 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1735755
無人水面載具(USV)·無人水下載具(UUV)的全球市場(2025年~2035年)Global Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market 2025-2035 |
||||||
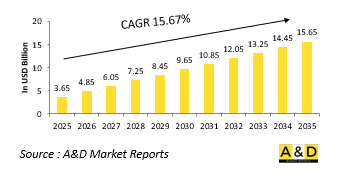
全球無人水面航行器 (USV) 和無人水下航行器 (UUV) 市場規模預計在 2025 年達到 36.5 億美元,預計到 2035 年將達到 156.5 億美元,在 2025-2035 年預測期內的複合年增長率為 15.67%。
科技對無人水面艇 (USV) 和無人水下艇 (UUV) 市場的影響
技術創新正在顯著重塑無人水面艇 (USV) 和無人水下艇 (UUV) 在國防行動中的角色和能力。這些系統如今利用先進的導航、推進和感測器技術,實現高度自主和精確的運作。艦載智慧系統使它們能夠規劃最佳路線、規避危險,並在最少的人工幹預下完成任務。水面艦艇透過整合雷達、光學追蹤和電子戰套件,增強了威脅偵測和交戰能力。另一方面,潛水器配備了聲納成像、磁異常感測器和聲學通訊系統,使其能夠在複雜的海底環境中導航和作業。人工智慧在實現自適應行為方面發揮關鍵作用,使艦艇能夠評估情況並即時調整戰術。增強型能源系統支援更長時間的作業,而低噪音推進系統則最大限度地降低了探測風險。安全的通訊框架確保即使在對抗環境中也能與指揮鏈和其他資產進行協調。這些技術還支援無人船與有人船、飛機和衛星網路協同作戰,從而實現一體化防禦。隨著軟體和硬體的不斷發展,這些平台正變得更具彈性、更有效率、用途更廣泛,突破了傳統海上交戰的界限,並為海戰效能樹立了新的標準。
無人水面航行器 (USV) 和無人水下航行器 (UUV) 市場的關鍵推動因素
無人水面航行器 (USV) 和無人水下航行器 (UUV) 在國防戰略中的崛起,是由幾個相互關聯的因素推動的,這些因素凸顯了它們的戰略價值。其中最重要的是擴大作戰範圍,同時最大限度地降低人員風險。這些平台可以部署在高威脅區域,執行重複性或危險任務,並且可以長時間作戰而不會疲勞。圍繞領海和水下資源的戰略競爭也促使各國加強其海軍情報和監視能力。無人船提供了一種經濟高效的持續監視解決方案,可以單獨運行,也可以作為更廣泛系統的一部分運行。此外,水雷和隱形潛艇的威脅日益增加,使得那些能夠在不危及有人船的情況下進行探測和掃蕩的平台重新受到關注。技術可行性使這些系統更具吸引力,因為自主性、續航能力和感測器整合度的提升提高了可靠性和作戰成功率。海上行動分散化的政策轉變進一步支持部署無人系統作為力量倍增器。無人系統能夠靈活應對從威懾到快速危機應變等一系列場景。簡而言之,戰略必要性、技術準備和作戰效率的整合正在推動全球部署這些先進海軍裝備的勢頭。
無人水面航行器 (USV) 和無人水下航行器 (UUV) 市場的區域趨勢
各區域對無人水面航行器 (USV) 和無人水下航行器 (UUV) 的國防部署方式反映了不同的安全優先事項和技術投資。在印度-太平洋地區,海上衝突和戰略水道保護正在推動水面和水下無人裝備的積極發展和部署。海岸監視、反入侵行動和海事感知是該地區多個國家的關鍵領域。北美軍隊正優先將這些系統納入大型海軍演習和艦隊現代化計劃,以保持遠程作戰和水下優勢。
本報告提供全球無人水面載具(USV)·無人水下載具(UUV)市場相關調查分析,提供今後10年成長促進因素,預測,各地區趨勢等資訊。
目錄
無人水面載具(USV)·無人水下載具(UUV)市場報告定義
無人水面載具(USV)·無人水下載具(UUV)市場區隔
各地區
各用途
按行動方式
今後10年的無人水面載具(USV)·無人水下載具(UUV)市場分析
無人水面載具(USV)·無人水下載具(UUV)市場技術
全球無人水面載具(USV)·無人水下載具(UUV)市場預測
地區的無人水面載具(USV)·無人水下載具(UUV)市場趨勢與預測
北美
促進因素,阻礙因素,課題
PEST
市場預測與情勢分析
主要企業
供應商層級格局
企業基準
歐洲
中東
亞太地區
南美
無人水面載具(USV)·無人水下載具(UUV)市場分析:各國
美國
最新消息
專利
這個市場上目前技術成熟度
市場預測與情勢分析
加拿大
義大利
法國
德國
荷蘭
比利時
西班牙
瑞典
希臘
澳洲
南非
印度
中國
俄羅斯
韓國
日本
馬來西亞
新加坡
巴西
無人水面載具(USV)·無人水下載具(UUV)市場機會矩陣
無人水面載具(USV)·無人水下載具(UUV)市場報告相關專家的意見
結論
關於Aviation and Defense Market Reports
The Global Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels market is estimated at USD 3.65 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 15.65 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 15.67% over the forecast period 2025-2035.

