 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1716511
可重複使用運載火箭市場機會、成長動力、產業趨勢分析及 2025 - 2034 年預測Reusable Launch Vehicles Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
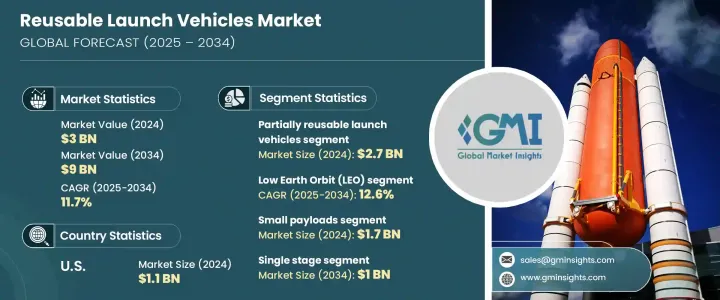
2024 年全球可重複使用運載火箭市場規模達 30 億美元,預計 2025 年至 2034 年期間的複合年成長率將達到 11.7%。對經濟高效且可靠的太空訪問的需求不斷成長,推動了這一成長,因為可重複使用運載火箭 (RLV) 為傳統消耗性火箭提供了更經濟的替代方案。隨著通訊、地球觀測、導航和防禦等應用的衛星發射頻率不斷增加,可重複使用解決方案的需求也變得更加明顯。這些飛行器能夠使用相同的硬體進行多次發射,從而顯著降低太空任務的成本,使太空探索和衛星部署更加永續和商業可行。
人們對太空旅遊的興趣日益濃厚,以及航太業私部門措施的不斷增加也促進了市場的成長。航太機構和私人公司都在大力投資開發下一代 RLV,以提高有效載荷能力、縮短週轉時間並提高營運效率。此外,材料、推進系統和人工智慧驅動的發射技術的進步有助於延長可重複使用零件的使用壽命,進一步推動這些飛行器的普及。全球市場正在見證政府和私人投資的增加,旨在建立強大的太空基礎設施,以支持科學研究、國防和商業應用的持續發射。
| 市場範圍 | |
|---|---|
| 起始年份 | 2024 |
| 預測年份 | 2025-2034 |
| 起始值 | 30億美元 |
| 預測值 | 90億美元 |
| 複合年成長率 | 11.7% |
可重複使用運載火箭市場按運載火箭類型和軌道範圍細分。運載工具類型包括部分可重複使用和完全可重複使用的運載工具。預計到 2034 年,完全可重複使用的運載火箭將創造 12 億美元的市場價值。該領域仍處於發展的早期階段,正在進行的研究和開發重點是縮短週轉時間並最大限度地降低營運成本。隨著人們對太空探索、衛星巨型星座和行星際任務的興趣日益成長,完全可重複使用的運載火箭將帶來巨大的長期利益,包括降低發射成本和加速部署週期。在改進熱屏蔽、著陸系統和快速翻新過程方面的投資不斷增加,正在加速未來任務中完全可重複使用系統的可行性。
市場也按軌道類型分類,包括地球靜止軌道 (GEO)、低地球軌道 (LEO)、中地球軌道 (MEO) 和超地球軌道 (BEO)。 2024 年,MEO 細分市場佔有 8.9% 的市場佔有率,主要原因是對安全軍事通訊的需求不斷成長,以及可重複使用的運載火箭能夠有效地將大型長壽命衛星部署到這些軌道上的能力。隨著軍事和商業應用的不斷擴大,使 MEO 更易於用於可重複使用運載火箭的進步預計將刺激進一步的市場成長。
2024 年,美國可重複使用運載火箭市場價值將達到 11 億美元,這得益於美國成熟的航太工業以及專門從事可重複使用發射技術的領先製造商的存在。美國航太發射活動數量的不斷增加,加上對提高成本效益和可靠性的關注,正在推動市場成長。隨著太空探索的不斷創新以及政府和私營部門的持續投資,美國預計將繼續保持可重複使用運載火箭開發和應用的全球領先地位。
目錄
第1章:方法論與範圍
第2章:執行摘要
第3章:行業洞察
- 產業生態系統分析
- 產業衝擊力
- 成長動力
- 對繞地球運行的衛星的需求不斷成長
- 增加政府和軍事投資
- 可重複使用性的技術進步
- 太空旅遊和亞軌道飛行的興起
- 太空製造和研究的增加
- 產業陷阱與挑戰
- 初期開發成本高
- 可重複使用周期有限
- 成長動力
- 成長潛力分析
- 監管格局
- 技術格局
- 未來市場趨勢
- 差距分析
- 波特的分析
- PESTEL分析
- 子系統分析
- 導引、導航和控制系統
- 推進系統
- 遙測、追蹤與指揮系統
- 電力系統
- 其他
第4章:競爭格局
- 介紹
- 公司市佔率分析
- 主要市場參與者的競爭分析
- 競爭定位矩陣
- 策略儀表板
第5章:市場估計與預測:按車型,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趨勢
- 部分可重複使用的運載火箭
- 完全可重複使用的運載火箭
第6章:市場估計與預測:按軌道類型,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趨勢
- 低地球軌道(LEO)
- 中地球軌道(MEO)
- 地球靜止軌道(GEO)
- 超越地球軌道(BEO)
第7章:市場估計與預測:依酬載容量,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趨勢
- 有效載荷較小(最多 2,000 公斤)
- 中等有效載重(2,000 公斤至 10,000 公斤)
- 重載(10,000 公斤以上)
第8章:市場估計與預測:依配置,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趨勢
- 單級
- 多級
第9章:市場估計與預測:按應用,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趨勢
- 衛星發射
- 太空探索
- 太空旅遊
- 貨物運輸
- 其他
第 10 章:市場估計與預測:依最終用途,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趨勢
- 政府
- 商業的
第 11 章:市場估計與預測:按地區,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趨勢
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 西班牙
- 義大利
- 荷蘭
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 韓國
- 拉丁美洲
- 巴西
- 墨西哥
- 阿根廷
- 中東和非洲
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
第12章:公司簡介
- Arianespace
- Blue Origin
- Boeing
- China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC)
- Lockheed Martin
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Northrop Grumman
- Relativity Space
- Rocket Lab
- Roscosmos
- Sierra Nevada Corporation
- SpaceX
- Virgin Galactic
