 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1773227
反芻動物甲烷減量市場機會、成長動力、產業趨勢分析及 2025 - 2034 年預測Ruminant Methane Reduction Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
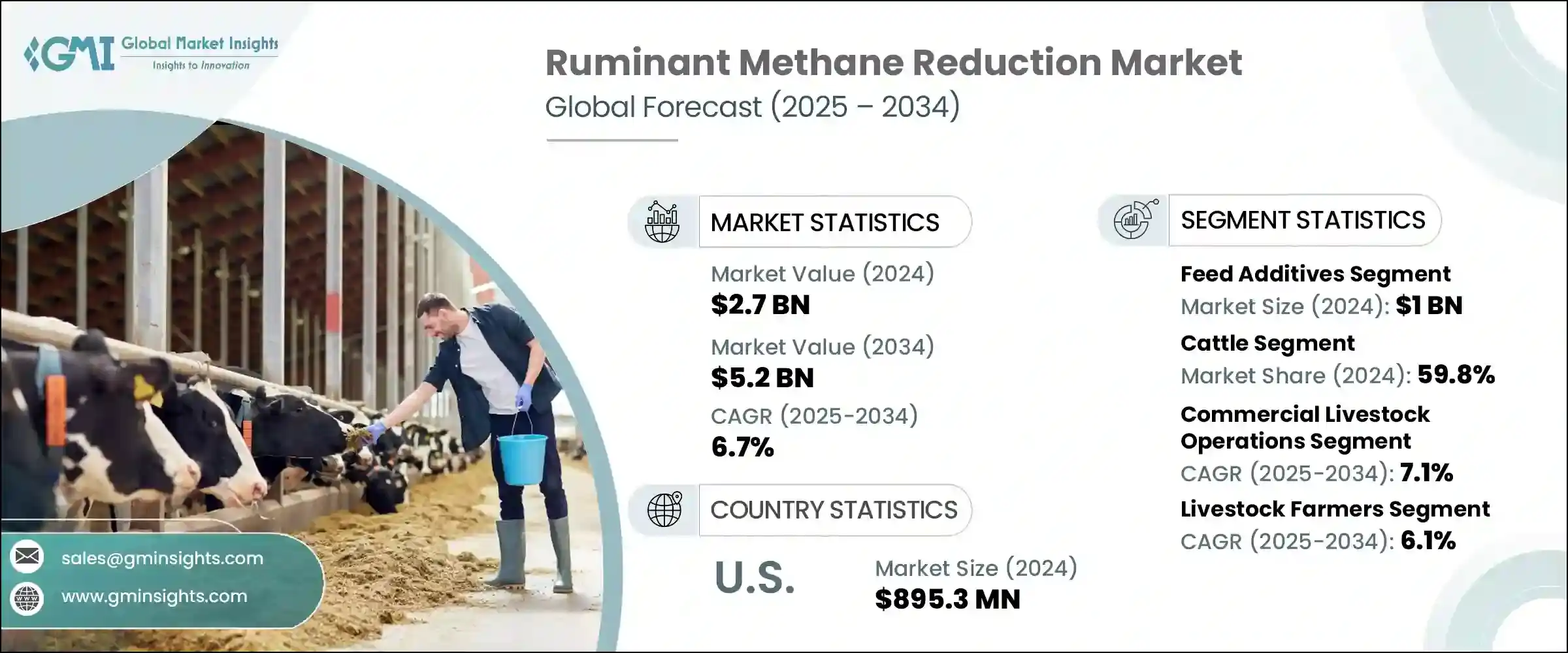
2024年,全球反芻動物甲烷減量市場規模達27億美元,預計到2034年將以6.7%的複合年成長率成長,達到52億美元。這一成長反映了減少牛、羊和山羊甲烷排放的迫切需求,這些甲烷排放主要來自腸道發酵。隨著全球對動物性蛋白質的需求不斷成長,降低反芻動物甲烷排放對於實現氣候目標、提高生產效率和支持永續農業實踐至關重要。
緩解措施包括日糧添加劑、基因選擇、牧場管理和提高畜群生產力。 3-硝基氧丙醇 (3-NOP) 等飼料添加劑和海藻衍生產品已被證明可在不影響動物生產性能的情況下減少高達 80% 的甲烷排放。國家和企業氣候計畫正在結合補貼、碳權額度系統和政策框架來推動相關措施的採用。儘管可擴展性和本地適應性挑戰依然存在,但將基於飼料的策略與糞便消化器等循環生物經濟解決方案相結合,正在進一步加強甲烷減排工作。
| 市場範圍 | |
|---|---|
| 起始年份 | 2024 |
| 預測年份 | 2025-2034 |
| 起始值 | 27億美元 |
| 預測值 | 52億美元 |
| 複合年成長率 | 6.7% |
儘管可擴展性和適應當地農業條件仍面臨諸多挑戰,但將以飼料為基礎的策略與更廣泛的循環生物經濟實踐相結合,已被證明在擴大甲烷減排力度方面日益有效。透過將甲烷抑制劑和天然飼料添加劑與糞便厭氧消化器等系統相結合,農場可以創建閉迴路營運,同時應對腸道發酵和廢物分解產生的排放。這種雙重方法不僅可以提升整體環境效益,還能創造額外的價值流,例如再生能源和有機肥料。
反芻動物甲烷減量市場中的飼料添加劑部分在2024年創造了10億美元的產值。這些飲食干預措施正成為甲烷減量工作的核心,尤其是在3-硝基氧丙醇(3-NOP)和溴仿基溶液等科學化合物持續證明其在降低腸道排放方面高效且不影響動物生產力的情況下。除合成抑制劑外,精油、植物萃取物和單寧等天然替代品也日益受到青睞,它們由於環保特性和影響瘤胃微生物群落的能力,正擴大被添加到飼料中。
2024年,牛市佔比59.8%,預計到2034年將以7.1%的複合年成長率成長。這種主導地位源自於其龐大的全球族群數量和高甲烷排放量,尤其是在乳牛和肉牛。乳牛的飲食週期頻繁,飼料利用率高,因此特別適合以飼料為基礎的減排策略。同時,肉牛通常在粗放型牧場系統中飼養,透過最佳化放牧、調整飲食和旨在降低排放強度的基因選擇,為減少甲烷排放提供了機會。
