 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1892732
自動駕駛長途卡車市場機會、成長促進因素、產業趨勢分析及預測(2025-2034年)Autonomous Long-Haul Trucking Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
2024 年全球自動駕駛長途卡車市場價值 27 億美元,預計到 2034 年將以 32% 的複合年成長率成長至 426 億美元。
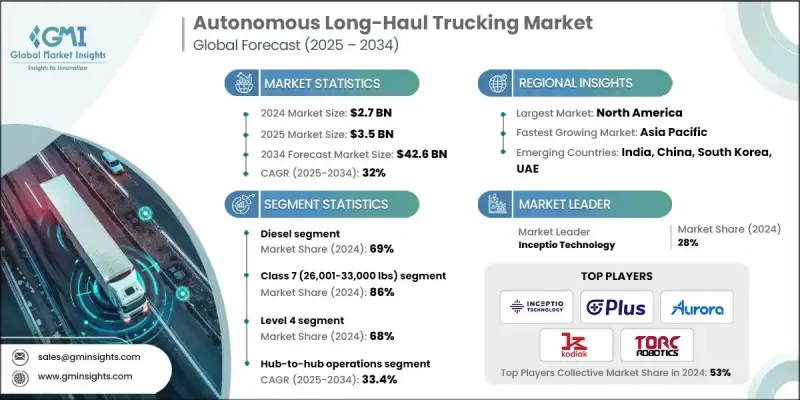
隨著L4級自動駕駛技術逐步投入商業應用,各大貨運網路正加速普及。人工智慧的進步、貨運量的成長以及持續存在的司機短缺問題,正推動自動駕駛卡車走向大規模部署。預計從2024年到2034年,市場規模將成長近20至25倍,主要得益於持續自動駕駛帶來的營運成本節省,最高可達40%。美國政府的監管支持也促進了市場發展,聯邦交通部門為安全部署自動化貨運業務提供了更清晰的路徑。多個州在自動駕駛技術研發方面發揮核心作用,強化了向長途自動駕駛運輸的轉型,並使物流公司能夠在長途運輸中更加依賴自動化系統。核心營運模式日益圍繞連接主要貨運樞紐展開,旨在提高效率、減少停機時間並最佳化長途運輸調度。這些因素共同表明,自動駕駛卡車正迅速融入國家供應鏈的各個環節。
| 市場範圍 | |
|---|---|
| 起始年份 | 2024 |
| 預測年份 | 2025-2034 |
| 起始值 | 27億美元 |
| 預測值 | 426億美元 |
| 複合年成長率 | 32% |
2024年,柴油動力總成市佔率達到69%,預計2025年至2034年將以32.2%的複合年成長率成長。柴油動力之所以持續領先,是因為它擁有成熟的基礎設施、高能量密度以及相對於新興替代能源更低的初始成本。與柴油平台整合的自動駕駛系統可以在無需車隊轉型使用陌生的推進技術的情況下,提高生產效率。儘管柴油動力仍然是長途運輸的首選,但加州和歐洲部分地區日益嚴格的排放法規給行業帶來了監管壓力,該行業必須應對這些壓力。
2024年,7級卡車市佔率達到86%,預計2025年至2034年間將以32.6%的複合年成長率成長。此重量等級涵蓋廣泛用於貨運、城市物流和工業收集服務的重型車輛。 7級卡車在自動駕駛應用領域保持領先地位,因為它們的運作模式與結構化的樞紐導向路線相契合。該細分市場受益於實用的載貨能力和更靈活的合規要求。不斷擴展的自動駕駛運輸網路、更廣泛的自動駕駛系統整合以及與原始設備製造商更深入的合作,都進一步推動了其成長。
美國自動駕駛長途卡車市場預計將在2025年至2034年間持續成長。由於強勁的貨運量、先進的高速公路自動化項目以及Aurora Innovation和Kodiak Robotics等公司不斷推出的創新技術,美國仍然是全球需求的最大貢獻者。全美各地的承運商和物流供應商都在投資自動化貨運技術,以提高可靠性、降低營運成本並改善關鍵樞紐之間的運輸效率。人工智慧驅動的工具,包括車隊分析、遠端支援功能和預測性服務,正成為該生態系統不可或缺的一部分。
目錄
第1章:方法論
第2章:執行概要
第3章:行業洞察
- 產業生態系分析
- 供應商格局
- 利潤率分析
- 成本結構
- 每個階段的價值增加
- 影響價值鏈的因素
- 中斷
- 產業影響因素
- 成長促進因素
- 卡車司機嚴重短缺
- 需要降低運輸成本
- 全天候不間斷營運
- 人工智慧、感測器和高速公路自動化技術的進步
- 擴大受控的樞紐間貨運網路
- 產業陷阱與挑戰
- 高昂的資本和技術成本
- 各地區的監管不確定性
- 市場機遇
- 為大型零售商和第三方物流公司提供自主貨運服務
- 與電動和氫燃料長途卡車的整合
- 遠端營運中心(ROC)和遠端駕駛服務
- 亞太地區的高成長市場
- 成長促進因素
- 成長潛力分析
- 監管環境
- 美國聯邦框架(NHTSA、FMCSA、DOT)
- 美國州級立法和許可(34個州+哥倫比亞特區)
- 聯合國歐洲經濟委員會工作小組29和GRVA國際協調
- 聯合國法規(R155 網路安全、R156 OTA、R157 ALKS)
- 4-5級系統的服務時間(HOS)影響
- 檢驗標準與CVSA強化型商用車檢驗計劃
- 資料記錄、隱私和ISMR報告要求
- 波特的分析
- PESTEL 分析
- 技術與創新格局
- 當前技術趨勢
- SAE 3-5級自動化能力
- 感測器融合架構(LiDAR、雷達、攝影機)
- 感知與規劃中的人工智慧與機器學習
- 冗餘和故障安全系統設計
- 新興技術
- V2X 通訊與連網車輛技術
- 高清地圖和定位
