 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1844541
技術陶瓷:市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Technical Ceramics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
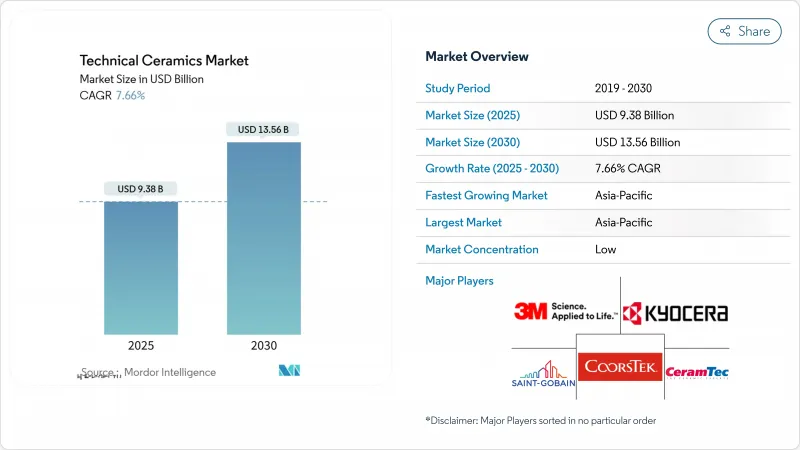
預計 2025 年技術陶瓷市場價值為 93.8 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 135.6 億美元,在市場估計和預測期(2025-2030 年)內複合年成長率為 7.66%。
需求主要集中在半導體基板、電動車 (EV) 熱控制組件和生物相容性植入,這些產品對故障的接受度幾乎為零,而材料科學是策略差異化因素。中國、日本和韓國的工廠建設正在加緊,推動氮化鋁和碳化矽封裝消費量的增加。同時,800V 電動車傳動系統架構迫使汽車製造商指定能夠散熱超過 200 W/mK 且不影響電氣絕緣的陶瓷散熱器。雖然供應鏈仍然容易受到關鍵礦物濃度的影響,但主要製造商正在透過擴大低風險管轄區的生產能力和加強回收循環來減少原料的暴露來應對。雖然整體配方仍然在產量中占主導地位,但陶瓷基質複合材料正經歷最快的成長,因為航太和國防主要企業為更輕、耐高溫的零件支付溢價,以減輕重量並提高燃油經濟性。
全球技術陶瓷市場趨勢與洞察
擴大亞太地區的半導體和家用電子電器生產
台灣、中國當地、日本和韓國的工廠建設正在重新設定氮化鋁和碳化矽基板的需求基準,這些基板可承受超過 1,000°C 的峰值鍵合溫度,同時確保介電完整性。追求氮化鎵架構的晶片設計人員正在將熱預算擴展到傳統導線架的能力之外,這使得陶瓷封裝成為提高產量的重要組成部分。京瓷公司正在日本投資 4.7 億美元建造一條專用生產線,以使陶瓷基板的可用性與下一代處理器節點同步。雖然將基板生長週期與微影術坡道同步仍然具有挑戰性,因為窯爐需要比半導體無塵室更長的檢驗循環,但一級設備製造商現在正在簽署多年的承購協議以鎖定供應。地方政府正在同時承銷先進材料叢集,以減少對海外原料的依賴,這項政策措施可以縮短前置作業時間並緩解價格波動。
電動車動力傳動系統的溫度控管需求
預計 2024 年全球電動車出貨量將超過 1,500 萬輛,目前幾乎所有平台升級都針對 800V 電氣架構,以便從更小的逆變器中榨取更多電力。碳化矽功率模組的散熱速度是矽元件的三倍,但允許的結溫仍然很嚴格,為導熱率超過 200 W/mK 的陶瓷散熱器創造了理想的設計窗口。 CeramTec 的晶片散熱器解決方案降低了熱阻,同時保持了介電隔離,這一組合延長了模組在高振動汽車環境中的使用壽命。雖然汽車製造商對價格敏感,但與熱故障相關的保固責任會使購買決策傾向於更可靠的陶瓷,即使單價更高。隨著中國、歐洲和美國汽車電氣化進程的加速,對陶瓷基板、匯流排和凝膠塗層冷卻板的需求也同步成長。
固有脆性和加工損失
硬度同時提供耐熱性和耐磨性,但它會增加燒結後研磨過程中斷裂的風險。 20-30%的產量比率損失會增加單位成本並延長前置作業時間。纖維增強陶瓷基質可以緩解裂紋擴展,但額外的分層和滲透步驟增加了工藝複雜性,抵消了耐久性方面的提升。積層製造提供了一種近淨成形的替代方案,但材料種類和產量仍落後於傳統壓機,限制了其在原型製作之外的應用。
細分分析
到2024年,整體陶瓷將佔據技術陶瓷市場46.68%的佔有率,這得益於成熟的壓制燒結生產線,這些生產線能夠大規模提供均勻的品質。隨著工業原始設備製造商(OEM)採用比鋼製陶瓷更耐用的氧化鋁陶瓷體維修泵浦、噴嘴和絕緣體,該細分市場仍有望實現中等個位數成長。然而,複合材料陶瓷將以8.84%的複合年成長率成長,累計整個技術陶瓷市場的發展,因為它們吸引了航太和國防預算,這些預算要求陶瓷減重超過30%,並能耐受1500°C以上的高溫。到2025年,光是引擎熱端部分就將佔據技術陶瓷市場的11億美元規模。快速強制空氣燒結等製程技術的突破正在將緻密化步驟從數小時縮短到數分鐘,從而縮短能源成本曲線,並縮小與整體陶瓷的價格差距。隨著這些效率的提高,複合材料有望減少整體材料的佔有率,但它們無法完全取代整體材料,因為汽車和工業工廠仍然重視可預測的收縮和低廢品率。
塗層市場是一條過渡路徑:原始設備製造商 (OEM) 可以透過在傳統金屬部件上噴塗氧化鋯或碳化矽來提高熱通量,而無需重新設計整個組件。這種改造方法在石化燃燒器和柴油顆粒過濾器中很受歡迎,因為這些設備的停機預算比較緊張。液化天然氣運輸船的貨艙中正在使用 1100°C 氣凝膠填充的紡織被,這再次表明,專業的性能認證在較小的細分市場中保持著較高的價格。
由於原料供應充足且製程控制完善,氧化鋁、氧化鋯和莫來石等氧化物系統佔2024年銷售額的63.37%。這些等級構成了各行業電容器電介質和耐磨板的基準。然而,碳化矽、氮化矽和新型碳化硼等非氧化物配方由於其密度較低且熱導率更接近銅,訂單成長速度更快。到2030年,非氧化物陶瓷的比例將達到7.86%,透過服務氧化物玻璃相無法生存的前沿設備,擴大了技術陶瓷市場。雖然成本仍然是一個障礙,但隨著生產線產量比率的提高和廢品率降至5%以下,非氧化物陶瓷的價格溢價正在縮小。燃油經濟性監管要求和資料中心熱通量的增加,都為這些高性能陶瓷等級帶來了永續的長期推動力。
