 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1844723
高溫隔熱材料:市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)High-temperature Insulation Materials - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
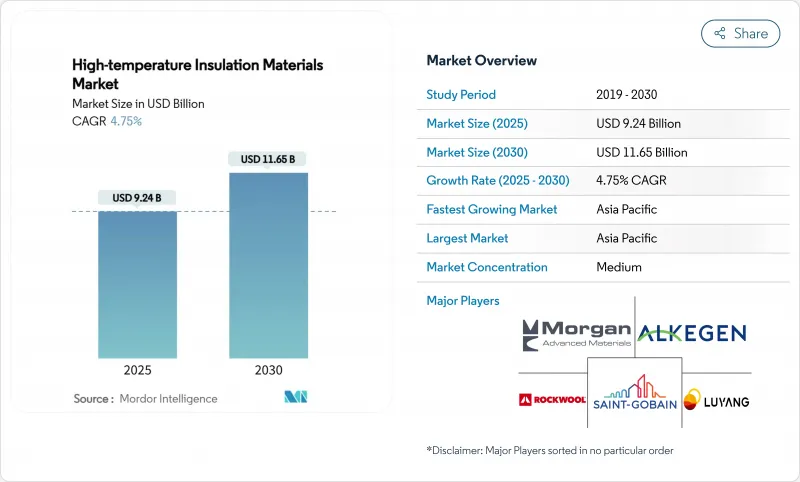
預計高溫隔熱材料市場規模在 2025 年將達到 92.4 億美元,到 2030 年預計將達到 116.5 億美元,預測期內(2025-2030 年)的複合年成長率為 4.75%。
目前的市場規模反映了能源密集型產業追求營運效率和排放帶來的穩定需求成長。嚴格的建築節能法規、亞太地區石化和金屬產能的快速擴張以及綠色氫電解槽的不斷增加構成了需求的支柱。製造商繼續優先考慮符合更嚴格職業暴露限值的不易燃、生物分解性更低的替代品。同時,垂直整合策略和區域產能擴張正在幫助主要供應商免受原料價格波動和物流瓶頸的影響。儘管氧化鋁、二氧化矽和氧化鋯的價格仍然波動,但降低燃料使用和維護成本的經濟回報正在推動其應用範圍的擴大。
全球高溫隔熱材料市場趨勢與洞察
節能工業爐需求激增
根據2024年《國際節能規範》,工業爐製造商面臨更嚴格的能源效率規定,降低了允許的熱損失,並嚴格控制了空氣洩漏率。業者正在指定使用陶瓷纖維毯和微孔板,這些材料能夠承受1000°C的高溫,且不會影響燃油經濟性。與傳統爐襯相比,其典型節能效果接近30%,儘管資本成本較高,仍能提供高投資報酬率。將智慧溫度控管系統與先進的隔熱材料結合,可以實現預測性維護並最佳化能耗,這使得高溫隔熱成為工業4.0轉型策略的關鍵組成部分。
加強建築能源法規對高溫隔熱隔熱的要求
國際節能規範 (IECC) 2024 年的修訂也提高了商業建築的外殼要求,促使人們更加關注連續隔熱和熱感橋緩解措施。歐盟的「Fit-for-55」指令要求在工業設施中採用互補的耐熱和防火解決方案,該指令越來越青睞兼具熱性能和防火安全性的材料,從而推動了對礦棉和陶瓷纖維系統等不燃材料的需求。建築業主面臨著不斷上漲的能源成本和碳定價機制,這使得高性能隔熱材料在建築的整個生命週期中具有經濟吸引力。能源效率要求和防火安全要求的整合為能夠同時滿足兩項監管要求的高溫隔熱材料創造了一個最佳平衡點。
合成玻璃纖維的職業暴露限值
美國職業安全與健康管理局 (OSHA) 規定耐火陶瓷纖維的允許暴露限值為每立方公分 0.2 根。英國健康與安全執行局 (COSHH) 將致癌性陶瓷纖維歸類為二類致癌物,要求根據 COSHH 法規採取嚴格的控制措施。歐洲立法越來越傾向於生物分解性較低的替代品,儘管鹼土矽酸鹽纖維成本較高且耐高溫性略有下降,但它們的市場佔有率仍在不斷擴大。生物可溶性纖維的監管趨勢限制了傳統陶瓷纖維的應用,同時也為創新製造商創造了機會。合規成本和責任問題正促使工業用戶轉向替代材料,即使存在性能方面的權衡。長期趨勢表明,持續的監管壓力將重塑競爭格局,並有利於擁有強大的生物可溶性較低纖維產品組合的公司。
細分分析
陶瓷纖維憑藉其1,260°C的使用極限、低密度以及適用於毯子、模組和板材等特性,將在2024年佔據市場收入的56.19%。這種領先地位在鋼鐵、非鐵金屬和石化等資產密集產業中根深蒂固,這些產業的停機成本高於材料價格。隨著亞太地區新設施的運作,陶瓷纖維高溫隔熱市場規模預計將以穩定的個位數成長。
其他材料類型,例如氣凝膠複合材料和微孔板,是成長最快的類別,複合年成長率為 6.18%。重量敏感的終端用途看重氣凝膠的電導率(0.020 W/m*K 或更低),並結合纖維增強材料以提高操作強度。監管主導下向低生物持久性化學品的轉變正在加速鹼土矽酸鹽棉的普及,尤其是在歐洲。多晶棉適用於 1,500°C 以上的特殊應用,而真空成型可適應現場噴補和搗打成本較高的複雜形狀。高溫隔熱產業持續改進燒結添加劑和纖維直徑,以平衡噴補含量、強度和抗熱震性。
區域分析
預計到2024年,亞太地區將佔據47.51%的市場佔有率,複合年成長率為5.66%。中國持續的鋼鐵、鋁和化工產能擴張將維持大宗需求,而印度國家基礎設施管道和氫能計畫的擴張將推動長期成長。東南亞國家也在增加其石化和可再生能源資產,這些資產需要耐火材料襯裡。政策制定者正在加強能源效率標準的執行,並將採購轉向低導熱係數纖維模組和氣凝膠。
北美按以金額為準排名第二。聯邦清潔能源信用額度和州級碳排放維修使得煉油廠、液化天然氣 (LNG) 終端和紙漿廠的保溫改造具有經濟吸引力。該地區半導體和電池製造業正在回流,推動超潔淨保溫板和纖維增強氣凝膠的消費成長。工業安全性的提高也加速了鹼土矽酸鹽棉的採用。
歐洲仍然以技術為中心,利用嚴格的環境法規和碳邊界調整來支持生物分解性較低的材料。歐盟綠色新政的投資正在推動現有工業資產的維修,採用多層內襯,既能隔熱又能防火。聚光型太陽光電和熱能儲存領域的創新先導計畫正在採用先進陶瓷,拓寬其應用範圍。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場狀況
- 市場概況
- 市場促進因素
- 節能工業爐需求激增
- 更嚴格的建築能源法規要求高溫隔熱
- 亞洲石化和金屬產業產能快速擴張
- 採用綠色氫電解槽需要高溫內襯