2024年,美國反芻動物甲烷減量市場產值達8.953億美元。美國在甲烷減排領域的領先地位得益於聯邦和州政府政策的不斷完善、企業日益重視氣候相關法規的實施以及減排飼料解決方案的快速創新。美國生產商,尤其是乳製品和牛肉生產商,正在迅速添加3-NOP、海藻基化合物和精油等添加劑,以符合自願減碳計劃和第三方永續性標準。環境、社會和治理 (ESG) 框架下的認證推動進一步推動了這些添加劑的大規模應用。
該市場的領先公司包括贏創工業股份公司、帝斯曼芬美意公司、嘉吉公司、阿徹丹尼爾斯米德蘭公司 (ADM) 和巴斯夫公司。為了鞏固市場地位,頂級反芻動物甲烷減排公司正在實施多項舉措,並大力投資研發,以開發出功效更高、成本效益更高、區域適應性更強的下一代添加劑。
與飼料製造商、畜牧整合商和研究機構的合作有助於加速產品驗證和規模化生產。企業也在全球範圍內啟動試點計畫和飼養試驗,以產生性能資料並獲得監管部門的批准。與農業合作社和以氣候為重點的計劃建立的戰略夥伴關係,正在透過補貼和碳權額度計劃擴大飼料添加劑的可及性。此外,產品多樣化方面的努力(例如將益生菌基質與甲烷抑制劑結合)正在幫助企業實現產品差異化,並滿足畜牧生產中新興的永續性標準。
目錄
第1章:方法論與範圍
第2章:執行摘要
第3章:行業洞察
- 產業生態系統分析
- 供應商格局
- 利潤率
- 每個階段的增值
- 影響價值鏈的因素
- 中斷
- 產業衝擊力
- 成長動力
- 產業陷阱與挑戰
- 市場機會
- 成長潛力分析
- 監管格局
- 北美洲
- 歐洲
- 亞太地區
- 拉丁美洲
- 中東和非洲
- 波特的分析
- Pestel 分析
- 價格趨勢
- 按地區
- 按產品
- 未來市場趨勢
- 技術和創新格局
- 當前的技術趨勢
- 新興技術
- 專利格局
- 貿易統計資料(HS 編碼)(註:僅提供重點國家的貿易統計資料)
- 主要進口國
- 主要出口國
- 永續性和環境方面
- 永續實踐
- 減少廢棄物的策略
- 生產中的能源效率
- 環保舉措
第4章:競爭格局
- 介紹
- 公司市佔率分析
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 歐洲
- 亞太地區
- 拉丁美洲
- MEA
- 按地區
- 公司矩陣分析
- 主要市場參與者的競爭分析
- 競爭定位矩陣
- 關鍵進展
- 併購
- 夥伴關係與合作
- 新產品發布
- 擴張計劃
第5章:市場估計與預測:按產品,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趨勢
- 飼料添加劑
- 甲烷抑制劑
- 3-硝基氧丙醇(3-nop)
- 溴仿化合物
- 其他化學抑制劑
- 天然化合物
- 精油
- 植物萃取物
- 海藻基添加劑
- 單寧
- 益生菌和益生元
- 減少甲烷的益生菌
- 益生元化合物
- 酵素
- 其他飼料添加劑
- 甲烷抑制劑
- 遺傳和育種解決方案
- 低甲烷遺傳學
- 選擇性育種計劃
- 基因組選擇工具
- 管理實踐
- 飲食調整
- 優質飼料
- 精料餵養
- 精密進料系統
- 放牧管理
- 畜群管理最佳化
- 飲食調整
- 生物技術解決方案
- 瘤胃微生物組改造
- 產甲烷菌抑制
- 疫苗研發
- 其他解決方案
- 替代蛋白質來源
- 甲烷捕獲技術
- 碳封存方法
第6章:市場估計與預測:按反芻動物 2021 – 2034 年
- 主要趨勢
- 牛
- 乳製品
- 牛肉
- 羊
- 山羊
- 水牛
- 其他反芻動物
- 鹿
- 羊駝和駱駝
- 其他物種
第7章:市場估計與預測:按應用,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趨勢
- 商業牲畜經營
- 大型乳牛養殖場
- 大規模牛肉養殖
- 飼養場
- 中小型農場
- 家庭乳牛場
- 混合農業經營
- 專業畜牧農場
- 牧場系統
- 粗放放牧系統
- 輪牧系統
- 林草系統
- 研究與開發
- 學術研究機構
- 政府研究項目
- 私人研發設施
第8章:市場估計與預測:依最終用途 2021 – 2034
- 主要趨勢
- 畜牧養殖戶
- 酪農
- 牛肉生產商
- 綿羊和山羊養殖戶
- 飼料生產商
- 商業飼料生產商
- 特種飼料公司
- 飼料添加劑生產者
- 食品和飲料公司
- 乳製品加工商
- 肉類加工商
- 食品服務公司
- 政府及科學研究機構
- 農業部門
- 環境機構
- 研究型大學
- 其他
- 碳權開發商
- 諮詢服務
- 技術整合商
第9章:市場估計與預測:按地區,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趨勢
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 歐洲其他地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 韓國
- 亞太其他地區
- 拉丁美洲
- 巴西
- 墨西哥
- 阿根廷
- 拉丁美洲其他地區
- 中東和非洲
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- MEA 其餘地區
第10章:公司簡介
- Agolin SA
- Alltech Inc.
- Archer Daniels Midland Company (ADM)
- ArkeaBio
- BASF SE
- Blue Ocean Barns
- Cargill, Incorporated
- Chr. Hansen Holding A/S
- DSM-Firmenich
- Elanco Animal Health Incorporated
- Evonik Industries AG
- FutureFeed Pty Ltd
- Kemin Industries, Inc.
- Lallemand Inc.
- Mootral SA
- Novozymes A/S
- Rumin8
- Symbrosia Inc.
- Volta Greentech
- Zelp Ltd
The Global Ruminant Methane Reduction Market was valued at USD 2.7 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 6.7% to reach USD 5.2 billion by 2034. This growth reflects the increasing imperative to reduce methane emissions from cattle, sheep, and goats, which largely result from enteric fermentation. With global demand for animal-based proteins on the rise, tackling ruminant methane output is essential to meet climate targets, enhance production efficiency, and support sustainable farming practices.

Mitigation approaches include dietary additives, genetic selection, pasture management, and increased herd productivity. Feed additives such as 3-nitrooxypropanol (3-NOP) and seaweed-derived products have shown methane reductions of up to 80% without sacrificing animal performance. National and corporate climate programs are combining subsidies, carbon credit systems, and policy frameworks to drive adoption. While scalability and local adaptation challenges persist, coupling feed-based strategies with circular bioeconomy solutions, like manure digesters, is further enhancing methane mitigation efforts.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $2.7 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $5.2 Billion |
| CAGR | 6.7% |
While scalability and adaptation to local farming conditions continue to pose hurdles, the integration of feed-based strategies with broader circular bioeconomy practices is proving increasingly effective in amplifying methane reduction efforts. By aligning methane inhibitors and natural feed additives with systems such as manure anaerobic digesters, farms can create closed-loop operations that tackle emissions from both enteric fermentation and waste decomposition. This dual approach not only boosts overall environmental impact but also generates additional value streams, such as renewable energy and organic fertilizers.
The feed additives segment in the ruminant methane reduction market generated USD 1 billion in 2024. These dietary interventions are becoming central to methane mitigation efforts, especially as science-backed compounds like 3-Nitrooxypropanol (3-NOP) and bromoform-based solutions continue to demonstrate high efficacy in lowering enteric emissions without compromising animal productivity. Alongside synthetic inhibitors, there is rising momentum behind natural alternatives such as essential oils, plant-derived extracts, and tannins, which are being increasingly incorporated into feed due to their environmentally friendly profiles and ability to influence the microbial populations in the rumen.
The cattle segment held a 59.8% share in 2024 and is expected to grow at 7.1% CAGR through 2034. This dominance stems from their significant global population and high levels of methane production, particularly among dairy and beef cattle. Dairy cows, with their frequent dietary cycles and efficient feed utilization, are especially compatible with feed-based reduction strategies. Meanwhile, beef cattle, often raised in extensive pasture systems, present opportunities for methane reduction through grazing optimization, dietary tweaks, and genetic selection aimed at lowering emissions intensity.
U.S. Ruminant Methane Reduction Market generated USD 895.3 million in 2024. The country's leadership is backed by a combination of evolving federal and state policies, increasing adoption of climate-focused corporate mandates, and rapid innovation in emission-reducing feed solutions. American producers, particularly in the dairy and beef sectors, are rapidly incorporating additives like 3-NOP, seaweed-based compounds, and essential oils to align with voluntary carbon reduction initiatives and third-party sustainability standards. The push for certification under environmental, social, and governance (ESG) frameworks further motivates the large-scale deployment of these additives.
Leading companies in this market include Evonik Industries AG, DSM Firmenich, Cargill Incorporated, Archer Daniels Midland Company (ADM), and BASF SE. To strengthen their market position, top ruminant methane reduction companies are implementing multiple initiatives They are investing heavily in R& D to develop next-gen additives with enhanced efficacy, cost-effectiveness, and regional adaptability.
Collaborations with feed manufacturers, livestock integrators, and research institutions help accelerate product validation and scale-up. Firms are also launching pilot programs and feeding trials globally to generate performance data and regulatory approvals. Strategic partnerships with agricultural cooperatives and climate-focused initiatives are expanding access to feed additives through subsidies and carbon-credit programs. Additionally, efforts in product diversification-such as combining probiotic matrices with methane inhibitors-are helping companies differentiate offerings and meet emerging sustainability standards in livestock production.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology and Scope
- 1.1 Market scope and definition
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Data mining sources
- 1.3.1 Global
- 1.3.2 Regional/country
- 1.4 Base estimates and calculations
- 1.4.1 Base year calculation
- 1.4.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.6 Forecast model
- 1.7 Research assumptions and limitations
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry 360° synopsis
- 2.2 Key market trends
- 2.2.1 Regional
- 2.2.2 Product
- 2.2.3 Ruminant
- 2.2.4 Application
- 2.2.5 End Use
- 2.3 TAM analysis, 2025-2034
- 2.4 Cxo perspectives: strategic imperatives
- 2.4.1 Executive decision points
- 2.4.2 Critical success factors
- 2.5 Future outlook and strategic recommendations
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.1.1 Supplier landscape
- 3.1.2 Profit margin
- 3.1.3 Value addition at each stage
- 3.1.4 Factor affecting the value chain
- 3.1.5 Disruptions
- 3.2 Industry impact forces
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.2.2 Industry pitfalls and challenges
- 3.2.3 Market opportunities
- 3.3 Growth potential analysis
- 3.4 Regulatory landscape
- 3.4.1 North America
- 3.4.2 Europe
- 3.4.3 Asia Pacific
- 3.4.4 Latin America
- 3.4.5 Middle East & Africa
- 3.5 Porter's analysis
- 3.6 Pestel analysis
- 3.6.1 Technology and innovation landscape
- 3.6.2 Current technological trends
- 3.6.3 Emerging technologies
- 3.7 Price trends
- 3.7.1 By region
- 3.7.2 By product
- 3.8 Future market trends
- 3.9 Technology and innovation landscape
- 3.9.1 Current technological trends
- 3.9.2 Emerging technologies
- 3.10 Patent landscape
- 3.11 Trade statistics (HS code) (note: the trade statistics will be provided for key countries only)
- 3.11.1 Major importing countries
- 3.11.2 Major exporting countries
- 3.12 Sustainability and environmental aspects
- 3.12.1 Sustainable Practices
- 3.12.2 Waste reduction strategies
- 3.12.3 Energy efficiency in production
- 3.12.4 Eco-friendly initiatives
Chapter 4 Competitive landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.2.1 By Region
- 4.2.1.1 North America
- 4.2.1.2 Europe
- 4.2.1.3 Asia Pacific
- 4.2.1.4 LATAM
- 4.2.1.5 MEA
- 4.2.1 By Region
- 4.3 Company matrix analysis
- 4.4 Competitive analysis of major market players
- 4.5 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.6 Key developments
- 4.6.1 Mergers & acquisitions
- 4.6.2 Partnerships & collaborations
- 4.6.3 New product launches
- 4.6.4 Expansion plans
Chapter 5 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Product, 2021 – 2034 (USD Billion) (Kilo Tons)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Feed additives
- 5.2.1 Methane inhibitors
- 5.2.1.1 3-nitrooxypropanol (3-nop)
- 5.2.1.2 Bromoform compounds
- 5.2.1.3 Other chemical inhibitors
- 5.2.2 Natural compounds
- 5.2.2.1 Essential oils
- 5.2.2.2 Plant extracts
- 5.2.2.3 Seaweed-based additives
- 5.2.2.4 Tannins
- 5.2.3 Probiotics & prebiotics
- 5.2.3.1 Methane-reducing probiotics
- 5.2.3.2 Prebiotic compounds
- 5.2.4 Enzymes
- 5.2.5 Other feed additives
- 5.2.1 Methane inhibitors
- 5.3 Genetic & breeding solutions
- 5.3.1 Low-methane genetics
- 5.3.2 Selective breeding programs
- 5.3.3 Genomic selection tools
- 5.4 Management practices
- 5.4.1 Dietary modifications
- 5.4.1.1 High-quality forages
- 5.4.1.2 Concentrate feeding
- 5.4.1.3 Precision feeding systems
- 5.4.2 Grazing management
- 5.4.3 Herd management optimization
- 5.4.1 Dietary modifications
- 5.5 Biotechnology solutions
- 5.5.1 Rumen microbiome modification
- 5.5.2 Methanogen inhibition
- 5.5.3 Vaccine development
- 5.6 Other solutions
- 5.6.1 Alternative protein sources
- 5.6.2 Methane capture technologies
- 5.6.3 Carbon sequestration methods
Chapter 6 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Ruminant 2021 – 2034 (USD Billion) (Kilo Tons)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Cattle
- 6.2.1 Dairy
- 6.2.2 Beef
- 6.3 Sheep
- 6.4 Goats
- 6.5 Buffalo
- 6.6 Other ruminants
- 6.6.1 Deer
- 6.6.2 Alpacas & llamas
- 6.6.3 Other species
Chapter 7 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Application, 2021 – 2034 (USD Billion) (Kilo Tons)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Commercial livestock operations
- 7.2.1 Large-scale dairy farms
- 7.2.2 Large-scale beef operations
- 7.2.3 Feedlots
- 7.3 Small & medium farms
- 7.3.1 Family dairy farms
- 7.3.2 Mixed farming operations
- 7.3.3 Specialty livestock farms
- 7.4 Pasture-based systems
- 7.4.1 Extensive grazing systems
- 7.4.2 Rotational grazing systems
- 7.4.3 Silvopastoral systems
- 7.5 Research & development
- 7.5.1 Academic research institutions
- 7.5.2 Government research programs
- 7.5.3 Private R&D facilities
Chapter 8 Market Estimates and Forecast, By End Use 2021 – 2034 (USD Billion) (Kilo Tons)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 Livestock farmers
- 8.2.1 Dairy farmers
- 8.2.2 Beef producers
- 8.2.3 Sheep & goat farmers
- 8.3 Feed manufacturers
- 8.3.1 Commercial feed producers
- 8.3.2 Specialty feed companies
- 8.3.3 Feed additive manufacturers
- 8.4 Food & beverage companies
- 8.4.1 Dairy processors
- 8.4.2 Meat processors
- 8.4.3 Food service companies
- 8.5 Government & research institutions
- 8.5.1 Agricultural departments
- 8.5.2 Environmental agencies
- 8.5.3 Research universities
- 8.6 Others
- 8.6.1 Carbon credit developers
- 8.6.2 Consulting services
- 8.6.3 Technology integrators
Chapter 9 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Region, 2021 – 2034 (USD Billion) (Kilo Tons)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 North America
- 9.2.1 U.S.
- 9.2.2 Canada
- 9.3 Europe
- 9.3.1 Germany
- 9.3.2 UK
- 9.3.3 France
- 9.3.4 Italy
- 9.3.5 Spain
- 9.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 9.4 Asia Pacific
- 9.4.1 China
- 9.4.2 India
- 9.4.3 Japan
- 9.4.4 Australia
- 9.4.5 South Korea
- 9.4.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 9.5 Latin America
- 9.5.1 Brazil
- 9.5.2 Mexico
- 9.5.3 Argentina
- 9.5.4 Rest of Latin America
- 9.6 Middle East and Africa
- 9.6.1 Saudi Arabia
- 9.6.2 South Africa
- 9.6.3 UAE
- 9.6.4 Rest of MEA
Chapter 10 Company Profiles
- 10.1 Agolin SA
- 10.2 Alltech Inc.
- 10.3 Archer Daniels Midland Company (ADM)
- 10.4 ArkeaBio
- 10.5 BASF SE
- 10.6 Blue Ocean Barns
- 10.7 Cargill, Incorporated
- 10.8 Chr. Hansen Holding A/S
- 10.9 DSM-Firmenich
- 10.10 Elanco Animal Health Incorporated
- 10.11 Evonik Industries AG
- 10.12 FutureFeed Pty Ltd
- 10.13 Kemin Industries, Inc.
- 10.14 Lallemand Inc.
- 10.15 Mootral SA
- 10.16 Novozymes A/S
- 10.17 Rumin8
- 10.18 Symbrosia Inc.
- 10.19 Volta Greentech
- 10.20 Zelp Ltd







