshot
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Solution
- 5.1.1 Hardware
- 5.1.2 Software
- 5.1.3 Services
- 5.2 By Technology
- 5.2.1 Culler-Facer-Canceller (CFC) Systems
- 5.2.2 Letter Sorters
- 5.2.3 Flat Mail Sorters
- 5.2.4 Parcel Sorters
- 5.2.5 Mixed-Mail Sorters
- 5.2.6 Coding and Printing/OCR Systems
- 5.2.7 Automated Guided Vehicles and Robotics
- 5.2.8 Others
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Parcel Sorting
- 5.3.2 Mail Sorting
- 5.3.3 Address Printing and Labelling
- 5.3.4 Data Capture and OCR
- 5.3.5 Last-Mile Delivery
- 5.3.6 Hub Automation
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 National Postal Operators
- 5.4.2 Courier, Express and Parcel (CEP) Companies
- 5.4.3 E-commerce Fulfilment Centers
- 5.4.4 Government Agencies and Others
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.2 Germany
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Asia
- 5.5.4 Middle East
- 5.5.4.1 Israel
- 5.5.4.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.4.3 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.4.4 Turkey
- 5.5.4.5 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5 Africa
- 5.5.5.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2 Egypt
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.6 South America
- 5.5.6.1 Brazil
- 5.5.6.2 Argentina
- 5.5.6.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 Siemens Logistics GmbH
- 6.3.2 Toshiba Infrastructure Systems and Solutions Corp.
- 6.3.3 NEC Corporation
- 6.3.4 Pitney Bowes Inc.
- 6.3.5 Vanderlande Industries B.V.
- 6.3.6 Beumer Group GmbH and Co. KG
- 6.3.7 Solystic SAS
- 6.3.8 Fives Group
- 6.3.9 Bowe Systec GmbH
- 6.3.10 Interroll Holding AG
- 6.3.11 BlueCrest Inc.
- 6.3.12 Opex Corporation
- 6.3.13 EuroSort Systems
- 6.3.14 Honeywell Intelligrated
- 6.3.15 Dematic (Kion Group)
- 6.3.16 KUKA AG
- 6.3.17 Zhejiang Libiao Robotics
- 6.3.18 Fluence Automation LLC
- 6.3.19 Leonardo S.p.A.
- 6.3.20 Engineering Production and Installation (EPI)
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment









