 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1842579
農業機械租賃:市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Farm Equipment Rental - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
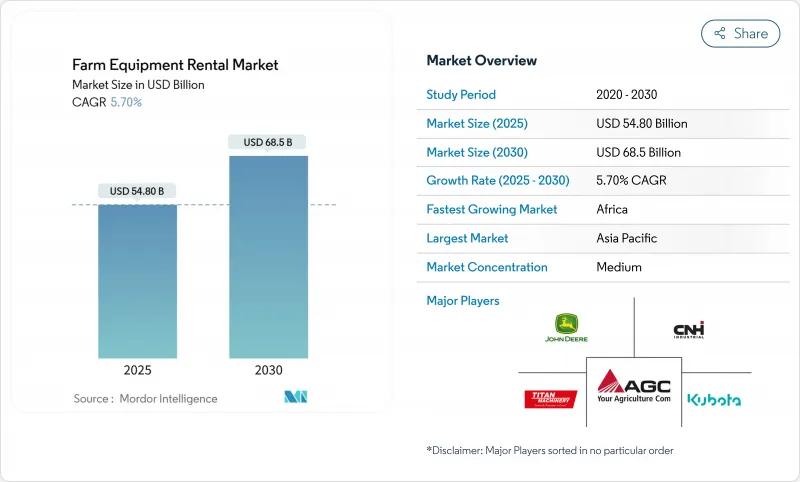
預計2025年農業機械租賃市場規模為5,48億美元,2030年將達685億美元,預測期間(2025-2030年)的複合年成長率為5.70%。
曳引機的穩定需求、數位租賃平台的快速成長以及政府機械化計畫目標支撐著這一穩步擴張。亞太地區的小農戶、北美短暫而密集的收穫季節以及歐洲的永續性法規,正在為每個地區塑造獨特的商業機會。將人工智慧車隊管理與按需預訂相結合的數位市場正在擴大使用機會,而與環境、社會和治理 (ESG) 掛鉤的融資正在推動供應商轉向電動車和低排放氣體車隊。如今,競爭的焦點在於使用情況分析、自動駕駛能力和最後一英里服務,這迫使領先設備製造商支持的經銷商和技術先行者完善資本高效、數據豐富的模型,以實現盈利成長。
全球農業機械租賃市場趨勢與洞察
智慧機器成本上升導致單位使用費上漲
配備GPS的曳引機和感測器的收割機的購買價格不斷上漲,加劇了亞太地區小農戶的負擔能力差距。由於平均設備價格上漲了25-30%,租賃需求激增了35%。印度的農業機械化提案在2014年至2024年期間提供了8.72億美元的撥款,用於建立74,144個客製化租賃中心,這些中心匯集資本密集型資產供村級使用。這些中心現在結合了物聯網車輛監控和智慧型手機預訂功能,使農民無需擁有折舊免稅額的設備即可實現精密農業。
季節性勞動力短缺刺激自動曳引機租賃
經合組織經濟體的勞動力短缺導致可用的田間勞動力減少了近五分之一,迫使生產商轉向靈活合約的自動駕駛曳引機。配備機器人、LiDAR和路線規劃軟體的租賃車輛可以在尖峰時段完成重複的耕作和噴灑任務,從而提高運轉率並緩解工資上漲。儘管圍繞純機械作業的道德和責任爭論依然存在,但即時診斷和地理圍欄可以減少停機時間並支持遵守安全義務。
撒哈拉以南小農對租賃經濟的認知較低
在許多非洲國家,儘管有行動優先的匹配應用程式,機械化率仍然低於6%。資訊不對稱和風險規避使農民即使在附近也不願使用機器。為了彌補這一差距,一些試點推廣計畫正在將客製化產品與作物保險掛鉤,但持續的推廣和微型培訓對於規模化發展至關重要。
細分分析
2024 年,受耕作、運輸和動力輸出應用持續需求的推動,曳引機創造了大部分收益。曳引機在農業機械租賃市場的 38.10% 佔有率反映了它們在所有車隊中的核心作用,並支持全季節運轉率。收割機雖然只佔農業機械租賃市場的一小部分,但由於其高昂的標價使短期租賃成為許多生產商唯一可行的選擇,因此有望達到 7.40% 的最快複合年成長率。新型收割機內建的精確產量測繪和自動駕駛控制正在提高每小時的價值,並鼓勵供應商實施基於性能的定價。撒佈機、打包機和播種機的租賃窗口狹窄,與作物候期相關,從而產生了調度高峰,數位平台可以透過需求預測演算法來平滑這些高峰。專用機具捆綁到多設備包中,增加了籃子尺寸並鎖定客戶的完整生產週期。
第二個趨勢是自動化從連作曳引機到收割機的轉變。北美的早期採用者現在正在尋求自動化聯合收割機,以在短暫的收穫季節降低人事費用。這種轉變將改變折舊免稅額曲線,迫使租賃公司重新調整殘值假設,並使租賃條款與快速的技術更新周期保持一致。隨著設備互聯程度的提高,產量地圖、土壤壓實洞察以及機器健康狀況的遠端檢測等數據的收益將成為除傳統租賃收入之外的第二大收入來源。
到 2024 年,71 至 130 匹馬力的中型曳引機將佔據農業機械租賃市場的 27.40%,其燃油效率和容量非常適合小塊田地作業。 250 匹馬力以上的大型曳引機雖然目前屬於小眾市場,但預計其年複合成長率將達到 8.50%,超過所有其他細分市場,因為農場整合和工時法規青睞更大、更聰明的機械。這些大馬力車輛的日租金很高,並且有嚴格的運輸和維護要求,只有全方位服務供應商才能滿足這些要求。 30 馬力以下的曳引機對於園藝和窄行作物仍然必不可少,而 131 至 250 馬力的型號則彌補了多功能中檔作業和專業重型作業之間的差距。不斷變化的動力結構正在鼓勵租賃公司實現車隊多樣化、對沖運作風險並製定與燃油成本和遠端資訊檢驗的負載率掛鉤的動態定價。
同時,原始設備製造商正在將 Tier 4-Final 引擎和混合動力傳動系統應用於各個功率等級,以滿足歐洲和加州日益嚴格的排放法規。利用 ESG 關聯融資的供應商正在降低資本成本,從而獲得更具競爭力的小時費率。遠端資訊處理支援的負載追蹤也使計費方式轉向基於使用量的交貨,使成本與交付的馬力小時數(而非日曆天數)保持一致。
農業機械租賃市場按設備類型(曳引機等)、功率輸出(小於30馬力等)、驅動類型(兩輪驅動等)、經營模式(線下經銷商及合作農場等)、最終用戶農場規模(小型(小於5公頃)、其他)、租賃期限(短期(小於300萬美元)、其他)及地區細分。市場預測以價值(美元)和數量(單位)表示。
區域分析