複合材料和混合材料將氧化物基體與非氧化物晶鬚或纖維結合在一起,具有協同增韌和導電性的潛力。人們越來越關注摻鑭氧化鋁混合物,因為它能夠承受高壓下的介電擊穿,這是電網級固體變壓器計劃的重點。這些交叉配方表明,未來市場佔有率的競爭將不再是氧化物與非氧化物的較量,而是混合材料與單相材料的較量,這拓寬了解決方案的空間,同時也增加了複雜性。
技術陶瓷市場報告按產品類型(層狀陶瓷、陶瓷基質複合材料、其他)、材料類別(氧化物陶瓷、非氧化物陶瓷、其他)、最終用戶行業(電氣和電子、汽車、其他)、主要應用(絕緣體和基板、溫度控管組件、其他)和地區(亞太地區、北美、歐洲、南美、中東和非洲)進行細分。
區域分析
到 2024 年,亞太地區將佔據技術陶瓷市場的主導地位,市佔率達到 43.87%,到 2030 年的複合年成長率為 7.91%。中國當地是氧化鋁粉末燒結的主要產地,因此在勞動密集的表面處理工程中可以實現成本套利。京瓷長崎工廠預計 2026 年投產,使中國的精細陶瓷產量提高 10%。韓國的記憶體晶片中心正在推動對低缺陷氮化基板的需求,而印度則透過對古吉拉突邦和泰米爾納德邦提供稅收優惠來吸引電動車供應鏈的投資者。地方政府也正在規劃回收走廊,以回收廢棄的氧化鋯和氧化釔,這項舉措可能會在長期內減少對原料進口的依賴。
北美是一個成熟且創新的地區,佔全球陶瓷基複合材料相關研發支出的近 30%。美國佔據了航太渦輪機和醫療植入訂單的大部分,因此需要 ISO 級窯爐和 USP VI 級無塵室通訊協定。聖戈班在紐約投資 4,000 萬美元的觸媒撐體工廠將創造 100 個就業崗位,並縮短向東海岸煉油廠的交貨週期。加拿大礦業公司供應礬土和稀土精礦,但大部分原料仍流向亞洲煉油廠。墨西哥正在成為電動車逆變器的組裝中心,基板製造商正在考慮近岸外包,以避免 USMCA 原產地規則徵收的關稅。
歐洲約佔全球銷售額的五分之一,在商業性成功與永續性需求之間取得平衡。德國工具機製造商正在指定耐磨氧化鋁導軌,以結合歐盟生態設計標準,減少60%的潤滑需求。法國和西班牙即將試驗氫能樞紐,需要數千平方公尺的固體氧化物電解槽板。該地區的REACH化學品安全框架要求嚴格的可追溯性,合規成本支持現有企業,同時減緩新企業的推出。英國脫歐後的政策傾向於“先進材料彈射器”,旨在三年內將大學實驗室的突破性成果轉化為試點生產線。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場狀況
- 市場概況
- 市場促進因素
- 擴大亞太地區的半導體和消費性電子產品生產
- 電動車動力傳動系統的溫度控管需求
- 在高價值醫療植入和醫療設備中的應用日益增多
- 氫電解器電堆組件
- 太空製造和衛星硬體
- 市場限制
- 資本和加工成本高
- 固有脆性和加工損失
- 對關鍵礦產供應鏈的影響
- 價值鏈分析
- 波特五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭程度
- 專利分析
- 定價分析
第5章市場規模及成長預測
- 依產品類型
- 單片陶瓷
- 陶瓷基質複合材料
- 陶瓷塗層
- 其他產品
- 按材料類別
- 氧化物陶瓷
- 非氧化物陶瓷
- 其他
- 按最終用戶產業
- 電氣和電子
- 車
- 能源和電力
- 醫療保健
- 航太/國防
- 其他最終用戶產業
- 按主要用途
- 絕緣體和基板
- 溫度控管元件
- 磨損件和軸承
- 植入和牙科
- 裝甲和防護
- 按地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 韓國
- 其他亞太地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 其他歐洲國家
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 南美洲其他地區
- 中東和非洲
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 其他中東和非洲地區
- 亞太地區
第6章 競爭態勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略舉措
- 市佔率(%)/排名分析
- 公司簡介
- 3M
- CeramTec GmbH
- CoorsTek Inc.
- Dyson Technical Ceramics
- Kyocera Corporation
- Mantec Technical Ceramics Ltd
- McDanel Advanced Ceramic Technologies
- Morgan Advanced Materials
- NGK SPARK PLUG CO., LTD.
- Ortech, inc.
- Rauschert GmbH
- Saint-Gobain
- Schott AG
- STC Material Solutions
