 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1687453
室內農業:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢和成長預測(2025-2030)Indoor Farming - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
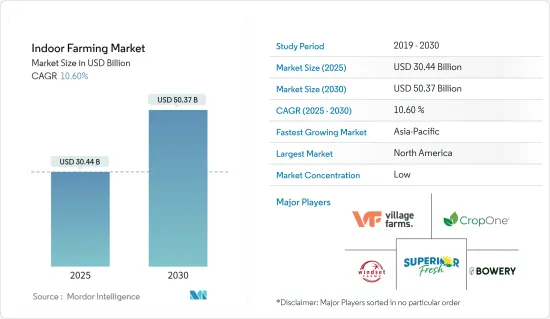
室內農業市場規模預計在 2025 年為 304.4 億美元,預計到 2030 年將達到 503.7 億美元,預測期內(2025-2030 年)的複合年成長率為 10.6%。
主要亮點
- 日益增強的健康意識和無殘留食品的消費為室內農業等先進技術的使用鋪平了道路。人們在自家小規模種植所需的作物,並透過獲取無蟲害食品來獲得更高的產量。
- 在各種種植類型中,土壤種植佔據市場主導地位。與傳統農業相比,它能夠改善植物的收穫週期,從而推動市場成長。根據設施類型,玻璃溫室和聚乙烯溫室佔據了市場佔有率,而室內深水栽培系統預計在預測期內將以最高的複合年成長率成長。中東對永續糧食生產的需求日益成長,這可以透過在農業中採用室內垂直農業技術來實現。
- 2021年,北美佔據了最大的市場佔有率。美國在該地區貢獻了最大的佔有率,其次是加拿大和墨西哥。室內農業越來越受歡迎的主要原因之一是它能夠利用更少的資源來實現更高的產量。例如,根據美國農業部 (USDA) 的數據,垂直農場種植的生菜的平均產量是傳統生菜的兩倍。受政府政策推動,亞太地區的室內農業市場正在快速成長。
室內農業市場趨勢
氣候條件對生產的影響
歐盟委員會預計,到2030年,歐盟農業用地面積可能從2017年的1.76億公頃下降到1.72億公頃,歐盟可耕地面積也將從2017年的1.065億公頃下降到1.04億公頃。
根據世界銀行統計,南亞地區耕地佔比將從2017年的43.2%下降到2020年的43%。因此,新興南亞國家耕地面積減少和污染加劇預計將增加對替代種植的需求,包括室內種植。
人均耕地面積正穩定減少,解決方法在於提高生產力。因此,需要產量作物來解決農地短缺問題,同時又不影響產量,而這可以透過室內農業來實現。農業用地減少的主要原因是各個開發中國家的都市化、土地向道路、工業和住宅等非農業用途的轉變以及土壤侵蝕和污染。中國約有3.34億英畝可耕地,其中約3,700萬英畝未開墾,人口成長帶來重大威脅。增加耕地面積的另一種方法是提高耕地的產量和生產力。這些包括產量品種、肥料和農藥管理、機械化、灌溉管理以及採用室內農業等新農業技術。
隨著全球可耕地面積的減少,室內農業可以透過使用水耕和人工照明為植物提供只有在戶外種植才能獲得的營養和光照來幫助提高產量。因此,預測期內對室內農業設備的需求可能會增加。
北美佔據市場主導地位
2021 年,北美佔據了全球室內農業市場佔有率。高效 LED 照明和加強的室內控制正在推動美國種植者採用大規模室內農業。預計此類做法將減少約 50% 的能源照明成本,並減少受控環境農業的碳足跡。根據美國農業部 (USDA) 的數據,垂直農業種植的生菜平均產量是傳統生菜的兩倍。目前,溫室種植是美國室內農業的主導。隨著紐約、芝加哥和密爾瓦基等都市區人口開始居住,廢棄的倉庫、廢棄的高層建築被維修以適應室內農業,增加了新鮮食品的產量。在美國,溫室番茄的需求正在推動水耕市場的需求。室內農業是美國發展最快的產業之一。
根據聯合國糧食及農業組織統計,墨西哥的旱地面積約為1.015億公頃,增加了對室內農業的需求。加拿大也正經歷成長趨勢,並且是全球水耕番茄出口的主要貢獻者。該地區水耕和氣氣耕系統的成長正在推動整個室內農業市場的發展,這主要是因為人們越來越注重採用創新和高效的技術來提高產量。北美國家在室內種植各種各樣的作物,包括葉菜類蔬菜、草本植物、水果、微型菜苗和花卉。室內垂直農業系統提供有機食品,北美消費者對不含殺蟲劑和除草劑的食品的需求日益成長,這是室內垂直農業的主要推動力。
室內農業產業概況
室內農業市場高度分散,主要企業佔有較小佔有率,其他較小參與者則佔有較大佔有率。
市場高度分散,主要收益公司如 Village Farms International Inc.、Superior Fresh Inc.、Crop One Holdings Inc.、Windest Farms Inc. 和 Bowery Inc. 佔據了部分市場佔有率。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 研究範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場動態
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 市場限制
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 購買者和消費者的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭強度
第5章市場區隔
- 栽培系統
- 水耕栽培
- 水耕
- 水產養殖
- 土壤基
- 混合
- 設施類型
- 玻璃或聚乙烯溫室
- 室內垂直農場
- 貨櫃農場
- 室內深水養殖系統
- 其他設施類型
- 作物類型
- 水果和蔬菜
- 綠葉
- 萵苣
- 羽衣甘藍
- 菠菜
- 其他葉菜類
- 番茄
- 草莓
- 茄子
- 其他水果和蔬菜
- 香草和微型菜苗
- 羅勒
- 草藥
- 香艾菊
- 小麥草
- 其他香草和微型菜苗
- 花朵
- 多年生植物
- 年度的
- 室內植物
- 其他花卉
- 其他作物
- 水果和蔬菜
- 地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地區
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 俄羅斯
- 西班牙
- 義大利
- 其他歐洲國家
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 澳洲
- 新加坡
- 韓國
- 其他亞太地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 南美洲其他地區
- 非洲
- 南非
- 其他非洲國家
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭格局
- 最受歡迎的策略
- 市場佔有率分析
- 公司簡介
- AeroFarms
- Bright Farms Inc.
- Bowery Inc.
- Crop One Holdings
- Metropolis Farms Inc.
- Garden Fresh Farms
- Village Farms International Inc.
- Green Sense Farms LLC
- Sky Greens(Sky Urban Solutions)
- Superior Fresh Farms
- Windset Farms
- Gotham Greens
第7章 市場機會與未來趨勢
The Indoor Farming Market size is estimated at USD 30.44 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 50.37 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 10.6% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Key Highlights
- An increase in health consciousness and consumption of residue-free food has paved the way for the usage of advanced techniques, like indoor farming. People are growing the necessary crops in their own houses on a small scale to have food free from pests, resulting in a higher yield.
- Among the various growing types, soil-based indoor farming dominates the market. Its ability to enhance the harvesting cycle of plants, when compared to traditional farming, is driving its market growth. By facility type, glass or poly greenhouses occupy a larger market share, while the indoor deep-water culture system is anticipated to witness the highest CAGR during the forecast period. There is an increase in the demand for sustainable food production in the Middle East, which is achievable by adopting indoor vertical farming technologies in agriculture.
- North America accounted for the largest market share in 2021. The US is a major contributor to the region's share, followed by Canada and Mexico. One of the primary reasons indoor farming has been gaining significant traction is because of its ability to produce more with fewer resources. For example, as per the US Department of Agriculture (USDA), the average yield of conventional lettuce farming doubled twofold when cultivated through vertical farming. The indoor farming market in the Asia-Pacific region is growing rapidly, with the industry benefiting from government policies.
Indoor Farming Market Trends
Effect of Climate Conditions on Production
According to the European Commission, the amount of land used for agricultural purposes may fall to 172 million ha in 2030 from the current level of 176 million ha in 2017, with a corresponding decline in the level of EU arable land, from 106.5 million hectares in 2017 to 104 million hectares in 2030.
According to the World Bank statistics, South Asia declined the arable land percentage of the total land from 43.2% in 2017 to 43% in 2020. Thus, a reduction in arable land and an increase in pollution in the developing countries of Southern Asia are expected to increase the demand for alternative cultivation, including indoor farming.
Due to the continuous decline in the per capita availability of farmland, the practice of increasing productivity is a way out. Thus, there is a need for high-yielding crops, which can solve the problem of farmland scarcity without compromising production volumes, which can be attained through indoor farming. The decline in agricultural land has been mainly due to diversion for non-agricultural purposes, such as urbanization, roads, industries, and housing, and soil erosion and pollution in various developing countries. In China, there are approximately 334 million acres of arable land, of which around 37 million acres are non-cultivable, and the growing population poses a major threat. The alternative to creating more arable land is to enhance the yield and productivity of cultivated land. These technologies include high-yielding varieties, the management of fertilizers and pesticides, mechanization, irrigation management, and employing new farming techniques, such as indoor farming.
As the cultivable land is decreasing globally, indoor farming may help increase production by using hydroponics and artificial lighting to provide plants with nutrients and light, as they would only receive when grown outdoors. Thus, the demand for equipment for indoor farming may increase during the forecast period.
North America Dominates the Market
North America accounted for the highest global indoor farming market share in 2021. With the help of high-efficiency LED lights and enhanced indoor management practices, US growers have adopted large-scale indoor farming. Such practices are expected to reduce energy lighting costs by about 50%, thus, reducing the carbon footprint of controlled environment agriculture. As per the US Department of Agriculture (USDA), the average yield of conventional lettuce farming doubled twofold when cultivated through vertical farming. Currently, the indoor farming industry in the US is predominantly dominated by greenhouse crop production. The onset of urban population dwellings across cities, such as New York, Chicago, and Milwaukee, has propelled the environment for indoor farming with activities such as revamping derailed vacant warehouses, derelict buildings, and high rises, which has, in turn, led to an increase in the production of fresh grown foods altogether. The demand for greenhouse tomatoes in the United States is driving the market demand for hydroponic operations. Indoor farming is one of the fastest-growing industries in the United States.
According to the UN Food and Agriculture Organization, drylands in Mexico occupy approximately 101.5 million hectares of land, thereby boosting the need for indoor farming practices. Canada has also seen a positive growth trend, contributing significantly to the world exports of hydroponically grown tomatoes. The region's growth of hydroponics and aeroponics systems is driving the overall indoor farming market, mainly due to the increasing focus on adopting innovative and efficient technologies to improve yields. A wide variety of crops, such as leafy vegetables, herbs, fruits, micro greens, and flowers, are grown through indoor farming in the countries of North America. Indoor vertical farming systems have provided organic food, which has become the major driving force for indoor vertical farming along with the increasing demand for pesticide- and herbicide-free food among the consumers of North America.
Indoor Farming Industry Overview
The market for indoor farming is highly fragmented, with the top players accounting for a minor share and the other small companies capturing a major share in the market.
The market is highly fragmented, with major revenue-generating companies, which are Village Farms International Inc., Superior Fresh, Crop One Holdings, Windest Farms, and Bowery Inc, among others, cornering some parts of the market share.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Growing System
- 5.1.1 Aeroponics
- 5.1.2 Hydroponics
- 5.1.3 Aquaponics
- 5.1.4 Soil-based
- 5.1.5 Hybrid
- 5.2 Facility Type
- 5.2.1 Glass or Poly Greenhouses
- 5.2.2 Indoor Vertical Farms
- 5.2.3 Container Farms
- 5.2.4 Indoor Deep Water Culture Systems
- 5.2.5 Other Facility Types
- 5.3 Crop Type
- 5.3.1 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.3.1.1 Leafy Vegetables
- 5.3.1.1.1 Lettuce
- 5.3.1.1.2 Kale
- 5.3.1.1.3 Spinach
- 5.3.1.1.4 Other Leafy Vegetables
- 5.3.1.2 Tomato
- 5.3.1.3 Strawberry
- 5.3.1.4 Eggplant
- 5.3.1.5 Other Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.3.2 Herbs and Microgreens
- 5.3.2.1 Basil
- 5.3.2.2 Herbs
- 5.3.2.3 Tarragon
- 5.3.2.4 Wheatgrass
- 5.3.2.5 Other Herbs and Microgreens
- 5.3.3 Flowers and Ornamentals
- 5.3.3.1 Perennials
- 5.3.3.2 Annuals
- 5.3.3.3 Ornamentals
- 5.3.3.4 Other Flowers and Ornamentals
- 5.3.4 Other Crop Types
- 5.3.1 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.4 Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 US
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Germany
- 5.4.2.2 UK
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Russia
- 5.4.2.5 Spain
- 5.4.2.6 Italy
- 5.4.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 Japan
- 5.4.3.3 India
- 5.4.3.4 Australia
- 5.4.3.5 Singapore
- 5.4.3.6 South Korea
- 5.4.3.7 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Africa
- 5.4.5.1 South Africa
- 5.4.5.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Most Adopted Strategies
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 AeroFarms
- 6.3.2 Bright Farms Inc.
- 6.3.3 Bowery Inc.
- 6.3.4 Crop One Holdings
- 6.3.5 Metropolis Farms Inc.
- 6.3.6 Garden Fresh Farms
- 6.3.7 Village Farms International Inc.
- 6.3.8 Green Sense Farms LLC
- 6.3.9 Sky Greens (Sky Urban Solutions)
- 6.3.10 Superior Fresh Farms
- 6.3.11 Windset Farms
- 6.3.12 Gotham Greens