- 對輕質、耐用隔熱材料的需求不斷成長
- 市場限制
- 合成玻璃纖維的職業暴露限值
- 氧化鋁和二氧化矽價格波動對轉爐利潤造成壓力
- 高純度氧化鋯前驅體供應鏈風險
- 價值鏈分析
- 五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 產業競爭
第5章市場規模及成長預測
- 依材料類型
- 玻璃纖維
- 陶瓷纖維
- 礦棉
- 鹼土金屬矽酸鹽 (AES)
- 矽酸鋁棉(ASW)或耐火陶瓷纖維(RCF)
- 多晶羊毛或纖維(PCW)
- 長纖維
- 真空成型隔熱產品
- 聚氨酯泡棉
- 聚苯乙烯
- 隔熱耐火磚(IFB)
- 其他材料類型(例如氣凝膠毯、微孔板)
- 按用途
- 隔熱材料
- 工業設備
- 其他用途(建築、消防等)
- 按最終用途行業
- 石化
- 工業的
- 發電
- 運輸
- 電氣和電子
- 建造
- 其他最終用途產業(例如金屬加工)
- 按地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 韓國
- 東南亞國協
- 其他亞太地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 俄羅斯
- 北歐國家
- 其他歐洲國家
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 南美洲其他地區
- 中東和非洲
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 其他中東和非洲地區
- 亞太地區
第6章 競爭態勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略舉措
- 市佔率(%)/排名分析
- 公司簡介
- 3M
- Alkegen
- Almatis
- Aspen Aerogels, Inc.
- BNZ Materials,Inc.
- Cabot Corporation
- Carlisle Companies Inc.
- Dyson Technical Ceramics
- Etex Group
- ISOLITE
- Knauf Insulation
- Luyang Energy-saving Materials Co., Ltd.
- ME Schupp Industriekeramik Gmbh
- Morgan Advanced Materials
- NUTEC Incorporated
- Pacor Inc.
- Pyrotek
- Rath-Group
- ROCKWOOL A/S
- Saint-Gobain
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The High-temperature Insulation Materials Market size is estimated at USD 9.24 Billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 11.65 Billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.75% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

The current market size reflects steady demand growth as energy-intensive industries pursue operational efficiency and lower emissions. Tight building-energy codes, rapid petrochemical and metals capacity additions in Asia-Pacific, and expanding green hydrogen electrolyser installations form the backbone of demand. Manufacturers continue to prioritize non-combustible and low-biopersistent alternatives that satisfy stricter occupational exposure limits. At the same time, vertical integration strategies and regional capacity expansions are helping large suppliers shield themselves from raw-material price swings and logistics bottlenecks. While alumina, silica, and zirconia pricing remains volatile, the economic payback from lower fuel use and maintenance costs keeps adoption on an upward trajectory.
Global High-temperature Insulation Materials Market Trends and Insights
Surging Demand for Energy-Efficient Industrial Furnaces
Industrial furnace builders face stricter energy-performance rules under the 2024 International Energy Conservation Code, which lowered allowable heat loss and tightened air-leakage rates. Operators specify ceramic fibre blankets and microporous panels that endure 1,000°C service without compromising fuel economy. Typical energy savings approach 30% over legacy linings, improving payback despite higher capital cost. Integrating smart thermal management systems with advanced insulation materials enables predictive maintenance and optimized energy consumption, positioning high-temperature insulation as a critical component in Industry 4.0 transformation strategies. .
Tightening Building-Energy Codes Requiring High-Temperature Insulation
The same 2024 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) revision also sharpened commercial building shell requirements, magnifying interest in continuous insulation and thermal-bridge mitigation. European Union Fit-for-55 directives demand complementary heat- and fire-resistant solutions in industrial facilities, increasingly favoring materials that combine thermal performance with fire safety, driving demand for non-combustible options like mineral wool and ceramic fiber systems. Building owners face escalating energy costs and carbon pricing mechanisms that make high-performance insulation economically attractive over building lifecycles. The convergence of energy efficiency mandates and fire safety requirements creates a sweet spot for high-temperature insulation materials that can address both regulatory imperatives simultaneously.
Occupational Exposure Limits on Synthetic Vitreous Fibres
Regulatory authorities worldwide are tightening occupational exposure limits for synthetic vitreous fibers, with OSHA maintaining permissible exposure limits of 0.2 fibers per cubic centimeter for refractory ceramic fibers . The Health and Safety Executive in the UK has classified refractory ceramic fiber as a category 2 carcinogen, necessitating stringent control measures under COSHH regulations that increase handling costs and limit application flexibility. European legislation increasingly favors low-biopersistent alternatives, driving market share gains for alkaline earth silicate fibers despite their higher costs and slightly reduced temperature capabilities. The regulatory trend toward biosoluble fibers creates opportunities for innovative manufacturers while constraining traditional ceramic fiber applications. Compliance costs and liability concerns are pushing industrial users toward alternative materials, even when performance trade-offs exist. The long-term trajectory suggests continued regulatory pressure that will reshape the competitive landscape in favor of companies with strong low-biopersistent fiber portfolios.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rapid Capacity Build-Out in Asian Petro-Chem and Metal Sectors
- Green-Hydrogen Electrolyser Adoption Needs High-Temperature Lining
- Volatile Alumina and Silica Prices Squeeze Converter Margins
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Ceramic fibre held 56.19% of 2024 revenue owing to its 1,260°C service limit, low density, and adaptability into blankets, modules, and boards. This leadership is anchored in asset-heavy industries, such as steel, non-ferrous metals, and petrochemicals, where downtime costs dwarf material prices. The high-temperature insulation materials market size for ceramic fibre is expected to post steady single-digit growth as new capacities in Asia-Pacific come on stream.
Other material types, such as aerogel composites and microporous panels, are the fastest-growing group at 6.18% CAGR. Weight-sensitive end uses value aerogels' sub-0.020 W/m*K (Watt per metre Kelvin) conductivity combined with fiber reinforcement that boosts handling strength. Regulatory-driven migration to low-biopersistent chemistries accelerates alkaline earth silicate wool uptake, especially in Europe. Polycrystalline wool supports specialized duties above 1,500°C, while vacuum-formed shapes address complex geometries that would require costly on-site gunning or ramming. The high-temperature insulation materials industry continues to refine sintering additives and fiber diameters to balance shot content, strength, and thermal shock resistance.
The High-Temperature Insulation Materials Market Report Segments the Industry Into Material Type (Fiberglass, Ceramic Fibre, Mineral Wool, Polyurethane Foam, and More), Application (Insulation, Industrial Eqipment, and Other Applications), End-User Industry (Petrochemicals, Construction, Transportation, and More), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific had a 47.51% market share in 2024 and is projected to advance at a 5.66% CAGR. China's ongoing capacity additions in steel, aluminum, and chemicals sustain bulk demand, while India's National Infrastructure Pipeline and expanding hydrogen plans reinforce long-term growth. Southeast Asian nations add petrochemical and renewables assets that likewise require refractory linings. Policymakers increasingly enforce energy-efficiency norms, shifting purchasing toward low-conductivity fibre modules and aerogels.
North America ranks second by value. Federal clean energy credits and state-level carbon caps make retrofit insulation economically attractive in refineries, liquidated natural gas (LNG) terminals, and pulp mills. The region's reshoring of semiconductor and battery manufacturing raises consumption of ultra-clean insulation boards and fiber-reinforced aerogels. Robust industrial safety enforcement also accelerates adoption of alkaline earth silicate wool.
Europe remains technology-focused, leveraging its stringent environmental rules and carbon-border adjustments to champion low-biopersistent materials. European Union (EU) Green Deal investments spur renovation of existing industrial assets with multilayer linings that marry insulation and fire-containment. Innovative pilot projects in concentrated solar power and thermal energy storage adopt advanced ceramics, broadening application footprints.
- 3M
- Alkegen
- Almatis
- Aspen Aerogels, Inc.
- BNZ Materials,Inc.
- Cabot Corporation
- Carlisle Companies Inc.
- Dyson Technical Ceramics
- Etex Group
- ISOLITE
- Knauf Insulation
- Luyang Energy-saving Materials Co., Ltd.
- M.E. Schupp Industriekeramik Gmbh
- Morgan Advanced Materials
- NUTEC Incorporated
- Pacor Inc.
- Pyrotek
- Rath-Group
- ROCKWOOL A/S
- Saint-Gobain
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surging Demand for Energy-Efficient Industrial Furnaces
- 4.2.2 Tightening Building-Energy Codes Requiring High-Temperature Insulation
- 4.2.3 Rapid Capacity Build-Out in Asian Petro-Chem and Metal Sectors
- 4.2.4 Green-Hydrogen Electrolyser Adoption needs High Temperature Lining
- 4.2.5 Growing Lightweight, Durable Insulation Material Demand
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Occupational Exposure Limits on Synthetic Vitreous Fibres
- 4.3.2 Volatile Alumina and Silica Prices Squeeze Converter Margins
- 4.3.3 Supply-Chain Risk for High-Purity Zirconia Precursors
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Industry Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Material Type
- 5.1.1 Fiberglass
- 5.1.2 Ceramic Fibre
- 5.1.3 Mineral Wool
- 5.1.3.1 Alkaline Earth Silicate (AES)
- 5.1.3.2 Aluminum Silicate Wool (ASW) or Refractory Ceramic Fibre (RCF)
- 5.1.3.3 Polycrystalline Wool or Fibre (PCW)
- 5.1.3.4 Long Fibre
- 5.1.4 Vacuum-Formed Insulating Products
- 5.1.5 Polyurethane Foam
- 5.1.6 Polystyrene
- 5.1.7 Insulating Fire-Bricks (IFB)
- 5.1.8 Other Material Types (Aerogel Blankets, Microporous Panels, etc.)
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Insulation
- 5.2.2 Industrial Eqipment
- 5.2.3 Other Applications (Building and Fire-Protection, etc.)
- 5.3 By End-use Industry
- 5.3.1 Petrochemicals
- 5.3.2 Industrial
- 5.3.3 Power Generation
- 5.3.4 Transportation
- 5.3.5 Electrical and Electronics
- 5.3.6 Construction
- 5.3.7 Other End-use Industries (Metal Processing, etc.)
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.1.1 China
- 5.4.1.2 Japan
- 5.4.1.3 India
- 5.4.1.4 South Korea
- 5.4.1.5 ASEAN Countries
- 5.4.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.2 North America
- 5.4.2.1 United States
- 5.4.2.2 Canada
- 5.4.2.3 Mexico
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.3.1 Germany
- 5.4.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.3.3 France
- 5.4.3.4 Italy
- 5.4.3.5 Spain
- 5.4.3.6 Russia
- 5.4.3.7 NORDIC Countries
- 5.4.3.8 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.2 South Africa
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share (%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 3M
- 6.4.2 Alkegen
- 6.4.3 Almatis
- 6.4.4 Aspen Aerogels, Inc.
- 6.4.5 BNZ Materials,Inc.
- 6.4.6 Cabot Corporation
- 6.4.7 Carlisle Companies Inc.
- 6.4.8 Dyson Technical Ceramics
- 6.4.9 Etex Group
- 6.4.10 ISOLITE
- 6.4.11 Knauf Insulation
- 6.4.12 Luyang Energy-saving Materials Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.13 M.E. Schupp Industriekeramik Gmbh
- 6.4.14 Morgan Advanced Materials
- 6.4.15 NUTEC Incorporated
- 6.4.16 Pacor Inc.
- 6.4.17 Pyrotek
- 6.4.18 Rath-Group
- 6.4.19 ROCKWOOL A/S
- 6.4.20 Saint-Gobain
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment
- 7.2 Lightweight Refractory Cements for Concentrated-Solar Receivers