The Global Reusable Launch Vehicles Market generated USD 3 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 11.7% between 2025 and 2034. The rising demand for cost-effective and reliable space access is fueling this growth, as reusable launch vehicles (RLVs) offer a more economical alternative to traditional expendable rockets. With the increasing frequency of satellite launches for applications such as communication, Earth observation, navigation, and defense, the need for reusable solutions is becoming more pronounced. These vehicles significantly reduce the cost of space missions by enabling multiple launches with the same hardware, making space exploration and satellite deployment more sustainable and commercially viable.

The growing interest in space tourism and the increasing number of private-sector initiatives in the aerospace industry are also contributing to market growth. Space agencies and private companies alike are investing heavily in developing next-generation RLVs to improve payload capacities, reduce turnaround times, and enhance operational efficiencies. Moreover, advancements in materials, propulsion systems, and AI-driven launch technologies are helping extend the lifespan of reusable components, further driving the adoption of these vehicles. The global market is witnessing increased government and private investments aimed at establishing a robust space infrastructure that supports continuous launches for scientific research, defense, and commercial applications.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $3 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $9 Billion |
| CAGR | 11.7% |
The market for reusable launch vehicles is segmented by vehicle type and orbital range. Vehicle types include partially reusable and fully reusable launch vehicles. Fully reusable launch vehicles are expected to generate USD 1.2 billion by 2034. This segment is still in the early stages of development, with ongoing research and development focused on enhancing turnaround times and minimizing operational costs. As interest in space exploration, satellite mega-constellations, and interplanetary missions grows, fully reusable launch vehicles are poised to offer substantial long-term benefits, including reduced launch costs and faster deployment cycles. Increasing investments in improving thermal shielding, landing systems, and rapid refurbishment processes are accelerating the viability of fully reusable systems for future missions.
The market is also classified by orbit type, including Geostationary Orbit (GEO), Low Earth Orbit (LEO), Medium Earth Orbit (MEO), and Beyond Earth Orbit (BEO). The MEO segment held an 8.9% market share in 2024, primarily driven by the increasing demand for secure military communications and the ability of reusable launch vehicles to efficiently deploy large, long-life satellites into these orbits. As military and commercial applications continue to expand, advancements in making MEO more accessible to reusable launch vehicles are expected to stimulate further market growth.
The U.S. reusable launch vehicles market was valued at USD 1.1 billion in 2024, driven by the country's well-established space industry and the presence of leading manufacturers specializing in reusable launch technologies. The growing number of space launch activities in the U.S., coupled with a focus on improving cost-efficiency and reliability, is propelling market growth. With continuous innovation in space exploration and sustained government and private sector investments, the U.S. is expected to remain a global leader in reusable launch vehicle development and adoption.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology and Scope
- 1.1 Market scope and definitions
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Base estimates and calculations
- 1.3.1 Base year calculation
- 1.3.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.4 Forecast model
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.5.2 Data mining sources
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry 3600 synopsis
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.2 Industry impact forces
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.2.1.1 Rising demand for satellites orbiting the Earth
- 3.2.1.2 Increasing government and military investments
- 3.2.1.3 Technological advancements in reusability
- 3.2.1.4 Rise of space tourism and suborbital flights
- 3.2.1.5 Increase in space-based manufacturing and research
- 3.2.2 Industry pitfalls and challenges
- 3.2.2.1 High initial development costs
- 3.2.2.2 Limited reusability cycles
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.3 Growth potential analysis
- 3.4 Regulatory landscape
- 3.5 Technology landscape
- 3.6 Future market trends
- 3.7 Gap analysis
- 3.8 Porter's analysis
- 3.9 PESTEL analysis
- 3.10 Subsystem analysis
- 3.10.1 Guidance, navigation & control systems
- 3.10.2 Propulsion systems
- 3.10.3 Telemetry, tracking & command systems
- 3.10.4 Electrical power systems
- 3.10.5 Others
Chapter 4 Competitive Landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.3 Competitive analysis of major market players
- 4.4 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.5 Strategy dashboard
Chapter 5 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Vehicle Type, 2021 – 2034 ($ Mn)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Partially reusable launch vehicles
- 5.3 Fully reusable launch vehicles
Chapter 6 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Orbit Type, 2021 – 2034 ($ Mn)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
- 6.3 Medium Earth Orbit (MEO)
- 6.4 Geostationary Orbit (GEO)
- 6.5 Beyond Earth Orbit (BEO)
Chapter 7 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Payload Capacity, 2021 – 2034 ($ Mn)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Small payloads (up to 2,000 kg)
- 7.3 Medium payloads (2,000 kg to 10,000 kg)
- 7.4 Heavy payloads (above 10,000 kg)
Chapter 8 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Configuration, 2021 – 2034 ($ Mn)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 Single stage
- 8.3 Multi-stage
Chapter 9 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Application, 2021 – 2034 ($ Mn)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 Satellite launch
- 9.3 Space exploration
- 9.4 Space tourism
- 9.5 Cargo transport
- 9.6 Others
Chapter 10 Market Estimates and Forecast, By End Use, 2021 – 2034 ($ Mn)
- 10.1 Key trends
- 10.2 Government
- 10.3 Commercial
Chapter 11 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Region, 2021 – 2034 ($ Mn)
- 11.1 Key trends
- 11.2 North America
- 11.2.1 U.S.
- 11.2.2 Canada
- 11.3 Europe
- 11.3.1 Germany
- 11.3.2 UK
- 11.3.3 France
- 11.3.4 Spain
- 11.3.5 Italy
- 11.3.6 Netherlands
- 11.4 Asia Pacific
- 11.4.1 China
- 11.4.2 India
- 11.4.3 Japan
- 11.4.4 Australia
- 11.4.5 South Korea
- 11.5 Latin America
- 11.5.1 Brazil
- 11.5.2 Mexico
- 11.5.3 Argentina
- 11.6 Middle East and Africa
- 11.6.1 Saudi Arabia
- 11.6.2 South Africa
- 11.6.3 UAE
Chapter 12 Company Profiles
- 12.1 Arianespace
- 12.2 Blue Origin
- 12.3 Boeing
- 12.4 China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC)
- 12.5 Lockheed Martin
- 12.6 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- 12.7 Northrop Grumman
- 12.8 Relativity Space
- 12.9 Rocket Lab
- 12.10 Roscosmos
- 12.11 Sierra Nevada Corporation
- 12.12 SpaceX
- 12.13 Virgin Galactic