在小農戶補貼計畫的支持下,亞太地區將在2024年創造44.25%的農業設備租賃市場收益。印度74,144個客製化租賃中心以及中國與補貼掛鉤的土地競標規則正在擴大機械化程度,同時又不會增加農場債務。智慧型手機和本地語言應用程式實現了透明的預訂和數位支付,從而提高了水稻、小麥和園藝價值鏈中設備的採用率。由於精密設備的成本仍然很高,供應商正在採用共用所有權結構,將技術成本分攤給廣泛的用戶群,並保持每公頃租賃價格在可負擔的範圍內。
北美市場正在經歷成熟與演變。玉米種植帶的豐收將推動近期對250馬力以上曳引機和聯合收割機的強勁需求,從而在9月和10月期間擴大價格溢價。科羅拉多和其他州正在頒布「維修權」法律,要求原始設備製造商提供診斷工具,並可能降低停機時間和租賃費用。自動維修和電力傳動系統可享受與氣候變遷相關的獎勵,這將鼓勵租賃巨頭和區域獨立公司更新其車隊。
在歐洲,差異性十分明顯。西歐生產商正在採用基於應用程式的租賃方式,以應對不斷上漲的土地價格和更嚴格的排放法規。 ESG 掛鉤融資降低了包含電動曳引機、生質燃料收割機和犁地機具的車隊的借貸成本。 《歐洲綠色新政》的永續性目標使租賃成為一種頗具吸引力的合規途徑,將重點從資產所有權轉向基於績效的服務。在中歐和東歐,中型家庭農場仍然占主導地位,透過自有核心曳引機和租賃專用機械的組合來平衡成本和技術。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場狀況
- 市場概況
- 市場促進因素
- 亞太地區智慧機器成本上漲將推動按次付費的採用
- 經合組織國家季節性勞動力短缺推動自動曳引機租賃
- 美國玉米帶收穫季節需求激增,短期租約增加
- 印度與社區健康中心掛鉤的補貼推動了村級租賃中心的發展
- 基於應用程式的車隊市場在西歐迅速擴張
- ESG相關融資輔助電動租賃車隊發展
- 市場限制
- 撒哈拉以南小農對租賃經濟的認知較低
- 北美收穫季節 250 匹馬力以下機組稀缺
- 亞太地區市場分散,首英里和最後一英里物流成本高昂
- 因設備誤用而增加維護停機時間和責任
- 監理展望
- 五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭強度
第5章市場規模及成長預測
- 依設備類型
- 聯結機
- 收割機
- 打包機
- 吊具
- 播種機和種植機
- 耕作及土壤耕作設備
- 其他器具
- 按輸出功率(HP)
- 低於30 HP
- 31-70HP
- 71-130HP
- 131-250HP
- 250馬力以上
- 按驅動類型
- 兩輪驅動
- 四輪驅動
- 按經營模式
- 線下經銷商和合作社
- 線上/基於應用程式的平台
- 按最終用戶農場規模
- 小型(小於5公頃)
- 中型(5-20公頃)
- 規模大(超過20公頃)
- 按租賃期限
- 短期(少於3個月)
- 季節(3-9個月)
- 年度/長期(9個月或以上)
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 北美其他地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 其他歐洲國家
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 韓國
- 其他亞太地區
- 中東和非洲
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 土耳其
- 南非
- 埃及
- 其他中東和非洲地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭態勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略舉措
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Deere & Company
- CNH Industrial NV
- AGCO Corporation
- Kubota Corporation
- Titan Machinery Inc.
- Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd.(Trringo)
- Farmease
- JFarm Services
- Pacific AG Rental LLC
- The Pape Group Inc.
- Messick's
- Flaman Group of Companies
- Premier Equipment Rental
- Friesen Sales & Rentals
- Aktio Corporation
- United Rentals(Agricultural Line)
- H&E Equipment Services Inc.
- Kwipped Inc.
- Ashtead Group plc(Sunbelt)