Introduction to Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market:
Defense unmanned surface and underwater vessels have become central to the modernization of naval forces worldwide. These platforms offer strategic capabilities that enhance situational awareness, extend operational reach, and reduce the exposure of personnel in dangerous maritime environments. By operating autonomously or under remote control, these vessels support a wide range of missions such as anti-submarine warfare, mine countermeasures, intelligence collection, and maritime patrols. Surface units navigate above water to perform visible deterrence and surveillance, while underwater systems execute stealth missions that involve detection, reconnaissance, or precision strikes. The demand for these technologies is accelerating as maritime challenges evolve, requiring persistent presence and rapid adaptability. With increased activity in littoral zones, contested waterways, and strategic choke points, navies are seeking reliable solutions that can perform effectively across various ocean conditions. The modular nature of these systems allows for mission-specific configurations, making them suitable for both routine security and high-threat operations. Defense organizations are integrating unmanned maritime vessels into their existing fleets to complement traditional assets and support distributed operational models. As maritime threats become more unpredictable and technologically sophisticated, unmanned surface and underwater systems are proving indispensable in maintaining maritime dominance and executing complex naval strategies with greater precision and flexibility.
Technology Impact in Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market:
Technological innovation is dramatically reshaping the roles and capabilities of unmanned surface and underwater vessels in defense operations. These systems now leverage advanced navigation, propulsion, and sensor technologies to execute missions with high levels of autonomy and accuracy. Onboard intelligence enables them to chart optimal routes, avoid hazards, and complete tasks with minimal human input. In surface vessels, integration of radar, optical tracking, and electronic warfare suites enhances threat detection and engagement. Meanwhile, underwater vehicles benefit from sonar imaging, magnetic anomaly sensors, and acoustic communication systems that allow them to navigate and operate in complex sub-sea environments. Artificial intelligence plays a crucial role in enabling adaptive behavior, allowing vessels to assess conditions and adjust tactics in real time. Enhanced energy systems support longer missions, while low-noise propulsion minimizes detection risk. Secure communication frameworks ensure coordination with command structures and other assets, even in contested environments. These technologies also support the use of unmanned vessels in coordinated operations with manned ships, aircraft, and satellite networks, enabling a unified defense approach. As software and hardware continue to evolve, these platforms are becoming more resilient, efficient, and versatile, pushing the boundaries of traditional naval engagement and setting new standards in maritime warfare effectiveness.
Key Drivers in Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels market:
The rise of unmanned surface and underwater vessels in defense strategy is propelled by multiple interrelated factors that underscore their strategic value. Foremost is the need to extend operational reach while minimizing the risk to personnel. These platforms can be deployed in high-threat zones, perform repetitive or hazardous tasks, and conduct long-endurance missions without fatigue. Strategic competition over maritime territories and underwater resources is also prompting nations to enhance their naval intelligence and surveillance capabilities. Unmanned vessels offer cost-effective solutions for persistent monitoring and can operate independently or as part of a broader system. The increasing threat of underwater mines and stealthy submarines has also led to a renewed focus on platforms capable of conducting detection and clearance without endangering manned vessels. Technological feasibility has made these systems more attractive, as improvements in autonomy, durability, and sensor integration have increased their reliability and mission success rates. Policy shifts toward distributed maritime operations further support the deployment of unmanned systems as force multipliers. They enable flexible response to a variety of scenarios, from deterrence to rapid crisis response. Ultimately, the convergence of strategic necessity, technological readiness, and operational efficiency is driving the global momentum behind the deployment of these advanced naval assets.