- 網路安全與OTA軟體更新管理
- 當前技術趨勢
- 定價分析
- 技術成本結構
- 車輛購置成本溢價
- 營運成本經濟性
- 旅行即服務 (TaaS) 定價模型與費率結構
- 成本削減路線圖(2024-2034)
- 生產統計
- 生產中心
- 消費中心
- 進出口
- 成本細分分析
- 總擁有成本 (TCO) 和經濟回報分析
- 自動駕駛卡車與傳統卡車的總體擁有成本框架
- 資本支出分析
- 營運支出分析
- 收入和利用率影響
- 依部署模型進行投資回收期分析
- 專利分析
- 按技術領域分類的專利申請趨勢(2015-2024 年)
- 主要專利受讓人(原始設備製造商、ADS開發商、供應商)
- 關鍵專利集群:感知、規劃、控制、冗餘
- 地理專利活動(美國專利商標局、歐洲專利局、中國國家智慧財產局)
- 永續性和環境方面
- 永續實踐
- 減少廢棄物策略
- 生產中的能源效率
- 環保舉措
- 碳足跡考量
- 運行部署模式
- 樞紐間營運及轉運樞紐經濟
- 專用走廊策略
- 工業及受控環境應用
- 混合式人機協作車隊管理
- 安全與效能基準測試
- 安全案例框架和驗證方法
- 實際無人駕駛行駛里程(2023-2025 年)
- 脫離接觸與重大事件報告
- 與人類駕駛員基線性能的比較
- 保險與責任框架演變
- 目前責任歸屬挑戰
- 傳統商業汽車保險與自動駕駛專用產品
- 產業試點計畫和保險公司合作關係
- 責任框架中的監管漏洞
- 真實世界績效資料與離職分析
- 主要參與者累積的無人駕駛里程
- 脫離率定義與衡量標準
- 關鍵事件分類
- 天氣與環境性能
- 比較分析:自動駕駛與人類駕駛事故率
第4章:競爭格局
- 介紹
- 公司市佔率分析
- 北美洲
- 歐洲
- 亞太地區
- 拉丁美洲
- MEA
- 主要市場參與者的競爭分析
- 競爭定位矩陣
- 戰略展望矩陣
- 關鍵進展
- 併購
- 合作夥伴關係與合作
- 新產品發布
- 擴張計劃和資金
第5章:市場估算與預測:以推進方式分類,2021-2034年
- 柴油引擎
- 電的
- 混合
第6章:市場估算與預測:依類別分類,2021-2034年
- 7級(26,001-33,000磅)
- 8級(33,001磅以上)
第7章:市場估計與預測:依自主程度分類,2021-2034年
- 3級
- 4級
- 5級
第8章:市場估算與預測:依應用領域分類,2021-2034年
- 長途貨運
- 高速公路編隊行駛
- 跨境物流
- 樞紐到樞紐的營運
- 港口和碼頭物流
- 其他
第9章:市場估算與預測:依最終用途分類,2021-2034年
- 物流公司
- 零售與電子商務
- 快速消費品和食品供應鏈
- 工業品供應商
- 其他
第10章:市場估計與預測:依地區分類,2021-2034年
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 俄羅斯
- 北歐
- 葡萄牙
- 克羅埃西亞
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 韓國
- 新加坡
- 泰國
- 印尼
- 越南
- 拉丁美洲
- 巴西
- 墨西哥
- 阿根廷
- MEA
- 南非
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 土耳其
第11章:公司簡介
- 全球參與者
- Aurora Innovation
- Daimler Truck / Freightliner
- Einride
- Inceptio Technology
- Kodiak Robotics
- Locomation
- Navistar
- Paccar
- Plus (PlusAI)
- Tesla
- Torc Robotics
- TRATON
- TuSimple
- Volvo Autonomous Solutions
- Waymo
- 區域玩家
- Gatik
- Voyage / Geely-backed autonomous trucking unit
- Waabi
- 新興及小眾玩家
- Applied Intuition
- Embark Trucks
- Ike Robotics
- Outrider
- Stack AV
The Global Autonomous Long-Haul Trucking Market was valued at USD 2.7 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 32% to reach USD 42.6 billion by 2034.