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Technical Ceramics Market size is estimated at USD 9.38 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 13.56 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 7.66% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Demand is clustering around semiconductor substrates, electric-vehicle (EV) thermal control parts, and biocompatible implants, where failure tolerance is virtually zero and material science is a strategic differentiator. Rising fab construction across China, Japan, and South Korea is lifting consumption of aluminum nitride and silicon carbide packages, while 800 V EV drive-train architectures force automakers to specify ceramic heat spreaders that can dissipate more than 200 W/mK without compromising electrical insulation. Supply chains remain vulnerable to critical-mineral concentration, yet leading producers are countering with capacity additions in lower-risk jurisdictions and tighter recycling loops that reduce virgin material exposure. Monolithic formulations still dominate volume, but ceramic-matrix composites are accelerating fastest as aerospace and defense primes pay premiums for lighter, hotter-capable components that cut mass and raise fuel efficiency.
Global Technical Ceramics Market Trends and Insights
Expanding Semiconductor & Consumer-Electronics Output in Asia Pacific
Fab build-outs across Taiwan, mainland China, Japan, and South Korea are resetting the demand baseline for aluminum nitride and silicon carbide substrates that can survive peak junction temperatures exceeding 1,000 °C while ensuring dielectric integrity. Chip designers pursuing gallium nitride architectures are widening thermal budgets faster than legacy metal lead-frames can handle, making ceramic packages an essential throughput enabler. Kyocera is funneling USD 470 million into a dedicated Japanese line to synchronize ceramic substrate availability with next-generation processor nodes. Synchronizing substrate growth cycles with lithography ramp-ups remains difficult because kilns require longer validation loops than semiconductor clean-rooms, but tier-one device makers are now signing multi-year offtake agreements to lock in supply. Regional governments are simultaneously underwriting advanced-materials clusters to reduce reliance on overseas feedstocks, a policy move that could compress lead times and moderate pricing volatility.
EV Power-Train Thermal-Management Needs
Global EV shipments surpassed 15 million units in 2024, and nearly every platform upgrade now targets 800 V electrical architectures that squeeze more power through smaller inverters. Silicon carbide power modules dissipate heat at triple the rate of silicon devices, yet the allowable junction temperature band remains tight, creating a design window ideally served by ceramic heat spreaders boasting greater than 200 W/mK conductivity. CeramTec's chip-on-heatsink solution lowers thermal resistance while maintaining dielectric separation, a combination that lengthens module life in high-vibration automotive environments. Automakers are price-sensitive, but warranty liabilities linked to thermal failures tip purchasing decisions toward high-reliability ceramics despite higher unit costs. As fleet electrification accelerates in China, Europe, and the United States, demand for ceramic substrates, busbars, and gel-coated cooling plates is scaling in parallel.
Intrinsic Brittleness & Machining Losses
Hardness that delivers heat and wear resistance simultaneously increases fracture risk during post-sinter grinding. Yield losses of 20-30% inflate unit costs and lengthen lead times. Fiber-reinforced ceramic-matrix composites mitigate crack propagation but add layer-up and infiltration steps that offset durability gains with higher process complexity. Additive manufacturing offers near-net-shape alternatives, yet material palettes and throughput still lag conventional presses, limiting adoption outside prototyping.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rising Use in High-Value Medical Implants & Devices
- Hydrogen-Electrolyzer Stack Components
- Critical-Minerals Supply-Chain Exposure
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Monolithic ceramics retained 46.68% technical ceramics market share in 2024 due to mature press-and-sinter lines that deliver uniform quality at scale. The segment should still post mid-single-digit gains as industrial OEMs retrofit pumps, nozzles, and insulators with alumina bodies that outlast steel equivalents. Composite grades, however, will lift the overall technical ceramics market as their 8.84% CAGR attracts aerospace and defense budgets chasing weight savings above 30% alongside thermal ceilings beyond 1,500 °C. In 2025, the engine hot-section segment alone accounts for a USD 1.1 billion slice of the technical ceramics market size. Processing breakthroughs such as rapid forced-air sintering are collapsing densification steps from hours to minutes, trimming energy cost curves, and narrowing price spreads with monolithics. As these efficiencies propagate, composites are expected to erode monolithic share, but not displace them outright, because automotive and industrial plants still prize predictable shrinkage and low scrap rates.
The coatings niche serves as a transitional pathway: OEMs can spray zirconia or silicon carbide onto legacy metal parts, achieving incremental heat-flux gains without redesigning the entire assembly. This retrofit approach is popular in petrochemical burners and diesel particulate filters where shutdown budgets are tight. Ceramic fibers remain small in tonnage yet influential in insulation markets; aerogel-filled fiber quilts rated to 1,100 °C are seeing uptake in LNG ship cargo holds, another indicator that specialized performance credentials sustain premium pricing in smaller sub-segments.
Oxide families such as alumina, zirconia, and mullite delivered 63.37% of 2024 revenue owing to abundant raw material availability and well-documented process controls. These grades form the baseline for capacitor dielectrics and wear plates across multiple industries. Yet silicon carbide, silicon nitride, and emerging boron carbide non-oxide formulations are booking faster order growth because they combine lower density with thermal conductivities approaching copper. The non-oxide cohort is on a 7.86% trajectory through 2030, expanding the technical ceramics market by servicing frontier devices where oxide glass phases cannot survive. Cost barriers persist, but as fab line yields improve and reject rates fall below 5%, non-oxide price premiums are narrowing. Regulatory fuel-economy mandates and data-center heat-flux escalation both point to sustained long-run tailwinds for these higher-performance grades.
Composite or hybrid material classes merge oxide matrices with non-oxide whiskers or fibers, delivering synergistic toughness and conductivity. Interest is building in lanthanum-doped alumina blends that resist dielectric breakdown at elevated voltages, a property valued by grid-scale solid-state transformer projects. These cross-over formulations validate the thesis that future share battles will not be oxide versus non-oxide but hybrid versus single-phase, adding complexity yet widening solution space.
The Technical Ceramics Market Report is Segmented by Product Type (Monolithic Ceramics, Ceramic Matrix Composites, and More), Material Class (Oxide Ceramics, Non-Oxide Ceramics, Others), End-User Industry (Electrical and Electronics, Automotive, and More), Key Application (Insulators & Substrates, Thermal Management Components, and More), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, Middle East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific dominated the technical ceramics market with 43.87% share in 2024 and is tracking a 7.91% CAGR to 2030. Mainland China hosts the majority of alumina powder calcination and offers cost arbitrage in labor-intensive finishing steps, yet rising electricity tariffs and environmental compliance fees are eroding the historic savings gap. Japan is repositioning toward ultra-clean, high-value substrates that align with national semiconductor revival incentives; Kyocera's Nagasaki site will lift domestic fine-ceramic output by 10% upon its 2026 start-up. South Korea's memory-chip epicenter drives demand for low-defect silicon nitride boards, while India is luring EV supply-chain investors with tax holidays in Gujarat and Tamil Nadu. Regional governments are also mapping recycling corridors to capture scrap zirconia and yttria, an initiative that may dilute raw-material import dependencies over the long term.