Regional Trends in Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market:
Regional approaches to defense unmanned surface and underwater vessels reflect diverse security priorities and technological investments. In the Indo-Pacific, maritime disputes and the protection of strategic waterways have driven aggressive development and deployment of both surface and sub-sea unmanned assets. Coastal surveillance, anti-intrusion missions, and maritime domain awareness are key focus areas for several nations in this region. North American forces are emphasizing the integration of these systems into large-scale naval exercises and fleet modernization programs, seeking to maintain an edge in long-range operations and undersea dominance. European nations are balancing innovation with collaborative frameworks, often pooling resources to develop interoperable platforms suitable for both national and allied missions. This cooperative model enables broader surveillance coverage and cost efficiency. Middle Eastern countries are increasingly turning to unmanned surface vehicles to monitor critical maritime infrastructure and shipping lanes, especially in areas with a history of sabotage and asymmetric threats. African and Latin American defense entities, while at earlier stages of adoption, are beginning to invest in these technologies for coastal security, anti-smuggling efforts, and environmental monitoring. Across all regions, the trend is clear: unmanned surface and underwater vessels are transitioning from experimental tools to vital components of modern naval defense, driven by specific regional imperatives and evolving maritime threats.
Key Defense Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Program:
HII announced that its Mission Technologies division has been awarded a contract to produce nine small unmanned undersea vehicles (SUUVs) for the U.S. Navy's Lionfish System program. The agreement includes the potential for expansion to up to 200 vehicles over the next five years, with a total contract value exceeding $347 million. The Lionfish System is derived from HII's REMUS 300-a compact, two-person-deployable SUUV featuring an open architecture and flexible payload configurations. In early 2022, the REMUS 300 was designated as the Navy's official program of record for its next-generation SUUV platform. Managed by Naval Sea Systems Command, the contract covers the production and support of these advanced SUUVs, along with associated afloat and auxiliary support equipment and engineering services. The vehicles, equipped with cutting-edge autonomous and unmanned technologies, are intended to perform vital undersea missions for the Navy.
Table of Contents
Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market Report Definition
Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market Segmentation
By Region
By Application
By Mode of Operation
Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year unmanned surface and underwater vessels market analysis would give a detailed overview of unmanned surface and underwater vessels market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market Forecast
The 10-year unmanned surface and underwater vessels market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market Trends & Forecast
The regional unmanned surface and underwater vessels market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.
Conclusions
About Aviation and Defense Market Reports
List of Tables
- Table 1: 10 Year Market Outlook, 2025-2035
- Table 2: Drivers, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 3: Restraints, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 4: Challenges, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 5: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 6: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 7: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 8: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 9: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 10: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 11: Drivers, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 12: Restraints, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 13: Challenges, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 14: Drivers, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 15: Restraints, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 16: Challenges, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 17: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 18: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Control, 2025-2035
- Table 19: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Application, 2025-2035
- Table 20: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 21: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Control, 2025-2035
- Table 22: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Application, 2025-2035
List of Figures
- Figure 1: Global Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 2: Global Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market Forecast, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 3: Global Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market Forecast, By Control, 2025-2035
- Figure 4: Global Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market Forecast, By Application, 2025-2035
- Figure 5: North America, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 6: Europe, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 7: Middle East, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 8: APAC, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 9: South America, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 10: United States, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 11: United States, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 12: Canada, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 13: Canada, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 14: Italy, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 15: Italy, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 16: France, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 17: France, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 18: Germany, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 19: Germany, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 20: Netherlands, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 21: Netherlands, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 22: Belgium, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 23: Belgium, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 24: Spain, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 25: Spain, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 26: Sweden, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 27: Sweden, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 28: Brazil, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 29: Brazil, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 30: Australia, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 31: Australia, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 32: India, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 33: India, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 34: China, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 35: China, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 36: Saudi Arabia, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 37: Saudi Arabia, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 38: South Korea, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 39: South Korea, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 40: Japan, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 41: Japan, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 42: Malaysia, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 43: Malaysia, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 44: Singapore, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 45: Singapore, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 46: United Kingdom, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 47: United Kingdom, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 48: Opportunity Analysis, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, By Region (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 49: Opportunity Analysis, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, By Region (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 50: Opportunity Analysis, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, By Control (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 51: Opportunity Analysis, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, By Control (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 52: Opportunity Analysis, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, By Application (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 53: Opportunity Analysis, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, By Application (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 54: Scenario Analysis, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Cumulative Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 55: Scenario Analysis, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Global Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 56: Scenario 1, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 57: Scenario 1, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 58: Scenario 1, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, By Control, 2025-2035
- Figure 59: Scenario 1, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, By Application, 2025-2035
- Figure 60: Scenario 2, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 61: Scenario 2, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 62: Scenario 2, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, By Control, 2025-2035
- Figure 63: Scenario 2, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, By Application, 2025-2035
- Figure 64: Company Benchmark, Unmanned Surface and Underwater Vessels Market, 2025-2035










