 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1641921
網路切片:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2025-2030 年)Network Slicing - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
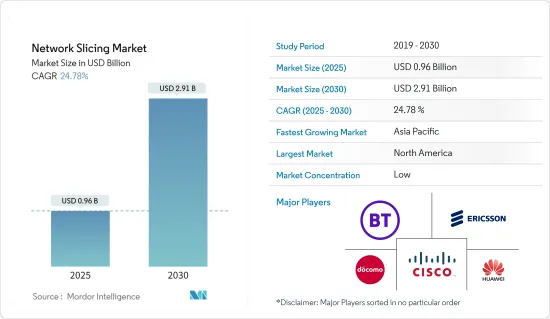
預計 2025 年網路切片市場規模為 9.6 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 29.1 億美元,預測期內(2025-2030 年)的複合年成長率為 24.78%。
據 GSMA 稱,網路切片與其他推動因素和功能相結合,將幫助營運商在 2025 年前獲得價值 3,000 億美元的商機。
關鍵亮點
- 5G網路和網路切片的結合將使企業客戶能夠享受根據其特定業務需求量身定做的連接和資料處理,並遵守與行動通訊業者商定的服務等級協議(SLA)。可自訂的網路功能包括資料速度、延遲、品質、安全性和服務。隨著高速網路覆蓋需求的增加,這將為市場開闢新的途徑。
- 然而,由於頻寬有限和缺乏基礎設施,5G 在新興國家難以起飛。例如,印度兩年前啟動的智慧城市計畫一直未能取得任何重大進展。除了面臨眾多地方監管和結構性挑戰外,實現智慧城市的願景還需要增加頻譜的可用性或確保足夠的頻譜。
- 物聯網的廣泛應用以及連接各種設備、系統和服務的機器對機器(M2M)通訊網路的不斷改進正在改變各個行業。 5G 網路切片將實現的眾多使用案例之一就是物聯網。高功率、低延遲應用(如行動視訊監控)和低功耗、低延遲、遠距物聯網應用(如智慧城市和智慧工廠)是兩類物聯網應用需求。為了滿足日益成長的物聯網應用的需求(其特點是大規模基於機器的通訊和關鍵任務應用),5G技術的演進預計將加速。
- 然而,網路切片的安全性是CIO們關注的重點,因為它可能會對企業和服務供應商造成重大損失。 SDN、NFV和雲端原生架構都被用來建構新的網路基礎架構。網路功能分佈在本地、區域和中央資料中心,並與支援基礎設施分離。雲端化5G網路中大部分網路服務將透過公有雲和私有雲端基礎設施來實現。
- 疫情極大地刺激了對寬頻服務的需求,行動網路和遠端存取服務正在擴展到零售、電訊、IT 和醫療保健等許多行業。此外,隨著世界各地的企業開始重新開業,通訊服務供應商正在重新關注 5G 部署並加強網路切片。此外,COVID-19 增加了人們對機器人、遠端醫療、遠端教育和遠距辦公等 5G使用案例的興趣,所有這些都為網路切片市場做出了貢獻。
網路切片市場趨勢
醫療領域佔市場主導地位
- 數以百萬計的醫療設備,從家用臨床診斷設備到價值數百萬美元的醫院影像系統,越來越需要連接性作為關鍵的增值功能。愛立信預測,到 2026 年,通訊業者利用 5G 轉型醫療保健將帶來 760 億美元的商機。
- 5G 將在醫療保健領域實現許多新方法,包括影像處理、診斷和資料分析。例如,醫院可以透過客製化的5G網路切片使用虛擬實境來安排遠端機器人手術,使外科醫生看起來就像就在病人旁邊一樣。
- 它還可以用於醫療資料管理,例如管理電子健康記錄和引入救護車無人機。醫療設備製造商可以利用5G即時監控產品功能,並提供預防性和預測性維護協助,以防止設備缺陷造成的負面後果。醫療保健領域的某些關鍵應用需要極低的延遲和高度一致的頻寬。
- 歐洲電信網路營運商協會預測,到2025年醫療保健領域的物聯網連接數量將達到103.4億。這是透過醫療物聯網 (IoMT) 實現的,醫療物聯網是一個由相互連接的醫療設備、軟體程式和醫療系統組成的網路,它使用邊緣運算和 5G 無線技術在更靠近源頭的地方處理資料。
- 根據歐洲通訊網路營運商協會(ETNO)的調查,未來幾年活躍的物聯網醫療連接數量預計將增加。 2016年連線數為87萬個,預計到2025年將達到1,034萬個連線。
亞太地區將經歷最高成長
- 預計中國、印度和日本等亞太新興經濟體的網路切片產業將快速擴張。這些國家一貫鼓勵和支持工業和技術進步。此外,這些國家擁有先進的技術基礎設施,正在推動各個業務領域採用網路切片解決方案。雲端基礎的解決方案以及物聯網、巨量資料分析和行動性等最尖端科技的日益普及正在推動亞太網路產業的發展。亞太地區是最大的連網型設備市場之一。
- 由於網路基礎設施的發展和 5G 成為最重要的通訊趨勢,預計亞太地區將以最快的速度成長。據GSMA稱,亞太地區行動電話營運商計劃在2022年至2025年期間投資2,270億美元部署5G。這筆金額龐大,很可能會產生重大影響。這些新網路不僅能實現創新的新型消費者服務,還將推動經濟成長並幫助轉型商業和製造業。
- 在亞太地區努力從疫情中復甦之際,連結性對於該地區的重組和增強其抵禦未來衝擊的能力至關重要。 5G網路、雲端服務、邊緣運算、人工智慧、巨量資料和物聯網對於充分發揮後疫情時代數位經濟的潛力都至關重要。
- 5G 的網路切片功能將使通訊業者能夠為關鍵服務供應商提供自己的私有 5G 網路,並提供安全、即時的雲端連接,滿足不斷變化的基礎設施需求並簡化營運。
- 5G 網路切片與 i.Private 網路、多接取邊緣運算(MEC) 等一起添加到目前的技術堆疊中預計將是漸進且有益的。隨著 5G 進入大眾市場階段,行動通訊業者的收益可能性開始透過更具適應性、即時的營運支援系統和業務支援系統 (OSS/BSS) 功能實現。
網路切片產業概況
網路切片市場是分散的,參與企業合作提供所需的可用性、指定的延遲、資料速率和安全性。網路切片管理解決方案還能幫助通訊業者實現網路切片生命週期管理,為5G做好準備。主要參與企業包括愛立信公司、華為科技公司、思科系統公司和英國電信集團。
- 2022 年11 月- 為了在無線WAN 架構中建立安全性、SD-WAN 和零信任,Cradlepoint 推出了一種新的針對5G 最佳化的SD-WAN 解決方案,該解決方案“支援網路切片”,作為其今年稍早宣布的NetCloud Exchange 解決方案的一部分。使用 NetCloud Exchange,組織現在可以建立「與 5G 獨立 (SA) 網路中定義的切片實例一致的大量數據機 WAN 介面」。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3 個月的分析師支持
目錄
第 1 章 簡介
- 調查結果
- 調查前提
- 研究範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場動態
- 市場概況
- 採用市場促進因素與限制因素
- 市場促進因素
- 對高速、大容量網路的需求不斷成長,推動市場
- 市場限制
- 新興國家5G普及率低是市場成長的挑戰
- 產業吸引力-波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 購買者/消費者的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭強度
第5章 市場區隔
- 按應用
- 即時監控
- 網路功能虛擬
- 按服務
- 專業的
- 託管
- 按最終用戶產業
- 醫療
- 車
- 電能
- 航空
- 媒體與娛樂
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 歐洲
- 亞太地區
- 拉丁美洲
- 中東和非洲
第6章 競爭格局
- 公司簡介
- Ericsson Inc.
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- BT Group PLC
- NTT DOCOMO Inc.
- NEC Corporation
- ZTE Corporation
- CloudStreet Ltd(Nokia Networks)
- Mavenir Inc.
- Affirmed Networks Inc.
- Argela Technologies
- Aria Networks Ltd
第7章投資分析
第8章 市場機會與未來趨勢
The Network Slicing Market size is estimated at USD 0.96 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 2.91 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 24.78% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

According to GSMA, network slicing, in combination with other enablers and capabilities, will aid operators in addressing a revenue opportunity worth USD 300 billion by 2025.
Key Highlights
- 5G networks, in combination with network slicing, allow business customers to enjoy connectivity and data processing that are tailored to the specific business requirements and adhere to a Service Level Agreement (SLA) as agreed with the mobile operator. Customizable network capabilities include data speed, latency, quality, security, and services. Thus as the demand for high-speed network coverage is progressing, it will open new avenues for the market.
- However, 5G is struggling to keep pace in emerging economies due to low bandwidth and a lack of infrastructure. For instance, India's smart city initiative launched two years ago has struggled to make significant progress. Beyond the numerous local regulatory and structural challenges, there needs to be more spectrum or even the right spectrum bands available for the smart city vision to be realized.
- Various industries are being transformed by the widespread use of IoT and ongoing improvements in Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communication networks, which are connecting all different kinds of equipment, systems, and services. One of the many use cases that network slicing-enabled 5G will allow is the Internet of Things, which would provide communication between a significant number of sensors and linked devices. High-power, low-latency applications (such as mobile video surveillance) and low-power, low-latency, long-range IoT applications are two categories of IoT application requirements (smart cities and smart factories). To meet these needs for growing IoT applications, which are characterized as huge machine-type communication and mission-critical applications, the evolution of 5G Technology is anticipated to pick up speed.
- However, Network slicing security, which may cause significant losses for enterprises and service providers, is a major worry for CIOs. SDN, NFV, and cloud-native architecture have all been used to construct the new network infrastructure. Network functions are spread across local, regional, and central data centers and are decoupled from supporting infrastructure. The vast majority of network services in a 5G network based on the cloud are implemented through public and private cloud infrastructure.
- With the aid of expanding mobile networking and remote access services in a number of industries, including retail, telecom, IT, and healthcare, the pandemic has considerably driven demand for broadband services. Additionally, as businesses all around the world have begun to reopen, communications service providers are refocusing on 5G rollouts and stepping up their network-slicing efforts. Additionally, COVID-19 has increased interest in 5G use cases, including robotics, telemedicine, remote education, and remote offices, all contributing to the network-slicing market.
Network Slicing Market Trends
Healthcare Sector to Dominate the Market
- Millions of medical devices, from at-home clinical diagnostic equipment to hospital-based multimillion-dollar imaging systems, increasingly demand connectivity as a key value-added feature. Ericsson estimates a USD 76 billion revenue opportunity in 2026 for operators addressing healthcare transformation with 5G.
- It will enable many new approaches in the healthcare sector in terms of imaging, diagnosis, and data analytics. For instance, hospitals could arrange remote robotic surgeries, as if the surgeon is right next to the patient, using virtual reality via a customized 5G network slice.
- Also, it can be used in medical data management by maintaining electronic health records or introducing ambulance drones. Medical device makers can utilize 5G to monitor their products' functionality in real-time, providing proactive and predictive maintenance assistance and preventing negative outcomes brought on by faulty equipment. Certain crucial applications in healthcare demand extremely low latency and highly stable bandwidth.
- European Telecommunications Network Operator's Association forecasts that the number of IoT connections in healthcare will reach 10.34 billion by 2025. This is made feasible by the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), a network of interconnected medical equipment, software programs, and health systems that use edge computing and 5G wireless technology to process data close to the source.
- According to an ETNO-European Telecommunications Network Operators' Association survey, the number of IoT healthcare active connections was expected to increase through the years. It was at 0.87 million connections in 2016 and is expected to reach 10.34 million by 2025.
Asia-Pacific to Witness the Highest Growth
- Several developing economies in APAC, including China, India, and Japan, are anticipated to have rapid expansion in the network-slicing industry. These nations have consistently encouraged and supported the advancement of industry and technology. They also have a sophisticated technological infrastructure that is encouraging the adoption of network-slicing solutions in various business sectors. The increased use of cloud-based solutions, cutting-edge technologies like the IoT, big data analytics, and mobility are what is driving the network industry in APAC. One of the largest markets for connected devices is in APAC.
- APAC is expected to grow at the fastest rate owing to the development of network infrastructure and 5G being the biggest telecom trend. According to GSMA, the Asia Pacific area mobile operators plan to spend USD 227 billion between 2022 and 2025 on 5G deployments. That is a significant sum of money and will have a significant effect. In addition to enabling innovative new consumer services, these new networks are assisting in the transformation of business and manufacturing as well as promoting economic growth.
- Connectivity will be essential to rebuilding Asia-economies Pacific and making them more resilient to future shocks as the region attempts to recover from the pandemic. In order to fully realize the potential of a post-pandemic digital economy, 5G networks, cloud services, edge computing, artificial intelligence (AI), big data, and the Internet of Things will all be crucial.
- 5G's network slicing capabilities will allow telcos to offer critical service providers their own private 5G networks for secure and real-time connectivity to the cloud, helping to meet their ever-evolving infrastructure needs and improve operational efficiency.
- It is expected to increase and will profit from the addition of 5G network slicing to the current technology stack, i.e., together with private networks, Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC), etc. As 5G enters the mass-market phase, the monetization potential for mobile operators is beginning to take shape along with more adaptable and real-time Operations Support System and Business Support System (OSS/BSS) capabilities.
Network Slicing Industry Overview
The Network Slicing Market is fragmented, with players collaborating to provide the required availability, a specified latency, data rate, and security. Network slice management solutions can also help carriers implement network slice lifecycle management in the preparation of 5G. Some major players are Ericsson Inc., Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd, Cisco Systems Inc., and BT Group PLC.
- November 2022 - To include security, SD-WAN, and zero trust into a wireless WAN architecture, Cradlepoint unveiled a new "network slicing-ready" 5G-optimized SD-WAN as part of the company's NetCloud Exchange solution it unveiled earlier this year. Organizations can now construct "many modem WAN interfaces aligned to slice instances defined by 5G standalone (SA) networks" using NetCloud Exchange.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Deliverables
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
- 1.3 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Introduction to Market Drivers and Restraints
- 4.3 Market Drivers
- 4.3.1 Increasing Demand For High-speed And Large Network Coverage is Major Driving Force
- 4.4 Market Restraints
- 4.4.1 Low 5G Penetration in Emerging Economies is Challenging the Market Growth
- 4.5 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Force Analysis
- 4.5.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.5.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Application
- 5.1.1 Real-Time Surveillance
- 5.1.2 Network Function Virtualization
- 5.2 By Service
- 5.2.1 Professional
- 5.2.2 Managed
- 5.3 By End-user Industry
- 5.3.1 Healthcare
- 5.3.2 Automotive
- 5.3.3 Power & Energy
- 5.3.4 Aviation
- 5.3.5 Media & Entertainment
- 5.4 Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 Latin America
- 5.4.5 Middle East & Africa
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Company Profiles
- 6.1.1 Ericsson Inc.
- 6.1.2 Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
- 6.1.3 Cisco Systems Inc.
- 6.1.4 BT Group PLC
- 6.1.5 NTT DOCOMO Inc.
- 6.1.6 NEC Corporation
- 6.1.7 ZTE Corporation
- 6.1.8 CloudStreet Ltd (Nokia Networks)
- 6.1.9 Mavenir Inc.
- 6.1.10 Affirmed Networks Inc.
- 6.1.11 Argela Technologies
- 6.1.12 Aria Networks Ltd












