 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1892709
快速充電電動汽車電池化學市場機會、成長促進因素、產業趨勢分析及預測(2025-2034年)Fast-Charging EV Battery Chemistries Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
2024 年全球快速充電電動車電池化學市場價值為 177 億美元,預計到 2034 年將以 18.8% 的複合年成長率成長至 986 億美元。
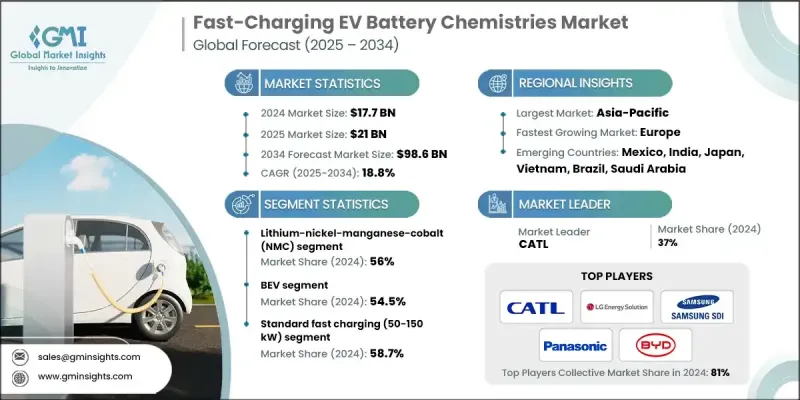
隨著世界各國政府和各產業致力於減少溫室氣體排放並支持淨零排放目標,向電動車的快速轉型成為關鍵促進因素。光是交通運輸業就佔全球排放量的25%以上,因此,電動車的普及已成為一項迫切需求,而不僅僅是消費者的選擇。隨著電動車保有量的成長,里程焦慮和充電基礎設施的不足推動了對先進電池技術的需求,這些技術能夠在10-30分鐘內將電量從10%充至80%。超快速充電技術的創新,包括350千瓦以上的系統和800伏特等高壓架構,使得在短短10到15分鐘內即可顯著提升續航里程。這一趨勢正在推動對鋰鎳錳鈷(NMC)、磷酸鐵鋰(LFP)和鋰鎳鈷鋁(NCA)等電池技術的投資,這些技術能夠提供更高的效率、更長的壽命和更快的充電速度。
| 市場範圍 | |
|---|---|
| 起始年份 | 2024 |
| 預測年份 | 2025-2034 |
| 起始值 | 177億美元 |
| 預測值 | 986億美元 |
| 複合年成長率 | 18.8% |
到 2024 年,鋰鎳錳鈷 (NMC) 電池市佔率將達到 56%。電動車的普及以及鋰成本的下降,正在加速對 NMC 電池的需求,而 NMC 電池因其快速充電能力而受到汽車製造商的廣泛青睞。
預計到2024年,純電動車(BEV)市場佔有率將達到54.5%。由於純電動車電池組容量更大,且消費者對充電時間的期望日益提高,因此對快速充電電池技術的需求也隨之成長。鋰離子電池和磷酸鋰電池技術的進步正在提升充電速度、能量儲存能力和電池安全性,同時延長電池的整體使用壽命。
預計2024年,美國快速充電電動車電池市場規模將達29億美元。政府政策,例如《通貨膨脹抑制法案》(IRA),透過提供稅收優惠和推廣使用本地材料,正在加速國內生產。這些措施鼓勵汽車製造商在合規的供應鏈中專注於NMC、LFP和其他先進的快速充電電池技術,以降低成本並支持永續發展。
目錄
第1章:方法論
第2章:執行概要
第3章:行業洞察
- 產業生態系分析
- 供應商格局
- 利潤率
- 成本結構
- 每個階段的價值增加
- 影響價值鏈的因素
- 中斷
- 產業影響因素
- 成長促進因素
- 消費者對縮短充電時間的需求日益成長
- 政府對零排放車輛的強制規定
- 擴展高功率充電基礎設施網路
- 電池成本下降推動了快速充電技術的普及。
- 產業陷阱與挑戰
- 快速充電帶來的電池衰減和循環壽命問題
- 原料供應受限
- 市場機遇
- 重型和商用車輛電氣化
- 超快速充電技術發展
- 固態電池商業化
- 車網互動(V2G)與快速充電的融合
- 成長促進因素
- 成長潛力分析
- 監管環境
- 北美洲
- 歐洲
- 亞太地區
- 拉丁美洲
- 中東和非洲
- 波特的分析
- PESTEL 分析
- 技術與創新格局
- 當前技術趨勢
- 新興技術
- 技術路線圖與演進
- 技術採納生命週期分析
- 價格趨勢
- 按地區
- 依產品
- 成本細分分析
- 專利分析
- 消費者認知與接受障礙
- 消費者對充電時間的期望與接受程度
- 里程焦慮與快速充電可用性之間的權衡
- 快速充電功能的價格溢價意願
- 電池衰減問題及保固預期
- 充電基礎設施可近性感知
- 熱退化與安全分析
- 全球充電標準格局
- 功率水平標準化
- 通訊協定
- 兆瓦充電系統
- 標準化差距和互通性挑戰
- 生命週期成本和總擁有成本 (TCO) 分析
- TCO 方法論及假設
- 快速充電進階成本分析
- 能源成本和充電效率
- 維護和更換成本
- 案例研究
第4章:競爭格局
- 介紹
- 公司市佔率分析
- 北美洲
- 歐洲
- 亞太地區
- 拉丁美洲
- MEA
- 主要市場參與者的競爭分析
- 競爭定位矩陣
- 戰略展望矩陣
- 關鍵進展
- 併購
- 合作夥伴關係與合作
- 新產品發布
- 擴張計劃和資金
- 供應商選擇標準
第5章:市場估計與預測:依電池化學類型分類,2021-2034年
- 磷酸鐵鋰(LFP)
- 鋰鎳錳鈷(NMC)
- 鎳鈷鋁合金(NCA)
- 其他
第6章:市場估算與預測:依動力總成分類,2021-2034年
- 純電動車
- 插電式混合動力汽車
- 戊型肝炎病毒
第7章:市場估價與預測:依車輛類型分類,2021-2034年
- 搭乘用車
- SUV
- 轎車
- 掀背車
- 商用車輛
- 低容量性狀
- MCV
- C型肝炎
- 二輪車
第8章:市場估算與預測:依充電技術分類,2021-2034年
- 標準快速充電(50-150千瓦)
- 超快速充電(150度以上)
第9章:市場估算與預測:依銷售管道分類,2021-2034年
- OEM
- 售後市場
第10章:市場估計與預測:依地區分類,2021-2034年