With Level 4 capabilities progressing into commercial use, adoption is accelerating across major freight networks. Advancements in artificial intelligence, rising cargo movement, and persistent driver shortages are pushing autonomous trucking toward large-scale deployment. From 2024 through 2034, the overall market size is projected to increase by nearly 20 to 25 times, supported by operational savings that can reach as much as 40% due to continuous autonomous operation. Supportive regulatory guidance in the United States is also encouraging market movement, as federal transportation authorities provide clearer pathways for the safe rollout of automated freight operations. Several states remain central to development efforts, reinforcing the shift toward long-distance autonomous transport and enabling logistics companies to rely more heavily on automated systems for extended routes. Core operating models increasingly revolve around connecting major freight hubs to improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and streamline long-haul scheduling. These combined forces indicate that autonomous trucking is moving rapidly toward broader integration across national supply chains.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $2.7 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $42.6 Billion |
| CAGR | 32% |
The diesel powertrain segment held a 69% share in 2024 and is projected to grow at a 32.2% CAGR from 2025 to 2034. Diesel continues to lead because it offers an established infrastructure, high energy density, and lower initial costs relative to emerging alternatives. Autonomous systems integrated with diesel platforms can deliver improved productivity without requiring fleets to transition to unfamiliar propulsion technologies. Although diesel remains the preferred option for long-distance hauling, tightening emissions mandates in regions such as California and parts of Europe introduce regulatory pressures that the industry must navigate.
The Class 7 truck segment held an 86% share in 2024 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 32.6% between 2025 and 2034. This weight class covers heavy-duty vehicles widely used for freight movement, urban logistics, and industrial collection services. Class 7 models maintain a leading position within autonomous applications because their operational patterns align with structured, hub-oriented routes. This segment benefits from practical load capacity and more flexible compliance requirements. Growth is reinforced by expanding autonomous transport networks, broader integration of self-driving systems, and deeper collaboration with original equipment manufacturers.
United States Autonomous Long-Haul Trucking Market is projected to see sustained expansion from 2025 to 2034. The country remains the largest contributor to global demand due to strong freight volumes, advanced highway-automation initiatives, and ongoing innovations introduced by companies such as Aurora Innovation and Kodiak Robotics. Carriers and logistics providers across the nation are investing in automated freight technologies to raise reliability, cut operating expenses, and improve movement between key hubs. Tools driven by artificial intelligence, including fleet analytics, remote support functions, and predictive servicing, are becoming essential to the ecosystem.
Leading companies in the Global Autonomous Long-Haul Trucking Market include Aurora Innovation, Einride, Inceptio Technology, Kodiak Robotics, Locomation, Plus.ai, Tesla, Torc Robotics, TuSimple, and Waymo. Companies in the Autonomous Long-Haul Trucking Market are reinforcing their positions by expanding testing programs, advancing Level 4 software, and increasing investment in purpose-built platforms. Many firms are partnering with freight carriers, fleet operators, and truck manufacturers to accelerate integration and secure long-term commercial pathways. To strengthen competitiveness, businesses are improving sensor technology, refining AI-driven perception, and enhancing safety-critical redundancies. Several organizations are also building scalable operational centers to manage autonomous fleets and support remote oversight. Cost efficiency, reliability, and regulatory compliance remain top priorities, driving continuous improvements in system performance.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology
- 1.1 Market scope and definition
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Data mining sources
- 1.3.1 Global
- 1.3.2 Regional/Country
- 1.4 Base estimates and calculations
- 1.4.1 Base year calculation
- 1.4.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.6 Forecast model
- 1.7 Research assumptions and limitations
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry 3600 synopsis, 2021 - 2034
- 2.2 Key market trends
- 2.2.1 Regional
- 2.2.2 Propulsion
- 2.2.3 Class
- 2.2.4 Autonomy Level
- 2.2.5 Application
- 2.2.6 End Use
- 2.3 TAM Analysis, 2025-2034
- 2.4 CXO perspectives: Strategic imperatives
- 2.4.1 Executive decision points
- 2.4.2 Critical success factors
- 2.5 Future outlook and strategic recommendations
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.1.1 Supplier landscape
- 3.1.2 Profit margin analysis
- 3.1.3 Cost structure
- 3.1.4 Value addition at each stage
- 3.1.5 Factor affecting the value chain
- 3.1.6 Disruptions
- 3.2 Industry impact forces
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.2.1.1 Severe truck driver shortage
- 3.2.1.2 Need for lower transportation costs
- 3.2.1.3 24/7 continuous operations
- 3.2.1.4 Advancements in AI, sensors, and highway automation
- 3.2.1.5 Expansion of controlled hub-to-hub freight networks
- 3.2.2 Industry pitfalls and challenges
- 3.2.2.1 High capital and technology costs
- 3.2.2.2 Regulatory uncertainty across regions
- 3.2.3 Market opportunities
- 3.2.3.1 Autonomous freight services for major retailers and 3PLs
- 3.2.3.2 Integration with electric and hydrogen long-haul trucks
- 3.2.3.3 Remote operations centers (ROC) and tele-driving services
- 3.2.3.4 High-growth markets in Asia-Pacific
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.3 Growth potential analysis
- 3.4 Regulatory landscape
- 3.4.1 United States federal framework (NHTSA, FMCSA, DOT)
- 3.4.2 US state-level legislation & permitting (34 states + DC)
- 3.4.3 UNECE WP.29 & GRVA international harmonization
- 3.4.4 UN regulations (R155 cybersecurity, R156 OTA, R157 ALKS)
- 3.4.5 Hours-of-service (HOS) implications for Level 4-5 systems
- 3.4.6 Inspection standards & CVSA enhanced CMV inspection program
- 3.4.7 Data recording, privacy & ISMR reporting requirements
- 3.5 Porter's analysis
- 3.6 PESTEL analysis
- 3.7 Technology and innovation landscape
- 3.7.1 Current technological trends
- 3.7.1.1 SAE levels 3-5 automation capabilities
- 3.7.1.2 Sensor fusion architectures (LiDAR, radar, camera)
- 3.7.1.3 AI & machine learning in perception & planning
- 3.7.1.4 Redundancy & fail-safe system design
- 3.7.2 Emerging technologies
- 3.7.2.1 V2X communication & connected vehicle technologies
- 3.7.2.2 HD mapping & localization
- 3.7.2.3 Cybersecurity & OTA software update management
- 3.7.1 Current technological trends
- 3.8 Pricing analysis
- 3.8.1 Technology cost structure
- 3.8.2 Vehicle acquisition cost premium
- 3.8.3 Operating cost economics
- 3.8.4 TaaS pricing models & rate structures
- 3.8.5 Cost reduction roadmap (2024-2034)
- 3.9 Production statistics
- 3.9.1 Production hubs
- 3.9.2 Consumption hubs
- 3.9.3 Export and import
- 3.10 Cost breakdown analysis
- 3.10.1 Total cost of ownership (TCO) & economic payback analysis
- 3.10.2 TCO framework for autonomous trucks vs conventional trucks
- 3.10.3 Capital expenditure analysis
- 3.10.4 Operating expenditure analysis
- 3.10.5 Revenue & utilization impacts
- 3.10.6 Payback period analysis by deployment model
- 3.11 Patent analysis