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Farm Equipment Rental Market size is estimated at USD 54.8 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 68.5 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.70% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Consistent demand for tractors, rapid growth in digital rental platforms, and targeted government mechanization programs underpin this steady expansion. Asia Pacific prevailing smallholder structure, North America's short but intense harvest windows, and Europe's sustainability regulations shape distinctly regional opportunities. Digital marketplaces that marry AI-driven fleet management with on-demand booking are widening access, while ESG-linked finance is nudging providers toward electric and low-emission fleets. Competition now hinges on utilization analytics, autonomous capabilities, and last-mile service, forcing both OEM-backed dealers and technology-first entrants to refine capital-light, data-rich models for profitable growth.
Global Farm Equipment Rental Market Trends and Insights
Smart-Machinery Cost Inflation Steering Pay-Per-Use
Rising acquisition prices for GPS-enabled tractors and sensor-rich harvesters are widening the affordability gap for Asia Pacific smallholders. Rental demand surged by 35% as average machinery prices climbed 25-30%. India's Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization issued USD 872 million in subsidies between 2014-2024, catalyzing 74,144 Custom Hiring Centers that pool capital-intensive assets for village-level access. These hubs, now pairing IoT fleet monitoring with smartphone booking, let farmers tap precision agriculture without owning depreciating equipment.
Seasonal Workforce Deficit Spurring Autonomous Tractor Rentals
Labor shortages in OECD economies have trimmed the available field workforce by nearly one-fifth, pushing growers toward autonomous tractors available on flexible contracts. Rental fleets outfitted with robotics, LiDAR, and route-planning software cover repetitive tillage and spraying tasks during peak periods, lifting utilization and mitigating wage inflation. Ethical and liability debates around machine-only operations persist, yet real-time diagnostics and geofencing reduce downtime and support compliance with safety mandates.
Low Awareness of Rental Economics Among Sub-Saharan Smallholders
Mechanization rates in many African nations remain below 6% despite mobile-first matching apps. Information asymmetries and risk aversion dampen uptake even when equipment is nearby. Pilot extension programs linking custom hire to crop-insurance premiums are beginning to bridge this gap, but sustained outreach and micro-training remain essential for scale.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- App-Based Fleet Marketplaces Scaling Rapidly in Western Europe
- ESG-Linked Finance Steering Electrified Rental Fleets
- High First-/Last-Mile Logistics Cost in Fragmented APAC Markets
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Tractors generated the bulk of revenue in 2024, aided by constant demand across tillage, hauling, and power-take-off applications. Their 38.10% farm equipment rental market share reflects a core role in every fleet and underpins whole-season utilization rates. Harvesters, though representing a smaller slice of the farm equipment rental market, are on track for the fastest 7.40% CAGR as their high sticker prices make short-window rental the only feasible option for many growers. Precision yield mapping and auto-steer controls embedded in newer harvester models raise per-hour value, encouraging providers to introduce outcome-based pricing. Sprayers, balers, and seeders occupy narrower rental windows tied to crop phenology, creating scheduling peaks that digital platforms smooth through predictive demand algorithms. Specialty implements are bundled into multiequipment packages, enhancing basket size and locking in customers for full production cycles.
A second trend is the migration of autonomy from row-crop tractors to harvest machines. Early adopters in North America now seek self-driving combines that cut labor bills during short harvest windows. This shift reshapes depreciation curves, compelling rental firms to recalibrate residual value assumptions and match lease terms to rapid technology refresh cycles. As equipment connectivity deepens, data monetization-yield maps, soil compaction insights, and machine health telemetry-emerges as a secondary revenue line alongside traditional rental income.
Mid-range 71-130 HP tractors anchored 27.40% of the 2024 farm equipment rental market size thanks to an optimal mix of fuel efficiency and capability across small-plot operations. Larger units above 250 HP, though currently niche, are forecast to outgrow all other brackets at 8.50% CAGR as farm consolidation and regulated labor hours favor bigger, smarter machinery. These high-horsepower vehicles command premium day rates and impose stringent transport and maintenance requirements that only full-service providers can meet. Sub-30 HP tractors remain vital for horticulture and tight-row crops, while 131-250 HP models bridge the gap between versatile mid-range and specialized heavy-duty tasks. The power-mix evolution pushes rental firms to diversify fleets, hedge utilization risks, and build dynamic pricing linked to fuel costs and telematics-verified load factors.
In parallel, OEMs embed Tier 4-Final engines and hybrid drivetrains across power classes, meeting tightening emission rules in Europe and California. Providers leveraging ESG-linked loans unlock lower capital costs that filter into competitive hourly rates. Telematics-enabled load tracking is also enabling a shift toward usage-based billing, aligning cost with delivered horsepower hours rather than calendar days.
The Farm Equipment Rental Market is Segmented by Equipment Type (tractors, and More), Power Output (Less Than 30 HP, and More), Drive Type (Two-Wheel Drive and More), Business Model (Offline Dealer & Co-Op Yards and More), End-User Farm Size (Small (less Than 5 Ha) and More), Rental Duration (Short-Term (less Than 3 M) and More) and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Units).
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific generated 44.25% of 2024 revenue for the farm equipment rental market, underpinned by smallholder-oriented subsidy schemes. India's 74,144 Custom Hiring Centers and China's subsidy-linked land tender rules are expanding mechanization without inflating farm debt. Smartphones and vernacular apps embed transparent booking and digital payments, lifting utilization across rice, wheat, and horticulture value chains. Precision hardware costs are still high, so providers use shared ownership structures to amortize technology over broader user bases, keeping per-hectare rental charges affordable.
North America presents a mature yet evolving landscape. Peak harvest in the Corn Belt drives intense, short-term demand for >250 HP tractors and combines, widening price premiums during September-October. Right-to-repair legislation in Colorado and other states now obliges OEMs to furnish diagnostic tools, potentially lowering downtime and rental rates. Autonomous retrofits and electric drivetrains qualify for climate-linked incentives, encouraging fleet renewal among rental giants and regional independents alike.
Europe exhibits pronounced heterogeneity. Western European growers adopt app-based rental to navigate high land prices and strict emission caps. ESG-linked finance reduces borrowing costs for fleets that integrate electric tractors, biofuel harvesters, and low-till implements. The European Green Deal's sustainability targets make rental an attractive compliance pathway, shifting emphasis from asset ownership to outcome-based service. Central and Eastern Europe, still dominated by mid-sized family holdings, balance cost and technology by mixing owned core tractors with rented specialty machines.
- Deere & Company
- CNH Industrial N.V.
- AGCO Corporation
- Kubota Corporation
- Titan Machinery Inc.
- Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd. (Trringo)
- Farmease
- JFarm Services
- Pacific AG Rental LLC
- The Pape Group Inc.
- Messick's
- Flaman Group of Companies
- Premier Equipment Rental
- Friesen Sales & Rentals
- Aktio Corporation
- United Rentals (Agricultural Line)
- H&E Equipment Services Inc.
- Kwipped Inc.
- Ashtead Group plc (Sunbelt)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Cost-inflation of Smart Machinery Accelerating Pay-per-Use Adoption in Asia Pacific
- 4.2.2 Seasonal Workforce Deficit in OECD Nations Driving Autonomous Tractor Rentals
- 4.2.3 Peak-Harvest Demand Spikes in US Corn-Belt Reinforcing Short-Term Leases
- 4.2.4 Indian CHC-Linked Subsidies Catalyzing Village-Level Rental Hubs
- 4.2.5 App-Based Fleet Marketplaces Scaling Rapidly in Western Europe
- 4.2.6 ESG-Linked Finance Steering Electrified Rental Fleets
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Low Awareness of Rental Economics among Sub-Saharan Smallholders
- 4.3.2 Scarcity of Less than 250 HP Units during North-American Harvest Window
- 4.3.3 High First-/Last-Mile Logistics Cost in Fragmented APAC Markets
- 4.3.4 Equipment Misuse Elevating Maintenance Downtime & Liability
- 4.4 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value (USD) and Volume (Units))
- 5.1 By Equipment Type
- 5.1.1 Tractors
- 5.1.2 Harvesters
- 5.1.3 Balers
- 5.1.4 Sprayers
- 5.1.5 Seeders & Planters
- 5.1.6 Tillage & Soil-Cultivation Equipment
- 5.1.7 Other Implements
- 5.2 By Power Output (HP)
- 5.2.1 Less than 30 HP
- 5.2.2 31-70 HP
- 5.2.3 71-130 HP
- 5.2.4 131-250 HP
- 5.2.5 More than 250 HP
- 5.3 By Drive Type
- 5.3.1 Two-Wheel Drive
- 5.3.2 Four-Wheel Drive
- 5.4 By Business Model
- 5.4.1 Offline Dealer & Co-op Yards
- 5.4.2 Online / App-Based Platforms
- 5.5 By End-User Farm Size
- 5.5.1 Small (Less than 5 ha)
- 5.5.2 Medium (5-20 ha)
- 5.5.3 Large (More than 20 ha)
- 5.6 By Rental Duration
- 5.6.1 Short-Term (Less than 3 m)
- 5.6.2 Seasonal (3-9 m)
- 5.6.3 Annual / Long-Term (More than 9 m)
- 5.7 By Geography
- 5.7.1 North America
- 5.7.1.1 United States
- 5.7.1.2 Canada
- 5.7.1.3 Rest of North America
- 5.7.2 South America
- 5.7.2.1 Brazil
- 5.7.2.2 Argentina
- 5.7.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.7.3 Europe
- 5.7.3.1 Germany
- 5.7.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.7.3.3 France
- 5.7.3.4 Italy
- 5.7.3.5 Spain
- 5.7.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.7.4 Asia Pacific
- 5.7.4.1 China
- 5.7.4.2 India
- 5.7.4.3 Japan
- 5.7.4.4 South Korea
- 5.7.4.5 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.7.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.7.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.7.5.2 UAE
- 5.7.5.3 Turkey
- 5.7.5.4 South Africa
- 5.7.5.5 Egypt
- 5.7.5.6 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.7.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles
- 6.4.1 Deere & Company
- 6.4.2 CNH Industrial N.V.
- 6.4.3 AGCO Corporation
- 6.4.4 Kubota Corporation
- 6.4.5 Titan Machinery Inc.
- 6.4.6 Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd. (Trringo)
- 6.4.7 Farmease
- 6.4.8 JFarm Services
- 6.4.9 Pacific AG Rental LLC
- 6.4.10 The Pape Group Inc.
- 6.4.11 Messick's
- 6.4.12 Flaman Group of Companies
- 6.4.13 Premier Equipment Rental
- 6.4.14 Friesen Sales & Rentals
- 6.4.15 Aktio Corporation
- 6.4.16 United Rentals (Agricultural Line)
- 6.4.17 H&E Equipment Services Inc.
- 6.4.18 Kwipped Inc.
- 6.4.19 Ashtead Group plc (Sunbelt)
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment











