 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1842451
微生物鑑定:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Microbial Identification - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
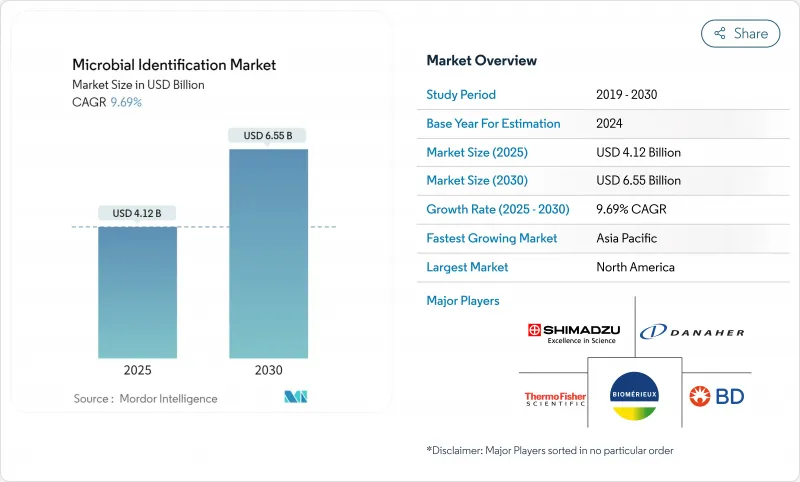
預計微生物鑑定市場在 2025 年的價值將達到 41.2 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 65.5 億美元,複合年成長率為 9.69%。
從基於培養的檢測方法向分子平台的轉變、抗菌素抗藥性監測的加強以及對快速週轉的期望是維持發展勢頭的關鍵因素。供應商正在擴展其技術組合,監管機構正在明確核准途徑,醫療保健系統正在投資即時數據整合。同時,人員短缺和高資本要求阻礙了資源受限環境的採用。隨著人工智慧工具擴展病原體庫以及新興經濟體食品安全法規的收緊,長期成長前景依然強勁。
全球微生物鑑定市場趨勢與洞察
MALDI-TOF MS 在常規診斷中的快速應用
使用每小時最多可處理 600 個樣本的高通量 MALDI-TOF 平台,實驗室現在可以在幾分鐘內(而非幾小時)完成物種級別的鑑定,並以更低的試劑成本獲得與 16S rRNA 測序精度相當的結果。憑藉涵蓋 4,300 多個物種的擴展參考資料資料庫,同一儀器可以支援食品、藥品和臨床工作流程。 2025 年 6 月,美國食品藥物管理局將這些系統歸類為具有特殊控制措施的 II 類系統,為製造商提供更清晰、更快捷的清關流程,同時保持安全標準。
抗菌素抗藥性監測計畫的成長
美國每年有超過280萬人感染抗藥性細菌,3.5萬人死亡,全基因組定序已納入監測網路。中國國家CHINET計畫報告稱,到2021年,分離出的腸桿菌菌株中10%對卡巴培南類抗生素抗藥性,這凸顯了全球對快速鑑定細菌的壓力。及時的細菌分析可以幫助藥師制定有效的治療方案,並減少住院時間。
昂貴的設備和維護成本
先進的MALDI-TOF系統資本支出超過20萬美元,服務合約每年使購買價格增加10-15%,限制了中型醫院的採用。 2024年通過的新《臨床實驗室改進法案》績效目標要求更嚴格的西格瑪指標,這可能會迫使小型實驗室提前升級或更換設備。
其他促進因素和限制因素分析
- 新興國家食品安全法規日益加強
- 人工智慧驅動的頻譜庫整合
- 熟練質譜技術人員短缺
細分分析
由於實驗室每次檢測都需要大量試劑和培養基,到2024年,耗材將佔總收入的47.15%,這將使微生物鑑定市場在經常性現金流方面保持韌性。軟體和服務雖然規模較小,但隨著實驗室升級到可自動進行資料移動和分析的雲端實驗室資訊系統,其複合年成長率達到11.78%,成為成長最快的細分市場。融合機器人技術和人工智慧的下一代「暗實驗室」展示了軟體層面如何在提高吞吐量的同時緩解勞動力短缺。
這一轉變也凸顯了分析儀錶板向訂閱授權模式的廣泛趨勢,這將為供應商提供可預測的利潤,並為用戶帶來快速的投資回報。隨著品管法規的收緊,能夠即時記錄儀器性能並標記偏差的雲端託管平台正變得越來越重要。預計到2030年,這類軟體的採用率將維持兩位數的成長,從而鞏固數位化流程作為整個微生物鑑定市場核心競爭優勢的地位。
由於無與倫比的快速結果獲取速度、低廉的單次檢測成本以及不斷擴展的生物庫,MALDI-TOF MS 將在 2024 年保持 57.50% 的收入佔有率。儘管 MALDI-TOF 平台的微生物鑑定市場規模仍在擴大,但隨著北美和歐洲的採用率不斷提高,其成長速度正在放緩。相較之下,隨著多重檢測板和照護現場模式在基層醫療診所的普及,PCR 和即時PCR將以 12.73% 的複合年成長率成為成長最快的技術。 2024 年,四款領先的綜合 PCR 分析儀獲得 FDA 批准,彰顯了監管的強勁勢頭。
混合工作流程正在興起,實驗室最初採用MALDI-TOF進行篩檢,然後轉向PCR和抗藥性基因定序,兼顧廣度和深度。跨平台資料融合正在催生新的耗材和服務組合,使製造商能夠保護市場佔有率,同時利用互補分子檢測帶來的收入成長。