- 3.11.1 Patent filing trends by technology domain (2015-2024)
- 3.11.2 Leading patent assignees (OEMs, ADS developers, suppliers)
- 3.11.3 Key patent clusters: perception, planning, control, redundancy
- 3.11.4 Geographic patent activity (USPTO, EPO, CNIPA)
- 3.12 Sustainability and environmental aspects
- 3.12.1 Sustainable practices
- 3.12.2 Waste reduction strategies
- 3.12.3 Energy efficiency in production
- 3.12.4 Eco-friendly Initiatives
- 3.12.5 Carbon footprint considerations
- 3.13 Operational deployment models
- 3.13.1 Hub-to-hub operations & transfer hub economics
- 3.13.2 Dedicated corridor strategies
- 3.13.3 Industrial & controlled environment applications
- 3.13.4 Hybrid human-autonomous fleet management
- 3.14 Safety & performance benchmarking
- 3.14.1 Safety case frameworks & validation methods
- 3.14.2 Real-world driverless miles achieved (2023-2025)
- 3.14.3 Disengagement & critical event reporting
- 3.14.4 Comparison to human driver baseline performance
- 3.15 Insurance & liability framework evolution
- 3.15.1 Current liability attribution challenges
- 3.15.2 Traditional commercial auto insurance vs autonomous-specific products
- 3.15.3 Industry pilot programs & insurer partnerships
- 3.15.4 Regulatory gaps in liability frameworks
- 3.16 Real-world performance data & disengagement analytics
- 3.16.1 Driverless miles accumulated by key players
- 3.16.2 Disengagement rate definitions & measurement standards
- 3.16.3 Critical event taxonomy
- 3.16.4 Weather & environmental performance
- 3.16.5 Comparative analysis: autonomous vs human driver incident rates
Chapter 4 Competitive Landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.2.1 North America
- 4.2.2 Europe
- 4.2.3 Asia Pacific
- 4.2.4 LATAM
- 4.2.5 MEA
- 4.3 Competitive analysis of major market players
- 4.4 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.5 Strategic outlook matrix
- 4.6 Key developments
- 4.6.1 Mergers & acquisitions
- 4.6.2 Partnerships & collaborations
- 4.6.3 New Product Launches
- 4.6.4 Expansion Plans and funding
Chapter 5 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Propulsion, 2021 - 2034 (USD Mn, Units)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Diesel
- 5.3 Electric
- 5.4 Hybrid
Chapter 6 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Class, 2021 - 2034 (USD Mn, Units)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Class 7 (26,001-33,000 lbs)
- 6.3 Class 8 (33,001+ lbs)
Chapter 7 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Autonomy Level, 2021 - 2034 (USD Mn, Units)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Level 3
- 7.3 Level 4
- 7.4 Level 5
Chapter 8 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Application, 2021 - 2034 (USD Mn, Units)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 Long-distance freight transport
- 8.3 Highway platooning
- 8.4 Cross-border logistics
- 8.5 Hub-to-hub operations
- 8.6 Port and terminal logistics
- 8.7 Others
Chapter 9 Market Estimates & Forecast, By End Use, 2021 - 2034 (USD Mn, Units)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 Logistics companies
- 9.3 Retail & e-commerce
- 9.4 FMCG & food supply chains
- 9.5 Industrial goods suppliers
- 9.6 Others
Chapter 10 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Region, 2021 - 2034 (USD Mn, Units)
- 10.1 Key trends
- 10.2 North America
- 10.2.1 US
- 10.2.2 Canada
- 10.3 Europe
- 10.3.1 Germany
- 10.3.2 UK
- 10.3.3 France
- 10.3.4 Italy
- 10.3.5 Spain
- 10.3.6 Russia
- 10.3.7 Nordics
- 10.3.8 Portugal
- 10.3.9 Croatia
- 10.4 Asia Pacific
- 10.4.1 China
- 10.4.2 India
- 10.4.3 Japan
- 10.4.4 Australia
- 10.4.5 South Korea
- 10.4.6 Singapore
- 10.4.7 Thailand
- 10.4.8 Indonesia
- 10.4.9 Vietnam
- 10.5 Latin America
- 10.5.1 Brazil
- 10.5.2 Mexico
- 10.5.3 Argentina
- 10.6 MEA
- 10.6.1 South Africa
- 10.6.2 Saudi Arabia
- 10.6.3 UAE
- 10.6.4 Turkey
Chapter 11 Company Profiles
- 11.1 Global Players
- 11.1.1 Aurora Innovation
- 11.1.2 Daimler Truck / Freightliner
- 11.1.3 Einride
- 11.1.4 Inceptio Technology
- 11.1.5 Kodiak Robotics
- 11.1.6 Locomation
- 11.1.7 Navistar
- 11.1.8 Paccar
- 11.1.9 Plus (PlusAI)
- 11.1.10 Tesla
- 11.1.11 Torc Robotics
- 11.1.12 TRATON
- 11.1.13 TuSimple
- 11.1.14 Volvo Autonomous Solutions
- 11.1.15 Waymo
- 11.2 Regional Players
- 11.2.1 Gatik
- 11.2.2 Voyage / Geely-backed autonomous trucking unit
- 11.2.3 Waabi
- 11.3 Emerging & Niche Players
- 11.3.1 Applied Intuition
- 11.3.2 Embark Trucks
- 11.3.3 Ike Robotics
- 11.3.4 Outrider
- 11.3.5 Stack AV