North America is mature yet innovation-heavy, claiming nearly 30% of global R&D outlays tied to ceramic matrix composites. The United States accounts for the bulk of aerospace turbine and medical implant orders, justifying ISO-class kilns and USP Class VI clean-room protocols that less regulated regions bypass. Saint-Gobain's USD 40 million catalyst-carrier plant in New York will add 100 jobs and shorten delivery cycles for East-Coast petro-refiners. Canadian mining houses supply bauxite and rare-earth concentrates, but still send most feedstock to Asian refineries. Mexico is emerging as an assembly hub for EV inverters, prompting substrate suppliers to weigh near-shoring steps that sidestep USMCA rules-of-origin tariffs.
Europe claims roughly one-fifth of global revenue and aligns commercial success with sustainability mandates. Germany's machine-tool builders specify wear-resistant alumina guides that cut lubrication demand by 60%, dovetailing with EU eco-design standards. France and Spain are piloting hydrogen hubs that will soon require thousands of square meters of solid-oxide electrolyzer plates. The region's REACH chemical-safety framework compels tight traceability, a compliance cost that props up incumbents but slows new venture launches. Post-Brexit United Kingdom policy leans toward advanced materials catapults, aiming to translate university lab breakthroughs into pilot lines within three years, yet significant scale will hinge on export markets, given limited domestic demand.
- 3M
- CeramTec GmbH
- CoorsTek Inc.
- Dyson Technical Ceramics
- Kyocera Corporation
- Mantec Technical Ceramics Ltd
- McDanel Advanced Ceramic Technologies
- Morgan Advanced Materials
- NGK SPARK PLUG CO., LTD.
- Ortech, inc.
- Rauschert GmbH
- Saint-Gobain
- Schott AG
- STC Material Solutions
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Expanding semiconductor and consumer-electronics output in Asia Pacific
- 4.2.2 EV power-train thermal-management needs
- 4.2.3 Rising use in high-value medical implants and devices
- 4.2.4 Hydrogen-electrolyser stack components
- 4.2.5 In-space manufacturing and satellite hardware
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High capital and processing cost
- 4.3.2 Intrinsic brittleness and machining losses
- 4.3.3 Critical-minerals supply-chain exposure
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Rivalry
- 4.6 Patent Analysis
- 4.7 Price Analysis
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Monolithic Ceramics
- 5.1.2 Ceramic Matrix Composites
- 5.1.3 Ceramic Coatings
- 5.1.4 Other Products
- 5.2 By Material Class
- 5.2.1 Oxide Ceramics
- 5.2.2 Non-Oxide Ceramics
- 5.2.3 Others
- 5.3 By End-user Industry
- 5.3.1 Electrical and Electronics
- 5.3.2 Automotive
- 5.3.3 Energy and Power
- 5.3.4 Medical
- 5.3.5 Aerospace and Defense
- 5.3.6 Other End-user Industries
- 5.4 By Key Application
- 5.4.1 Insulators and Substrates
- 5.4.2 Thermal Management Components
- 5.4.3 Wear-resistant Parts and Bearings
- 5.4.4 Bio-implants and Dental
- 5.4.5 Armor and Protection
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.1.1 China
- 5.5.1.2 Japan
- 5.5.1.3 India
- 5.5.1.4 South Korea
- 5.5.1.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.2 North America
- 5.5.2.1 United States
- 5.5.2.2 Canada
- 5.5.2.3 Mexico
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.2 South Africa
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share (%)/ Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 3M
- 6.4.2 CeramTec GmbH
- 6.4.3 CoorsTek Inc.
- 6.4.4 Dyson Technical Ceramics
- 6.4.5 Kyocera Corporation
- 6.4.6 Mantec Technical Ceramics Ltd
- 6.4.7 McDanel Advanced Ceramic Technologies
- 6.4.8 Morgan Advanced Materials
- 6.4.9 NGK SPARK PLUG CO., LTD.
- 6.4.10 Ortech, inc.
- 6.4.11 Rauschert GmbH
- 6.4.12 Saint-Gobain
- 6.4.13 Schott AG
- 6.4.14 STC Material Solutions
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment
- 7.2 Increasing Usage in Nano Technology