區域分析
2024年,北美仍將是最大的收入貢獻地區,佔全球整體的39.56%。這得益於其資金充足的醫療保健體系、可報銷的快速檢測費用以及強大的抗菌藥物抗藥性監測津貼。美國各地的實驗室正在利用美國疾病管制與預防中心(CDC)的抗菌藥物抗藥性實驗室網路,並採用聯網識別平台,將即時數據輸入國家資訊中心。加拿大也面臨類似的發展趨勢,但面臨技術人員短缺的問題,導致較小州的設備採用速度放緩。
亞太地區預計將以11.45%的複合年成長率成長,這得益於中國和印度公立醫院的擴張、東協計劃帶來的品質標準協調,以及蓬勃發展的區域生物製造基地。 CHINET計畫的多中心資料集展現了該地區資料的成熟度,以及由此帶來的生物分析在指南抗生素處方方面的加速發展。各國政府也正在為地方疾病管制中心的設備採購提供補貼,以擴大農村地區的藥物可近性。
歐洲保持了溫和成長,因為嚴格的體外診斷監管期限促使實驗室提前檢驗平台,從而確保了對相容套件的穩定需求。英國的ESPAUR報告指出,自2019年以來,抗菌藥物抗藥性負擔增加了3.5%,因此將快速識別列入了政策議程。雖然英國脫歐導致的海關變化可能導致供應鏈延遲,但歐洲大陸的採購框架在很大程度上保護了最終用戶免受短缺的影響。
中東和非洲地區尚處於採用的早期階段,但受益於海灣國家對三級醫療機構和捐助者資助的水病原體計劃的投資。隨著巴西和墨西哥與主要貿易夥伴協調出口要求並擴大農業實驗室的可近性,拉丁美洲的食品安全檢測量正在增加。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場狀況
- 市場概況
- 市場促進因素
- MALDI-TOF MS 在常規診斷中的快速應用
- 抗菌素抗藥性(AMR)監測計畫的成長
- 新興國家食品安全法規日益加強
- 人工智慧頻譜庫整合(漏報)
- 分散式 POCT 微生物辨識系統的擴展(報告不足)
- 市場限制
- 設備和維護成本高
- 熟練質譜儀技術人員短缺
- 環境分離株缺乏標準化(漏報)
- 雲端基礎的身份平台中未被充分通報的網路安全風險
- 價值/供應鏈分析
- 監管狀況
- 技術展望
- 五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章市場規模及成長預測
- 按產品/服務
- 裝置
- 耗材
- 軟體和服務
- 依技術
- MALDI-TOF MS
- PCR和即時PCR
- 定序(NGS、Sanger)
- 其他(生物化學、顯微鏡等)
- 按最終用戶
- 醫院和臨床實驗室
- 製藥和生物技術公司
- 食品飲料檢驗實驗室
- 環境和工業測試實驗室
- 按用途
- 臨床診斷
- 製藥製造品質控制
- 食品安全/品質
- 環境監測
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 其他歐洲國家
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 韓國
- 澳洲
- 其他亞太地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美
- 中東和非洲
- GCC
- 南非
- 其他中東和非洲地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭態勢
- 市場集中度
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- bioMerieux SA
- Bruker Corporation
- Becton, Dickinson and Company
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- Danaher Corporation(Beckman Coulter)
- Shimadzu Corporation
- Charles River Laboratories
- Biolog Inc.
- Qiagen NV
- Merck KGaA(MilliporeSigma)
- Liofilchem Srl
- bioNote Inc.
- MIDI Labs
- Eppendorf AG
- Hologic Inc.
- Roche Diagnostics
- Siemens Healthineers
- Revvity(PerkinElmer)
- Abbott Laboratories
- Agilent Technologies
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The microbial identification market was valued at USD 4.12 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 6.55 billion by 2030, advancing at a 9.69% CAGR.

The transition from culture-based assays to molecular platforms, intensified antimicrobial-resistance surveillance, and quicker turnaround expectations are the key forces sustaining momentum. Vendors are broadening technology portfolios, regulators are clarifying approval pathways, and healthcare systems are investing in real-time data integration. At the same time, staffing shortages and high capital requirements temper adoption in resource-constrained settings. Long-term growth prospects remain strong as artificial-intelligence tools extend pathogen libraries and as food-safety rules tighten across emerging economies.
Global Microbial Identification Market Trends and Insights
Rapid Adoption of MALDI-TOF MS in Routine Diagnostics
Laboratories now generate species-level identification within minutes rather than hours by using high-throughput MALDI-TOF platforms that process up to 600 samples per hour, matching the accuracy of 16S rRNA sequencing at lower reagent cost. Expanded reference databases covering more than 4,300 species enable the same instrument to support food, pharmaceutical, and clinical workflows. The United States Food and Drug Administration placed these systems in Class II with special controls in June 2025, giving manufacturers a clearer, faster clearance route while preserving safety standards .
Growth of Antimicrobial-Resistance Surveillance Programs
More than 2.8 million AMR infections occurred annually in the United States, resulting in 35,000 deaths, which prompted whole-genome sequencing adoption across surveillance networks. China's national CHINET program reported carbapenem resistance in 10% of Enterobacter isolates by 2021, highlighting convergent global pressure for rapid identification. Timely organism profiling helps pharmacists tailor effective therapy and shorten hospital stays.
High Instrument and Maintenance Costs
Capital expenditure for an advanced MALDI-TOF system can exceed USD 200,000, while service contracts add 10-15% of purchase price each year, restricting uptake in mid-tier hospitals. New Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments performance goals adopted in 2024 require tighter sigma metrics, which may oblige smaller labs to upgrade or replace equipment sooner than planned.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rising Food-Safety Regulations in Emerging Economies
- Integration of AI-Powered Spectral Libraries
- Shortage of Skilled Mass-Spectrometry Technicians
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Consumables generated 47.15% of 2024 revenues as labs relied on high-volume reagents and media needed for every run, giving the microbial identification market recurring cash flow resilience. Software and services, though smaller, are growing the fastest at 11.78% CAGR as laboratories upgrade to cloud laboratory-information systems that automate data movement and analytics. Next-generation "dark labs" showcasing robotics and AI illustrate how software layers mitigate staffing gaps while boosting throughput .
The shift also highlights a broader move toward subscription licensing for analytics dashboards, offering predictable margins to vendors and quicker payback for users. As quality-control regulations tighten, cloud-hosted platforms that log instrument performance and flag deviations in real time are becoming critical. This software uptake is expected to maintain double-digit growth through 2030, cementing digital processes as a core competitive differentiator across the microbial identification market.
MALDI-TOF MS retained a 57.50% revenue share in 2024 on the strength of unmatched speed-to-result, low per-test cost, and a continuously expanding organism library. The microbial identification market size for MALDI-TOF platforms is still expanding, yet growth is moderating as penetration rises in North America and Europe. PCR and real-time PCR, by contrast, will post the sharpest 12.73% CAGR through 2030 as multiplex panels and point-of-care formats reach primary-care clinics. Four separate FDA clearances for a flagship syndromic PCR analyzer in 2024 illustrate regulatory momentum.
Hybrid workflows are emerging in which laboratories first screen with MALDI-TOF, then reflex to PCR or sequencing for resistance genes, combining breadth with depth. Cross-platform data convergence is spurring new consumable and service bundles, allowing manufacturers to defend share while tapping incremental revenue from complementary molecular assays.
The Microbial Identification Market Report Segments by Products and Services (Instruments, Consumables and More), by Technology (MALDI-TOF, MSPCR & Real-Time and More ), by End User (Hospitals & Clinical Laboratories and More), by Application (Clinical Diagnostics, Pharmaceutical Manufacturing QC and More) and Geography (North America and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America remained the largest revenue contributor in 2024, claiming 39.56% of global spend, reflecting well-funded healthcare systems, reimbursed rapid tests, and robust AMR surveillance grants. Laboratories across the United States leverage the CDC's Antimicrobial Resistance Laboratory Network to adopt connected identification platforms that feed real-time data into national dashboards. Canada follows similar trajectories but faces greater technician shortages, delaying instrument rollouts in smaller provinces.
Asia-Pacific, forecast to rise at 11.45% CAGR, is propelled by public hospital expansion in China and India, harmonized quality standards under ASEAN initiatives, and a vibrant local biomanufacturing base. The CHINET program's multicenter datasets illustrate the region's data maturity and the resulting push for faster organism profiling to guide antibiotic formularies. Governments are also subsidizing instrument purchases for provincial disease-control centers, widening rural access.
Europe maintains moderate growth as stringent In-Vitro Diagnostic Regulation deadlines drive labs to validate platforms earlier than scheduled, ensuring steady demand for compliant kits. The United Kingdom's ESPAUR report cites a 3.5% rise in AMR burden since 2019, keeping rapid identification on policy agendas. Brexit customs changes create occasional supply chain delays, yet continental procurement frameworks largely shield end users from shortages.
The Middle East and Africa region is at an earlier adoption stage but benefits from Gulf state investment in tertiary care facilities and from donor-funded water-pathogen projects. Latin America sees rising food-safety testing volumes as Brazil and Mexico align export requirements with major trade partners, boosting uptake among agro-industry labs.
- bioMerieux
- Bruker
- Beckton Dickinson
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Danaher
- Shimadzu
- Charles River
- Biolog
- QIAGEN
- Merck KGaA (MilliporeSigma)
- Liofilchem Srl
- bioNote Inc.
- MIDI Labs
- Eppendorf
- Hologic
- Roche
- Siemens Healthineers
- Revvity (PerkinElmer)
- Abbott Laboratories
- Agilent Technologies
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rapid adoption of MALDI-TOF MS in routine diagnostics
- 4.2.2 Growth of antimicrobial-resistance (AMR) surveillance programs
- 4.2.3 Rising food-safety regulations in emerging economies
- 4.2.4 Integration of AI-powered spectral libraries (under-reported)
- 4.2.5 Expansion of decentralized POCT microbial ID systems (under-reported)
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High instrument & maintenance costs
- 4.3.2 Shortage of skilled mass-spectrometry technicians
- 4.3.3 Lack of standardization for environmental isolates (under-reported)
- 4.3.4 Cyber-security risks in cloud-based ID platforms (under-reported)
- 4.4 Value/ Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Product & Service
- 5.1.1 Instruments
- 5.1.2 Consumables
- 5.1.3 Software & Services
- 5.2 By Technology
- 5.2.1 MALDI-TOF MS
- 5.2.2 PCR & Real-time PCR
- 5.2.3 Sequencing (NGS, Sanger)
- 5.2.4 Others (Biochemical, Microscopy, etc.)
- 5.3 By End-User
- 5.3.1 Hospitals & Clinical Laboratories
- 5.3.2 Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
- 5.3.3 Food & Beverage Testing Labs
- 5.3.4 Environmental & Industrial Labs
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Clinical Diagnostics
- 5.4.2 Pharmaceutical Manufacturing QC
- 5.4.3 Food Safety & Quality
- 5.4.4 Environmental Monitoring
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 India
- 5.5.3.3 Japan
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 Australia
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 GCC
- 5.5.5.2 South Africa
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products & Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 bioMerieux SA
- 6.3.2 Bruker Corporation
- 6.3.3 Becton, Dickinson and Company
- 6.3.4 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- 6.3.5 Danaher Corporation (Beckman Coulter)
- 6.3.6 Shimadzu Corporation
- 6.3.7 Charles River Laboratories
- 6.3.8 Biolog Inc.
- 6.3.9 Qiagen N.V.
- 6.3.10 Merck KGaA (MilliporeSigma)
- 6.3.11 Liofilchem Srl
- 6.3.12 bioNote Inc.
- 6.3.13 MIDI Labs
- 6.3.14 Eppendorf AG
- 6.3.15 Hologic Inc.
- 6.3.16 Roche Diagnostics
- 6.3.17 Siemens Healthineers
- 6.3.18 Revvity (PerkinElmer)
- 6.3.19 Abbott Laboratories
- 6.3.20 Agilent Technologies
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment










