 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1844699
靜態 RAM (SRAM):市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
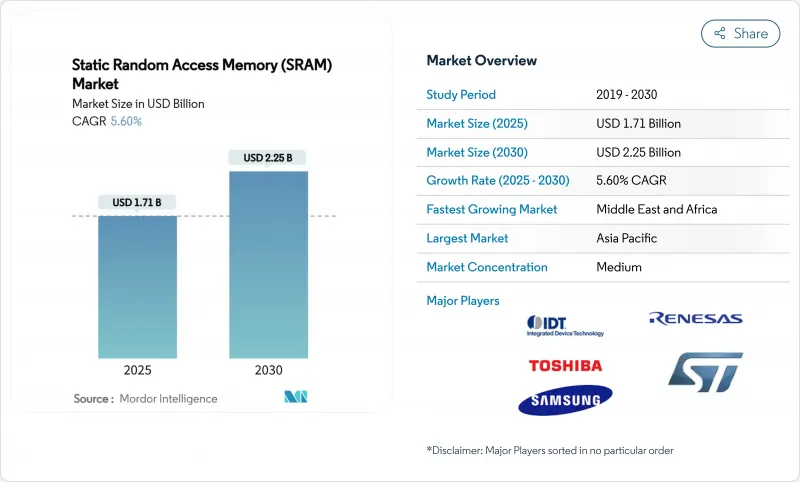
預計到 2025 年全球靜態 RAM (SRAM) 市場規模將達到 17.1 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 22.5 億美元,複合年成長率為 5.60%。
這一成長反映了向以人工智慧為中心的運算、5G 部署和即時邊緣處理的轉變,所有這些都依賴 SRAM 的超低延遲快取層。半導體供應商優先考慮在 2nm 節點縮小 SRAM 單元尺寸,以支援更大的 L2/L3 快取,同時保持嚴格的功耗預算。資料中心現代化推動了對交換器和加速器中高速緩衝器的需求,而消費設備的刷新週期則保持了穩定的基準。 2024 年台灣地震擾亂了晶圓代工廠的生產,使得供應鏈的彈性變得至關重要,並促使企業進行地理多元化。同時,MRAM 等新興非揮發性記憶體增加了電池供電設計中傳統 SRAM 的競爭壓力。
全球靜態 RAM (SRAM) 市場趨勢與洞察
對更快快取的需求不斷增加
2025 年推出的先進 CPU 和 GPU 配備了更大的片上快取,以降低推理延遲。英特爾至強 6 處理器憑藉快取最佳化實現了 1.4 倍的效能提升。台積電 2 奈米平台的 SRAM 單元密度高於競爭對手的 18A 節點,為超大規模客戶提供更高的每瓦 L3 快取。 Marvell 推出了一款配備 6GB 低功耗記憶體的 2 奈米客製化 SRAM,與先前的節點相比,功耗降低了 66%。這些創新使 AI 加速器能夠將模型參數移近運算單元,從而在保持吞吐量的同時減少 DRAM 流量。因此,靜態 RAM (SRAM) 市場受益於資料中心和邊緣晶片的迭代容量升級。
資料中心及5G網路建設
雲端營運商已將機架密度翻倍以承載人工智慧伺服器,這推動了基於靜態隨機存取記憶體 (SRAM) 的封包緩衝區在架頂式交換器中的使用。微軟在其伺服器機房中測試了 246-275GHz 無線背板,並依靠高速 SRAM 實現微秒緩衝。思科的融合 5G 傳輸提升了確定性延遲,並要求其路由器中擁有深度 SRAM 佇列。康寧預測每個人工智慧機架的光纖需求將激增 18 倍,這反映了基於同步 SRAM 建構的交換器緩衝區的擴展。這波基礎設施浪潮增強了靜態隨機存取記憶體 (SRAM) 市場的近期收益前景。
與 DRAM/NAND 相比,每比特高成本
SRAM 的每比特成本比商用 DRAM 上漲了數倍,迫使設計人員減少其在大批量設備中的使用。 2025 年上半年,DDR4 模組價格上漲了約 50%,顯示整個記憶體堆疊市場波動劇烈。三星利用供應緊縮的機會提高了 LPDDR4 的價格,但這種策略可能會加速 OEM 廠商對混合 SRAM-DRAM 架構的興趣,從而降低材料成本。因此,靜態 RAM (SRAM) 市場在入門級消費市場遭遇了強烈衝擊,直到密度/成本平衡得到改善。
細分分析
到2024年,同步SRAM將佔據靜態RAM (SRAM) 58.4%的市場佔有率,這對於CPU、GPU和網路ASIC中的確定性快取操作至關重要。汽車MCU使用同步陣列來滿足駕駛輔助工作負載的嚴苛即時要求。隨著先進節點擴展頻率範圍並降低核心電壓,該領域將保持領先。
非同步 SRAM 的複合年成長率為 6.4%,這得益於物聯網穿戴式裝置和邊緣閘道的普及,在這些裝置中,功耗預算優先於延遲目標。節能設計消除了時脈樹並簡化了基板佈局。這種差異凸顯了靜態 RAM (SRAM) 市場朝著針對特定應用進行最佳化而非一刀切效能的趨勢。
偽 SRAM 將 DRAM 單元嵌入 SRAM 式介面後面,以實現高密度,無需系統層級刷新管理,到 2024 年將佔據 54.4% 的市場佔有率。 RAAAM Memory Technologies 和 NXP 聲稱,與傳統的高密度 SRAM 相比,其面積節省了 50%,功耗節省了 10 倍,對大眾市場微控制器具有吸引力。
由於工廠和汽車對斷電期間資料完整性的要求越來越高,非揮發性 SRAM 的複合年成長率高達 8.7%。工業自動化公司選擇 nvSRAM 模組來保護製程變數並避免代價高昂的停機。儘管該細分市場規模較小,但憑藉其增值的彈性特性,它豐富了靜態 RAM (SRAM) 的市場格局。
區域分析
受台灣代工主導地位、韓國記憶體創新以及中國大陸規模化擴張的推動,亞太地區將在2024年維持61.4%的靜態隨機存取記憶體(SRAM)市場佔有率。 SK海力士已發展壯大,佔據全球DRAM產量的36%,凸顯了該地區的技術實力。然而,2024年台灣地震暴露了集中風險,促使日本和新加坡建造晶圓廠以應對緊急情況。日本預測2026會計年度的半導體設備銷售額將達到5.51兆日圓(383.5億美元),並強調將持續擴大產能。
中東和非洲的複合年成長率最高,達到7.5%,這得益於主權財富基金的投入,旨在將沿岸地區打造為三大洲的資料中心。到2025年,該地區的倉庫自動化市場規模將以17.5%的複合年成長率成長,達到16億美元,這將推動對可靠板載快取的需求。預計到2030年,非洲能源計劃的新資本投資將達到7,300億美元,這需要依賴SRAM實現確定性反應的工業控制系統。
北美正專注於部署人工智慧資料中心,而歐洲則透過430億歐元的《晶片法案》加倍強調其主權。意法半導體已獲得50億歐元(54億美元)用於在義大利建造碳化矽園區,以增強其在電力電子領域的區域競爭力,該領域也需要專用的SRAM。然而,人才短缺威脅著其擴張,阿斯麥公司警告稱,如果邊境管制更加嚴格,可能會轉向其他領域。這些截然不同的舉措凸顯了塑造靜態隨機存取記憶體(SRAM)市場的多元化區域因素。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場狀況
- 市場概況
- 市場促進因素
- 對更快快取的需求不斷增加
- 資料中心及5G網路建設
- 物聯網和穿戴式裝置的普及
- 用於小晶片的 3D 整合 SRAM
- 適用於低地球軌道衛星的抗輻射 SRAM
- 採用記憶體內AI 加速器
- 市場限制
- 與 DRAM/NAND 相比,每位元成本更高
- 5nm節點以下功耗上升
- 新興 NVM (MRAM/ReRAM) 替代品
- 微影術的差異導致產量比率
- 價值鏈分析
- 監管狀況
- 技術展望
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭的激烈程度
- 宏觀經濟因素的影響
第5章市場規模及成長預測
- 按功能
- 異步SRAM
- 同步SRAM
- 依產品類型
- 偽SRAM(PSRAM)
- 非揮發性SRAM(nvSRAM)
- 其他產品類型
- 按內存密度
- 8 Mb 或更少
- 8~64 Mb
- 64~256 Mb
- 超過 256 Mb
- 按最終用戶
- 消費性電子產品
- 產業
- 通訊基礎設施
- 汽車和航太
- 其他最終用戶
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲國家
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 韓國
- 印度
- 台灣
- 其他亞太地區
- 中東和非洲
- 中東
- 土耳其
- 以色列
- 海灣合作理事會國家
- 其他中東地區
- 非洲
- 南非
- 奈及利亞
- 其他非洲國家
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭態勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略舉措
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- GSI Technology Inc.
- Cypress Semiconductor Corp.(Infineon)
- Renesas Electronics Corp.
- Integrated Silicon Solution Inc.
- Alliance Memory Inc.
- Everspin Technologies Inc.
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- Toshiba Electronic Devices & Storage Corp.
- STMicroelectronics NV
- SK hynix Inc.
- Micron Technology Inc.
- Nanya Technology Corp.
- Winbond Electronics Corp.
- Elite Semiconductor Memory Technology Inc.
- Chiplus Semiconductor Corp.
- Powerchip Semiconductor Mfg. Corp.
- Puya Semiconductor Technology Co., Ltd.
- Lyontek Inc.
- ON Semiconductor Corporation
- Texas Instruments Incorporated
- Integrated Device Technology Inc.
- NXP Semiconductors NV
- Etron Technology Inc.
- Espressif Systems(Shanghai)Co., Ltd.
- SKYHigh Memory Ltd.
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The global Static Random Access Memory market size stood at USD 1.71 billion in 2025 and is forecast to advance at a 5.60% CAGR to reach USD 2.25 billion by 2030.

Growth reflected the transition toward AI-centric compute, 5G roll-outs, and real-time edge processing, all of which rely on SRAM's ultra-low latency for cache hierarchies. Semiconductor vendors prioritized shrinking SRAM cells at 2 nm to support larger L2/L3 caches while keeping power budgets in check. Data-center modernization drove demand for high-speed buffers in switches and accelerators, whereas consumer device refresh cycles maintained a steady baseline. Supply-chain resilience became pivotal after the 2024 Taiwan earthquake disrupted foundry output, prompting geographic diversification initiatives. Meanwhile, emerging non-volatile memories such as MRAM intensified competitive pressure on conventional SRAM in battery-backed designs.
Global Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) Market Trends and Insights
Rising demand for faster cache memories
Advanced CPUs and GPUs shipped in 2025 featured larger on-chip caches to cut inference latency, with Intel's Xeon 6 showing a 1.4X performance lift tied to cache optimization. TSMC's 2 nm platform delivered higher SRAM cell density than competing 18A nodes, giving hyperscale customers more L3 cache per watt. Marvell unveiled 2 nm custom SRAM that packs 6 Gb of low-power memory, reducing energy use by 66% versus prior nodes. Such innovations enabled AI accelerators to keep model parameters closer to compute units, sustaining throughput while containing DRAM traffic. Consequently, the Static Random Access Memory market benefited from recurring capacity upgrades across data-center and edge silicon.
Data-center and 5G network build-out
Cloud operators doubled rack densities to host AI servers, prompting wider use of SRAM-based packet buffers in top-of-rack switches. Microsoft tested 246-275 GHz wireless backplanes in server halls, where microsecond-scale buffering relied on high-speed SRAM. Cisco's converged 5G transport promoted deterministic latency, necessitating deep SRAM queues in routers. Corning forecasts an 18X jump in fiber demand per AI rack, mirroring the scaling of switch buffers built on synchronous SRAM. This infrastructure wave reinforced near-term revenue visibility for the Static Random Access Memory market.
High cost per bit vs. DRAM/NAND
SRAM remained several times more expensive per bit than commodity DRAM, pressuring designers to trim usage in mass-market gadgets. DDR4 module prices climbed roughly 50% in H1 2025, illustrating volatility across the memory stack. Samsung leveraged tightening supply to lift LPDDR4 pricing, but that tactic risked accelerating OEM interest in hybrid SRAM-DRAM architectures to curb bills of materials. Consequently, the Static Random Access Memory market faced pushback in entry-level consumer segments until density-versus-cost trade-offs improved.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- IoT and wearable device proliferation
- In-memory AI accelerators adoption
- Emerging NVM (MRAM/ReRAM) displacement
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Synchronous SRAM captured 58.4% Static Random Access Memory market share in 2024, underscoring its indispensability for deterministic cache operation in CPUs, GPUs, and network ASICs. Automotive MCUs used synchronous arrays to meet stringent real-time requirements for driver-assistance workloads. The segment will maintain leadership as advanced nodes extend frequency envelopes and reduce core voltages.
Asynchronous SRAM expanded at a 6.4% CAGR and increasingly served IoT wearables and edge gateways where power budgets override latency targets. Energy-efficient designs eliminated clock trees and simplified board layouts, a boon for battery-operated healthcare devices employing Syntiant's neural coprocessors. This divergence emphasized the Static Random Access Memory market trend toward application-specific optimization rather than one-size-fits-all performance chasing.
Pseudo-SRAM held a 54.4% share in 2024 by embedding DRAM cells behind an SRAM-style interface, achieving higher density without refresh management at the system level. RAAAM Memory Technologies and NXP claimed 50% area and 10X power savings versus classic high-density SRAM, appealing to mass-market microcontrollers.
Non-volatile SRAM grew fastest at 8.7% CAGR as factories and vehicles demanded data integrity during brownouts. Industrial automation players selected nvSRAM modules to protect process variables, avoiding costly downtime. Although niche, this cohort enriched the Static Random Access Memory market landscape with value-added resilience features.
Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) Market is Segmented by Function (Asynchronous SRAM, and Synchronous SRAM), Product Type (Pseudo SRAM, Non-Volatile SRAM, and Other Product Types), Memory Density (<=8 Mb, 8-64 Mb, 64-256 Mb, and >256 Mb), End User (Consumer Electronics, Industrial, Communication Infrastructure, and More), and Geography (North America, South America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Middle East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific retained 61.4% Static Random Access Memory market share in 2024, fueled by Taiwan's foundry dominance, South Korea's memory innovation, and China's scale-up efforts. SK Hynix's rise to 36% of global DRAM output highlighted the region's technology depth. Yet the 2024 Taiwan quake exposed concentration risk, prompting contingency fabs in Japan and Singapore. Japan projected semiconductor equipment sales of JPY 5.51 trillion (USD 38.35 billion) in FY26, underscoring continued capacity build-out.
Middle East and Africa charted the fastest 7.5% CAGR, anchored by sovereign-fund spending to position the Gulf as a tri-continent data hub. Warehouse automation in the region was set for 17.5% annual growth to USD 1.6 billion by 2025, driving demand for reliable on-board caches. Africa's energy projects earmarked USD 730 billion in new capex to 2030, requiring industrial control systems that lean on SRAM for deterministic response.
North America focused on AI datacenter roll-outs, while Europe doubled down on sovereignty through the EUR 43 billion Chips Act. STMicroelectronics secured EUR 5 billion (USD 5.4 billion) for a Silicon Carbide campus in Italy, widening regional competency in power electronics that also consume specialized SRAM. Talent shortages, however, threatened expansion, with ASML warning it might shift operations if immigration tightened. These contrasts highlight diverse regional levers shaping the Static Random Access Memory market.
- GSI Technology Inc.
- Cypress Semiconductor Corp. (Infineon)
- Renesas Electronics Corp.
- Integrated Silicon Solution Inc.
- Alliance Memory Inc.
- Everspin Technologies Inc.
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- Toshiba Electronic Devices & Storage Corp.
- STMicroelectronics N.V.
- SK hynix Inc.
- Micron Technology Inc.
- Nanya Technology Corp.
- Winbond Electronics Corp.
- Elite Semiconductor Memory Technology Inc.
- Chiplus Semiconductor Corp.
- Powerchip Semiconductor Mfg. Corp.
- Puya Semiconductor Technology Co., Ltd.
- Lyontek Inc.
- ON Semiconductor Corporation
- Texas Instruments Incorporated
- Integrated Device Technology Inc.
- NXP Semiconductors N.V.
- Etron Technology Inc.
- Espressif Systems (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
- SKYHigh Memory Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising demand for faster cache memories
- 4.2.2 Data-center and 5G network build-out
- 4.2.3 IoT and wearable device proliferation
- 4.2.4 3D-integrated SRAM for chiplets
- 4.2.5 Radiation-hardened SRAM for LEO satellites
- 4.2.6 In-memory AI accelerators adoption
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High cost per bit vs. DRAM/NAND
- 4.3.2 Escalating power at <=5 nm nodes
- 4.3.3 Emerging NVM (MRAM/ReRAM) displacement
- 4.3.4 Yield loss from lithography variability
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Rivalry
- 4.8 Impact of Macroeconomic Factors
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Function
- 5.1.1 Asynchronous SRAM
- 5.1.2 Synchronous SRAM
- 5.2 By Product Type
- 5.2.1 Pseudo SRAM (PSRAM)
- 5.2.2 Non-Volatile SRAM (nvSRAM)
- 5.2.3 Other Product Types
- 5.3 By Memory Density
- 5.3.1 <=8 Mb
- 5.3.2 8 - 64 Mb
- 5.3.3 64 - 256 Mb
- 5.3.4 >256 Mb
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Consumer Electronics
- 5.4.2 Industrial
- 5.4.3 Communication Infrastructure
- 5.4.4 Automotive and Aerospace
- 5.4.5 Other End Users
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Russia
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 Japan
- 5.5.4.3 South Korea
- 5.5.4.4 India
- 5.5.4.5 Taiwan
- 5.5.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 Turkey
- 5.5.5.1.2 Israel
- 5.5.5.1.3 GCC Countries
- 5.5.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.5.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 GSI Technology Inc.
- 6.4.2 Cypress Semiconductor Corp. (Infineon)
- 6.4.3 Renesas Electronics Corp.
- 6.4.4 Integrated Silicon Solution Inc.
- 6.4.5 Alliance Memory Inc.
- 6.4.6 Everspin Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.7 Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.8 Toshiba Electronic Devices & Storage Corp.
- 6.4.9 STMicroelectronics N.V.
- 6.4.10 SK hynix Inc.
- 6.4.11 Micron Technology Inc.
- 6.4.12 Nanya Technology Corp.
- 6.4.13 Winbond Electronics Corp.
- 6.4.14 Elite Semiconductor Memory Technology Inc.
- 6.4.15 Chiplus Semiconductor Corp.
- 6.4.16 Powerchip Semiconductor Mfg. Corp.
- 6.4.17 Puya Semiconductor Technology Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.18 Lyontek Inc.
- 6.4.19 ON Semiconductor Corporation
- 6.4.20 Texas Instruments Incorporated
- 6.4.21 Integrated Device Technology Inc.
- 6.4.22 NXP Semiconductors N.V.
- 6.4.23 Etron Technology Inc.
- 6.4.24 Espressif Systems (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.25 SKYHigh Memory Ltd.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment









