 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1842516
vEPC(虛擬化演進分組核心):市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計、成長預測(2025-2030 年)Virtualized Evolved Packet Core - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
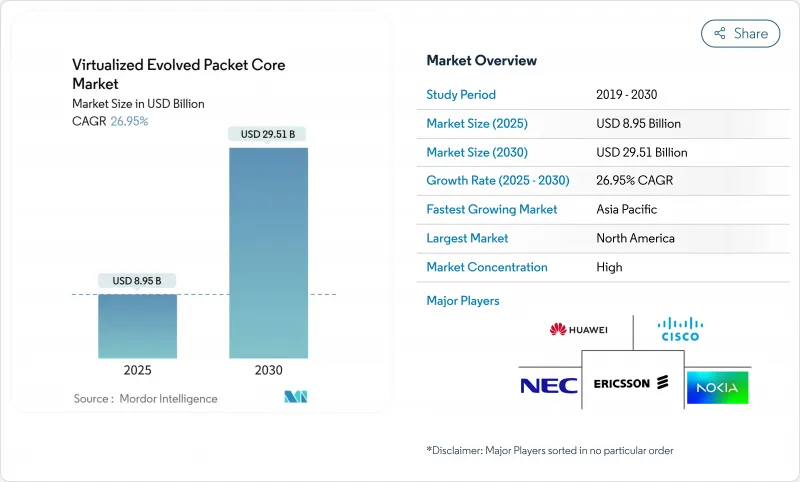
虛擬化演進分組核心 (vEPC) 市場規模預計在 2025 年為 89.5 億美元,預計到 2030 年將達到 295.1 億美元,預測期內(2025-2030 年)的複合年成長率為 26.95%。
5G獨立組網的部署、企業對私有行動網路日益成長的需求,以及通訊業者對節能虛擬化核心網路的永續性發展要求,共同推動此成長。通訊業者正在加速軟體定義網路功能,以降低資本支出和營運支出,而超大規模公有公共雲端夥伴關係則有助於加快服務發布和全球覆蓋範圍。亞太地區在政府支持的數位化計畫的支持下,正在推動其應用,而北美地區則透過網路切片和邊緣雲端的協同效應,推動差異化發展。同時,在歐洲,對合規性和能源效率的關注正在影響技術需求和供應商選擇。
全球 vEPC(虛擬化演進分組核心)市場趨勢與洞察
加速 5G 部署需要雲端原生核心
雲端原生、以服務為基礎的架構對於真正的 5G 獨立組網至關重要,這使得 vEPC 對於追求網路切片和高階服務的營運商而言成為一項不可或缺的投資。愛立信已於 2024 年底獲得超過 120 個 5G 商用核心網契約,並在全球範圍內為 37 個 5G SA 現網提供支持,這為其商用準備就緒提供了有力證據。 T-Mobile 等參與企業已利用全國範圍的 5G SA 推出網路切片視訊通話,並建立了差異化的定價模式。競爭壓力將迫使通訊業者加速現代化轉型,否則將面臨流失風險。雲端原生核心網路還能讓規模較小的行動虛擬網路營運商快速進入企業物聯網領域。因此,vEPC(虛擬化演進分組核心)市場將在短期內經歷一個良莠不齊的採用週期。
透過網路功能虛擬化節省資本支出/營運支出
隨著 vEPC 設定將工作負載轉移到商用硬體和共用雲端資源,營運商的成本節省顯著提升。研究表明,與單晶片硬體核心相比,vEPC 的資本支出減少了 68%,營運成本降低了 67%。在遷移到基於意圖的虛擬化核心自動化營運後,Digital Nasional Berhad 的網路執行時間達到了 99.8%,客戶投訴解決時間縮短了 90%。節能措施進一步提高了 22% 的效率,實現了預算和永續性目標。加速服務發布將收益時間從一年多縮短到不到六個月。這些經濟效益正在將 vEPC 從一項可選功能轉變為董事會級投資計劃中的必備功能。供應商目前正在整合 AI 驅動的編配,以進一步減少營運工作負載。
操作員對傳統物理 EPC 的慣性
沉沒投資和對關鍵任務風險的規避正在減緩虛擬化計畫。英國的Three公司僅在被迫進行現代化升級時才更換其二手諾基亞CloudBand網路,凸顯了其不願中斷穩定的流量。 Verizon拖延的5G SA推出表明,即使是創新領導者也難以應對遷移的複雜性。在成熟市場,監管審查的加強和嚴格的服務水準預期使變更管理更具挑戰性。因此,實體核心的效用超過了其經濟效益,抑制了vEPC(虛擬化演進分組核心)市場的短期成長動能。
報告中分析的其他促進因素和限制因素
- 用於工業 4.0 和園區連接的私有 LTE/5G 網路
- 通訊業者在節能核心網路方面的永續性義務
- 多租戶雲端中的安全性和合規性問題
細分分析
到2024年,雲端部署將佔據虛擬化演進分組核心網路 (vEPC) 市場佔有率的63%,這反映了通訊業者對彈性擴展和快速服務迭代的偏好。隨著超大規模營運商不斷增強其通訊功能集,雲端部署預計將以32%的複合年成長率成長,超越本地部署和混合部署。三星、TELUS和AWS建構了北美首個虛擬漫遊閘道器,證明了跨境服務創新可以透過在公有公共雲端上原生運行的控制平面元素蓬勃發展。這些案例凸顯了從基礎設施所有權到敏捷性的更廣泛轉變。
將資料在地化的營運商正在採用過渡性混合模式,以在不犧牲雲端經濟效益的情況下滿足主權規則。愛立信的緊湊型分組核心網 (Compact Packet Core) 將部署複雜性降低了 80%,能耗降低了 30%,這使得雲端就緒捆綁包對二級營運商具有吸引力。隨著越來越多的合約指定基於結果的定價,vEPC(虛擬化演進分組核心網路)市場正在整合託管服務附加元件,例如人工智慧輔助營運。規模較小的區域通訊業者和行動虛擬網路營運商 (MVNO) 正在利用 SaaS 交付,在幾週內(而非幾季內)推出新產品,並擴大基本客群。
虛擬化演進分組核心 (vEPC) 市場報告按部署模式(雲端、本地、混合)、應用程式(物聯網和 M2M、行動專用網路 (MPN) 和 MVNO、寬頻無線存取 (BWA)、LTE/VoLTE/VoWiFi、5G 非獨立 (NSA) 核心、其他)、終端用戶(標準和電信服務)、國際企業和電信服務供應商、區域和電信)、公共
區域分析
到2024年,亞太地區將佔據虛擬化演進分組核心網 (vEPC) 市場規模的38%,這得益於中國目前已部署的5,325個5G專網,其中包括超過2萬個工業用例。政府的獎勵和頻譜政策正在加速製造業的採用,北京方面已投資30億美元用於5G-Advanced網路,力爭2025年涵蓋300個城市。印度5G SA覆蓋率為52%,遠高於歐洲的2%,顯示新興經濟體正透過雲端優先部署超越傳統架構。這些專案為廠商提供了在地化研發和生產的規模,鞏固了亞太地區在虛擬化演進分組核心網 (vEPC) 市場的領導地位。
在北美,營運商非常重視透過網路切片和 O-RAN 整合打造的高階服務層級。 Verizon 已部署超過 13 萬個支援 O-RAN 的無線存取點,推出了基於切片的視訊通話,並獲得了大量高價值用戶。企業間的合作催生了重要的案例研究:寶馬斯帕坦堡工廠透過採用私有 5G 提升了正常運作,三星、TELUS 和 AWS 則透過完全虛擬化的核心網展示了漫遊創新。頻寬租賃監管的明確性進一步支援了園區部署,並增強了區域對 vEPC(虛擬化演進分組核心網路)市場的貢獻。
在歐洲,我們看到了好壞參半的發展動能。英國的Three 授予愛立信一份 9 Tbps 的雲端原生核心契約,而 O2 Telefónica 在六個月內就突破了 100 萬 AWS 託管核心用戶。然而,受制於英國《電訊安全法》等嚴格的安全法規,以及優先考慮穩定性而非激進現代化的風險規避文化,5G SA 的整體可用性仍然只有 2%。通訊業者正專注於能源效率和開放式 RAN 實驗,正如德國電信的 O-RAN Town 計劃所示。雖然這些優先事項將限制短期支出,但它們將在 vEPC 市場中創造互通性、低功耗舉措演進分組核心 (vEPC) 解決方案的長期需求。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場狀況
- 市場概況
- 市場促進因素
- LTE/4G用戶快速成長
- 加速 5G 部署需要雲端原生核心
- 透過網路功能虛擬化節省資本支出/營運支出
- 用於工業 4.0 和校園連接的私人 LTE/5G 網路
- 邊緣雲協同實現分散式用戶平面卸載
- 通訊業者對節能核心網路的永續性要求
- 市場限制
- 操作員對傳統物理 EPC 的慣性
- 多租戶雲端中的安全性和合規性問題
- 開放核心與隔離核心之間的互通性差距
- 5G SA 工作負載的超大規模雲端 TCO 難以預測
- 價值/供應鏈分析
- 監管狀況
- 技術展望
- 投資分析(按基準)
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭強度
第5章市場規模及成長預測
- 依部署類型
- 雲端基礎
- 本地部署
- 混合
- 按用途
- 物聯網和 M2M
- 行動專用網路 (MPN) 和 MVNO
- 寬頻無線存取(BWA)
- LTE/VoLTE/VoWiFi
- 5G非獨立(NSA)核心
- 5G獨立(SA)核心
- 按最終用戶
- 通訊業者
- 按公司和行業
- 政府/公共
- 雲端服務供應商
- MVNE/MVNO
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 俄羅斯
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 其他歐洲國家
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 韓國
- 澳洲和紐西蘭
- 其他亞太地區
- 中東和非洲
- 中東
- 海灣合作理事會國家
- 土耳其
- 其他中東地區
- 非洲
- 南非
- 奈及利亞
- 埃及
- 其他非洲國家
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭態勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略舉措
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Ericsson
- Huawei Technologies
- Nokia
- Cisco Systems
- ZTE
- Samsung Electronics
- NEC Corporation
- Mavenir
- Microsoft(Affirmed Networks)
- Athonet(HPE)
- Telrad Networks
- Core Network Dynamics
- VMware
- Juniper Networks
- Red Hat(IBM)
- Intel
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise
- Casa Systems
- Parallel Wireless
- Druid Software
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Virtualized Evolved Packet Core Market size is estimated at USD 8.95 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 29.51 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 26.95% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Growth stems from 5G standalone rollouts, rising enterprise demand for private mobile networks, and operator sustainability mandates that favor energy-efficient virtualized cores. Telcos accelerate software-defined network functions to slash capital and operating outlays, while hyperscale public-cloud partnerships allow rapid service launches and global coverage. Asia Pacific drives adoption on the back of government-backed digital programs, whereas North America pushes differentiation through network slicing and edge-cloud synergies. Meanwhile, Europe emphasizes compliance and energy efficiency, a stance that shapes technical requirements and vendor selection.
Global Virtualized Evolved Packet Core Market Trends and Insights
Accelerated 5G Rollouts Demanding Cloud-Native Cores
Cloud-native service-based architectures are mandatory for true 5G standalone networks, making vEPC a non-negotiable investment for operators pursuing network slicing and premium-tier services. Ericsson secured more than 120 commercial 5G core contracts by late 2024, powering 37 live 5G SA networks worldwide, providing tangible proof of commercial readiness. Early movers such as T-Mobile leveraged nationwide 5G SA to introduce network-slice-enabled video calling, which positions them for differentiated pricing models. Competitive pressure compels lagging carriers to accelerate modernization or risk churn. Cloud-native cores also give smaller mobile virtual network operators fast-track entry into enterprise IoT niches. Consequently, the Virtualized Evolved Packet Core market experiences a compounding adoption cycle in the short term.
CapEx/OpEx Savings from Network-Function Virtualization
Operators record sizeable cost reductions as vEPC setups shift workloads to commodity hardware and shared cloud resources. Studies show 68% lower capital outlays and 67% savings on operating expense versus monolithic hardware cores. Digital Nasional Berhad achieved 99.8% network uptime and cut customer-complaint resolution time by 90% after moving to intent-based automated operations on a virtualized core. Energy savings add a further 22% efficiency, meeting both budget and sustainability goals. Faster service launches shorten time-to-revenue from over a year to less than six months. These economics shift vEPC from optional to essential in board-level investment plans. Vendors now embed AI-powered orchestration to shrink operational workloads even further.
Operator Inertia Toward Legacy Physical EPCs
Sunk investments and mission-critical risk aversion slow virtualization plans. Three UK replaced Nokia's end-of-life CloudBand only when forced to modernize, underscoring reluctance to disrupt stable traffic flows. Verizon's protracted 5G SA launch shows that even innovation leaders grapple with migration complexity. Mature markets face elevated regulatory oversight and stringent service-level expectations, making change management even more difficult. As a result, physical cores persist for longer than their economic utility justifies, dampening short-term momentum in the Virtualized Evolved Packet Core market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Private LTE/5G Networks for Industry 4.0 and Campus Connectivity
- Telco Sustainability Mandates for Energy-Efficient Core Networks
- Security and Compliance Concerns on Multi-Tenant Cloud
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Cloud implementations represented 63% of the Virtualized Evolved Packet Core market share in 2024, reflecting carriers' preference for elastic scaling and rapid service iteration. The cloud cohort is forecast to grow at 32% CAGR, outpacing on-premises and hybrid alternatives as hyperscalers strengthen telecom feature sets. Samsung, TELUS, and AWS created North America's first virtual roaming gateway, which proves that cross-border service innovations flourish when control-plane elements run natively on the public cloud. These examples underpin a broad shift where infrastructure ownership yields to agility.
Operators that retain data on-site embrace transitional hybrid models to satisfy sovereignty rules without forfeiting cloud economics. Ericsson's Compact Packet Core reduces deployment complexity by 80% and cuts energy use by 30%, making cloud-ready bundles attractive to tier-2 carriers. As more contracts stipulate outcome-based pricing, the Virtualized Evolved Packet Core market embeds managed-service add-ons such as AI-assisted operations. Small regional telcos and MVNOs leverage SaaS delivery to launch new offers in weeks rather than quarters, broadening the customer base.
The Virtualized Evolved Packet Core Market Report is Segmented by Deployment Mode (Cloud, On-Premise, and Hybrid), Application (IoT and M2M, Mobile Private Networks (MPN) and MVNO, Broadband Wireless Access (BWA), LTE/VoLTE/VoWiFi, 5G Non-Standalone (NSA) Core, and More), End-User (Telecom Operators, Enterprises and Industrial Verticals, Government and Public Safety, Cloud Service Providers, and MVNE/MVNOs), and Geography.
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific generated 38% of the 2024 Virtualized Evolved Packet Core market size, supported by China's 5,325 live private 5G networks that include more than 20,000 industrial use cases. Government incentives and spectrum policies accelerate manufacturing adoption, with Beijing investing USD 3 billion in 5G-Advanced coverage across 300 cities in 2025. India's 52% 5G SA coverage, well ahead of Europe's 2%, illustrates how emerging economies leapfrog legacy architectures via cloud-first rollouts. These programs supply scale that compels vendors to localize R&D and production, reinforcing Asia Pacific's leadership in the Virtualized Evolved Packet Core market.
North America emphasizes premium service tiers through network slicing and O-RAN integration. Verizon deployed more than 130,000 O-RAN-capable radios and launched slice-based video calling to capture high-value subscribers. Enterprise alliances produce headline case studies: BMW's Spartanburg plant realized uptime gains after adopting private 5G, and Samsung, TELUS, and AWS demonstrated roaming innovation via fully virtualized cores. Regulatory clarity around spectrum leasing further supports campus deployments, bolstering regional contribution to the Virtualized Evolved Packet Core market.
Europe shows mixed momentum. Three UK awarded Ericsson a 9 Tbps cloud-native core contract, and O2 Telefonica surpassed 1 million users on its AWS-hosted core within six months. Yet overall 5G SA availability stands at 2%, restrained by strict security rules such as the UK Telecoms Security Act and by a risk-averse culture that favors stability over aggressive modernization. Operators focus on energy efficiency and open-RAN experimentation, evidenced by Deutsche Telekom's O-RAN Town initiative. These priorities temper immediate spending but create long-term demand for highly interoperable, low-power vEPC solutions within the Virtualized Evolved Packet Core market.
- Ericsson
- Huawei Technologies
- Nokia
- Cisco Systems
- ZTE
- Samsung Electronics
- NEC Corporation
- Mavenir
- Microsoft (Affirmed Networks)
- Athonet (HPE)
- Telrad Networks
- Core Network Dynamics
- VMware
- Juniper Networks
- Red Hat (IBM)
- Intel
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise
- Casa Systems
- Parallel Wireless
- Druid Software
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rapid growth in LTE/4G subscriber base
- 4.2.2 Accelerated 5G roll-outs demanding cloud-native cores
- 4.2.3 CapEx / OpEx savings from network-function virtualization
- 4.2.4 Private LTE/5G networks for Industry 4.0 and campus connectivity
- 4.2.5 Edge-cloud synergies enabling distributed user-plane off-load
- 4.2.6 Telco sustainability mandates for energy-efficient core networks
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Operator inertia toward legacy physical EPCs
- 4.3.2 Security and compliance concerns on multi-tenant cloud
- 4.3.3 Inter-operability gaps across open, disaggregated cores
- 4.3.4 Unpredictable hyperscale cloud TCO for 5G SA workloads
- 4.4 Value/Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Investment Analysis (Baseline-specific)
- 4.8 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.8.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.8.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.8.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.8.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.8.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Deployment Mode
- 5.1.1 Cloud-based
- 5.1.2 On-premise
- 5.1.3 Hybrid
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 IoT and M2M
- 5.2.2 Mobile Private Networks (MPN) and MVNO
- 5.2.3 Broadband Wireless Access (BWA)
- 5.2.4 LTE/VoLTE/VoWiFi
- 5.2.5 5G Non-Standalone (NSA) Core
- 5.2.6 5G Standalone (SA) Core
- 5.3 By End User
- 5.3.1 Telecom Operators
- 5.3.2 Enterprises and Industrial Verticals
- 5.3.3 Government and Public Safety
- 5.3.4 Cloud Service Providers
- 5.3.5 MVNE/MVNOs
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 South America
- 5.4.2.1 Brazil
- 5.4.2.2 Argentina
- 5.4.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.3.1 Germany
- 5.4.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.3.3 France
- 5.4.3.4 Russia
- 5.4.3.5 Italy
- 5.4.3.6 Spain
- 5.4.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4.1 China
- 5.4.4.2 Japan
- 5.4.4.3 India
- 5.4.4.4 South Korea
- 5.4.4.5 Australia and New Zealand
- 5.4.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Middle East
- 5.4.5.1.1 GCC Countries
- 5.4.5.1.2 Turkey
- 5.4.5.1.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.4.5.2 Africa
- 5.4.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.4.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.4.5.2.3 Egypt
- 5.4.5.2.4 Rest of Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Ericsson
- 6.4.2 Huawei Technologies
- 6.4.3 Nokia
- 6.4.4 Cisco Systems
- 6.4.5 ZTE
- 6.4.6 Samsung Electronics
- 6.4.7 NEC Corporation
- 6.4.8 Mavenir
- 6.4.9 Microsoft (Affirmed Networks)
- 6.4.10 Athonet (HPE)
- 6.4.11 Telrad Networks
- 6.4.12 Core Network Dynamics
- 6.4.13 VMware
- 6.4.14 Juniper Networks
- 6.4.15 Red Hat (IBM)
- 6.4.16 Intel
- 6.4.17 Hewlett Packard Enterprise
- 6.4.18 Casa Systems
- 6.4.19 Parallel Wireless
- 6.4.20 Druid Software
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment