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 俄羅斯
- 北歐
- 比荷盧經濟聯盟
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 韓國
- 澳新銀行
- 新加坡
- 馬來西亞
- 印尼
- 越南
- 泰國
- 拉丁美洲
- 巴西
- 墨西哥
- 阿根廷
- 哥倫比亞
- MEA
- 南非
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 土耳其
第11章:公司簡介
- 全球公司
- CATL
- LG Energy Solution
- Samsung SDI
- Panasonic Energy
- SK On
- BYD Company
- Tesla
- Farasis Energy
- BorgWarner
- 區域公司
- Northvolt
- CALB
- Gotion High-Tech
- Envision AESC
- EVE Energy
- Automotive Cells Company
- 新興公司
- QuantumScape
- StoreDot
- Solid Power
- Sila Nanotechnologies
- Factorial Energy
- Enevate
- Amprius Technologies
- ProLogium Technology
- ONE
- Freyr Battery
- Cuberg
- Sunwoda Electronic
The Global Fast-Charging EV Battery Chemistries Market was valued at USD 17.7 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 18.8% to reach USD 98.6 billion by 2034.

The rapid transition toward electric vehicles is a key driver, as governments and industries worldwide focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and supporting net-zero targets. The transportation sector alone accounts for over 25% of global emissions, making EV adoption a critical necessity rather than just a consumer preference. As EV ownership rises, range anxiety and limited charging infrastructure have pushed the demand for advanced battery chemistries capable of charging from 10% to 80% in 10-30 minutes. Innovations in ultra-fast charging technologies, including 350 kW+ systems and high-voltage architectures like 800V platforms, are enabling substantial range gains in just 10 to 15 minutes. This trend is propelling investments in battery chemistries such as lithium-nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC), lithium iron phosphate (LFP), and lithium-nickel-cobalt-aluminum (NCA), which can deliver higher efficiency, longer life, and faster charge times.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $17.7 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $98.6 Billion |
| CAGR | 18.8% |
The lithium-nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) segment held a 56% share in 2024. Increasing EV adoption, combined with declining lithium costs, is accelerating demand for NMC batteries, which are widely preferred by automakers for their rapid charging capabilities.
The battery electric vehicle (BEV) segment held a 54.5% share in 2024. BEVs drive the need for fast-charging battery chemistries due to their larger battery packs and growing consumer expectations for reduced charging times. Advances in lithium-ion and LFP chemistries are enhancing charging speed, energy storage, and battery safety, while extending overall lifespan.
U.S. Fast-Charging EV Battery Chemistries Market reached USD 2.9 billion in 2024. Government policies, such as the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), are accelerating domestic production by providing tax incentives and promoting the use of local materials. These initiatives are encouraging automakers to focus on NMC, LFP, and other advanced fast-charging battery chemistries within compliant supply chains to reduce costs and support sustainability.
Key players in the Global Fast-Charging EV Battery Chemistries Market include BYD, SK On, Factorial Energy, LG Energy Solution, CATL, Samsung SDI, BorgWarner, Panasonic, Farasis Energy, and EVE Energy. Companies in the Global Fast-Charging EV Battery Chemistries Market are strengthening their positions by investing heavily in R&D to improve energy density, safety, and charge speed. Strategic partnerships with automakers and technology firms help accelerate the commercialization of next-generation chemistries. Many are expanding production capacity in strategic regions to reduce logistics costs and meet local content requirements. Firms are also pursuing patents, licensing agreements, and joint ventures to secure supply chains for critical raw materials while focusing on sustainability and recycling initiatives to appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology
- 1.1 Market scope and definition
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Data mining sources
- 1.3.1 Global
- 1.3.2 Regional/Country
- 1.4 Base estimates and calculations
- 1.4.1 Base year calculation
- 1.4.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.6 Forecast
- 1.7 Research assumptions and limitations
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry 360° synopsis
- 2.2 Key market trends
- 2.2.1 Regional
- 2.2.2 Battery Chemistry
- 2.2.3 Powertrain
- 2.2.4 Vehicle
- 2.2.5 Charging Technology
- 2.2.6 Sales Channel
- 2.3 TAM analysis, 2025-2034
- 2.4 CXO perspectives: Strategic imperatives
- 2.4.1 Executive decision points
- 2.4.2 Critical success factors
- 2.5 Future outlook and recommendations
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.1.1 Supplier landscape
- 3.1.2 Profit margin
- 3.1.3 Cost structure
- 3.1.4 Value addition at each stage
- 3.1.5 Factor affecting the value chain
- 3.1.6 Disruptions
- 3.2 Industry impact forces
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.2.1.1 Increasing consumer demand for reduced charging times
- 3.2.1.2 Government mandates for zero-emission vehicles
- 3.2.1.3 Expansion of high-power charging infrastructure networks
- 3.2.1.4 Declining battery costs enabling fast-charging adoption
- 3.2.2 Industry pitfalls and challenges
- 3.2.2.1 Battery degradation & cycle life concerns with fast charging
- 3.2.2.2 Raw material supply constraints
- 3.2.3 Market opportunities
- 3.2.3.1 Heavy-duty & commercial vehicle electrification
- 3.2.3.2 Extreme fast-charging technology development
- 3.2.3.3 Solid-state battery commercialization
- 3.2.3.4 Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) integration with fast-charging
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.3 Growth potential analysis
- 3.4 Regulatory landscape
- 3.4.1 North America
- 3.4.2 Europe
- 3.4.3 Asia Pacific
- 3.4.4 Latin America
- 3.4.5 Middle East & Africa
- 3.5 Porter's analysis
- 3.6 PESTEL analysis
- 3.7 Technology and innovation landscape
- 3.7.1 Current technological trends
- 3.7.2 Emerging technologies
- 3.7.3 Technology roadmaps & evolution
- 3.7.4 Technology adoption lifecycle analysis
- 3.8 Price trends
- 3.8.1 By region
- 3.8.2 By product
- 3.9 Cost breakdown analysis
- 3.10 Patent analysis
- 3.11 Consumer perception & adoption barriers
- 3.11.1 Consumer charging time expectations & acceptance thresholds
- 3.11.2 Range anxiety vs fast-charging availability trade-off
- 3.11.3 Price premium willingness for fast-charging capability
- 3.11.4 Battery degradation concerns & warranty expectations
- 3.11.5 Charging infrastructure accessibility perception
- 3.12 Thermal degradation & safety analysis
- 3.12.1 Global charging standards landscape
- 3.12.2 Power level standardization
- 3.12.3 Communication protocols
- 3.12.4 Megawatt charging system
- 3.12.5 Standardization gaps & interoperability challenges
- 3.13 Life cycle cost & total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis
- 3.13.1 TCO methodology & assumptions
- 3.13.2 Fast-charging premium cost analysis
- 3.13.3 Energy costs & charging efficiency
- 3.13.4 Maintenance & replacement costs
- 3.14 Case studies
Chapter 4 Competitive Landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.2.1 North America
- 4.2.2 Europe
- 4.2.3 Asia Pacific
- 4.2.4 LATAM
- 4.2.5 MEA
- 4.3 Competitive analysis of major market players
- 4.4 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.5 Strategic outlook matrix
- 4.6 Key developments
- 4.6.1 Mergers & acquisitions
- 4.6.2 Partnerships & collaborations
- 4.6.3 New product launches
- 4.6.4 Expansion plans and funding
- 4.7 Vendor selection criteria
Chapter 5 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Battery Chemistry, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP)
- 5.3 Lithium-Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt (NMC)
- 5.4 Nickel-Cobalt-Aluminum (NCA)
- 5.5 Others
Chapter 6 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Powertrain, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 BEV
- 6.3 PHEV
- 6.4 HEV
Chapter 7 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Vehicle, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Passenger Vehicles
- 7.2.1 SUVs
- 7.2.2 Sedans
- 7.2.3 Hatchbacks
- 7.3 Commercial Vehicles
- 7.3.1 LCV
- 7.3.2 MCV
- 7.3.3 HCV
- 7.4 Two-wheelers
Chapter 8 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Charging Technology, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 Standard Fast Charging (50-150 kW)
- 8.3 Ultra-Fast Charging (Above 150 kW)
Chapter 9 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Sales Channel, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 OEM
- 9.3 Aftermarket
Chapter 10 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Region, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 10.1 Key trends
- 10.2 North America
- 10.2.1 US
- 10.2.2 Canada
- 10.3 Europe
- 10.3.1 Germany
- 10.3.2 UK
- 10.3.3 France
- 10.3.4 Italy
- 10.3.5 Spain
- 10.3.6 Russia
- 10.3.7 Nordics
- 10.3.8 Benelux
- 10.4 Asia Pacific
- 10.4.1 China
- 10.4.2 India
- 10.4.3 Japan
- 10.4.4 South Korea
- 10.4.5 ANZ
- 10.4.6 Singapore
- 10.4.7 Malaysia
- 10.4.8 Indonesia
- 10.4.9 Vietnam
- 10.4.10 Thailand
- 10.5 Latin America
- 10.5.1 Brazil
- 10.5.2 Mexico
- 10.5.3 Argentina
- 10.5.4 Colombia
- 10.6 MEA
- 10.6.1 South Africa
- 10.6.2 Saudi Arabia
- 10.6.3 UAE
- 10.6.4 Turkey
Chapter 11 Company Profiles
- 11.1 Global companies
- 11.1.1 CATL
- 11.1.2 LG Energy Solution
- 11.1.3 Samsung SDI
- 11.1.4 Panasonic Energy
- 11.1.5 SK On
- 11.1.6 BYD Company
- 11.1.7 Tesla
- 11.1.8 Farasis Energy
- 11.1.9 BorgWarner
- 11.2 Regional companies
- 11.2.1 Northvolt
- 11.2.2 CALB
- 11.2.3 Gotion High-Tech
- 11.2.4 Envision AESC
- 11.2.5 EVE Energy
- 11.2.6 Automotive Cells Company
- 11.3 Emerging companies
- 11.3.1 QuantumScape
- 11.3.2 StoreDot
- 11.3.3 Solid Power
- 11.3.4 Sila Nanotechnologies
- 11.3.5 Factorial Energy
- 11.3.6 Enevate
- 11.3.7 Amprius Technologies
- 11.3.8 ProLogium Technology
- 11.3.9 ONE
- 11.3.10 Freyr Battery
- 11.3.11 Cuberg
- 11.3.12 Sunwoda Electronic





